"Satellite Internet access is Internet access provided through communications satellites. ...
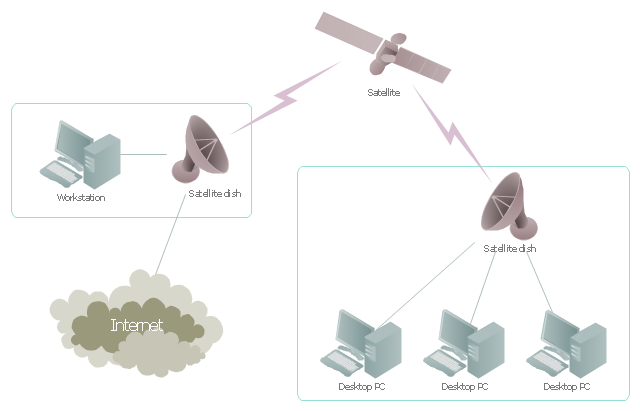
Satellite Internet generally relies on three primary components: a satellite in geostationary orbit (sometimes referred to as a geosynchronous Earth orbit, or GEO), a number of ground stations known as gateways that relay Internet data to and from the satellite via radio waves (microwave), and a VSAT (very-small-aperture terminal) dish antenna with a transceiver, located at the subscriber's premises. Other components of a satellite Internet system include a modem at the user end which links the user's network with the transceiver, and a centralized network operations center (NOC) for monitoring the entire system. Working in concert with a broadband gateway, the satellite operates a Star network topology where all network communication passes through the network's hub processor, which is at the center of the star. With this configuration, the number of remote VSATs that can be connected to the hub is virtually limitless." [Satellite Internet access. Wikipedia]
This satellite telecom network diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Telecommunication Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Satellite Internet generally relies on three primary components: a satellite in geostationary orbit (sometimes referred to as a geosynchronous Earth orbit, or GEO), a number of ground stations known as gateways that relay Internet data to and from the satellite via radio waves (microwave), and a VSAT (very-small-aperture terminal) dish antenna with a transceiver, located at the subscriber's premises. Other components of a satellite Internet system include a modem at the user end which links the user's network with the transceiver, and a centralized network operations center (NOC) for monitoring the entire system. Working in concert with a broadband gateway, the satellite operates a Star network topology where all network communication passes through the network's hub processor, which is at the center of the star. With this configuration, the number of remote VSATs that can be connected to the hub is virtually limitless." [Satellite Internet access. Wikipedia]
This satellite telecom network diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Telecommunication Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
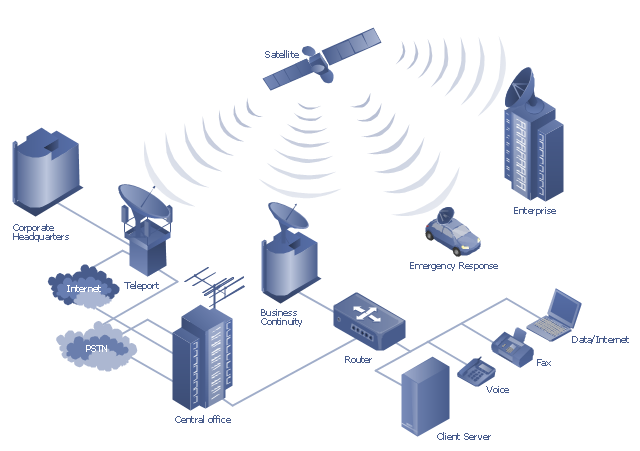
"A communications satellite or comsat is an artificial satellite sent to space for the purpose of telecommunications. Modern communications satellites use a variety of orbits including geostationary orbits, Molniya orbits, elliptical orbits and low (polar and non-polar) Earth orbits.
For fixed (point-to-point) services, communications satellites provide a microwave radio relay technology complementary to that of communication cables. They are also used for mobile applications such as communications to ships, vehicles, planes and hand-held terminals, and for TV and radio broadcasting." [Communications satellite. Wikipedia]
"Satellite telecommunication services:
Satellite crop monitoring,
Satellite Internet access,
Satellite navigation,
Satellite phone,
Satellite radio,
Satellite television." [Satellite. Wikipedia]
This hybrid satellite and common carrier network diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Telecommunication Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
For fixed (point-to-point) services, communications satellites provide a microwave radio relay technology complementary to that of communication cables. They are also used for mobile applications such as communications to ships, vehicles, planes and hand-held terminals, and for TV and radio broadcasting." [Communications satellite. Wikipedia]
"Satellite telecommunication services:
Satellite crop monitoring,
Satellite Internet access,
Satellite navigation,
Satellite phone,
Satellite radio,
Satellite television." [Satellite. Wikipedia]
This hybrid satellite and common carrier network diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Telecommunication Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
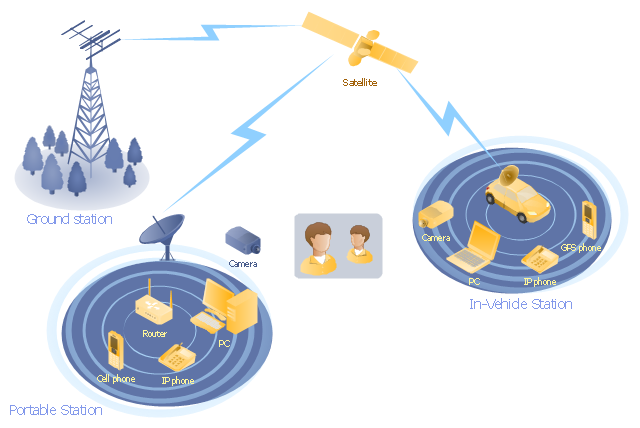
"Mobile satellite systems help connect remote regions, vehicles, ships, people and aircraft to other parts of the world and/ or other mobile or stationary communications units, in addition to serving as navigation systems." [Satellite. Mobile satellite systems. Wikipedia]
"A communications satellite or comsat is an artificial satellite sent to space for the purpose of telecommunications.
... communications satellites ... are ... used for mobile applications such as communications to ships, vehicles, planes and hand-held terminals, and for TV and radio broadcasting." [Communications satellite. Wikipedia]
This mobile satellite communication network diagram was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Telecommunication Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A communications satellite or comsat is an artificial satellite sent to space for the purpose of telecommunications.
... communications satellites ... are ... used for mobile applications such as communications to ships, vehicles, planes and hand-held terminals, and for TV and radio broadcasting." [Communications satellite. Wikipedia]
This mobile satellite communication network diagram was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Telecommunication Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Telecommunication Network Diagrams
Telecommunication Network Diagrams
Telecommunication Network Diagrams solution extends ConceptDraw PRO software with samples, templates, and great collection of vector stencils to help the specialists in a field of networks and telecommunications, as well as other users to create Computer systems networking and Telecommunication network diagrams for various fields, to organize the work of call centers, to design the GPRS networks and GPS navigational systems, mobile, satellite and hybrid communication networks, to construct the mobile TV networks and wireless broadband networks.
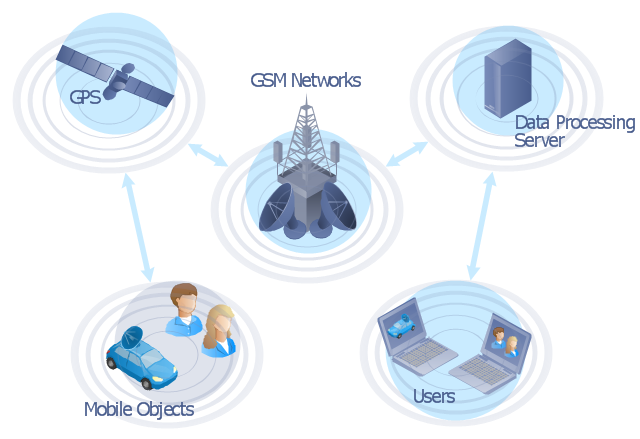
"The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a space-based satellite navigation system that provides location and time information in all weather conditions, anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites. The system provides critical capabilities to military, civil and commercial users around the world. It is maintained by the United States government and is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver." [Global Positioning System. Wikipedia]
This GPS operation diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Telecommunication Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This GPS operation diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Telecommunication Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This work flow chart sample was redesigned from the picture "Weather Forecast" from the article "Simulation Workflows".
[iaas.uni-stuttgart.de/ forschung/ projects/ simtech/ sim-workflows.php]
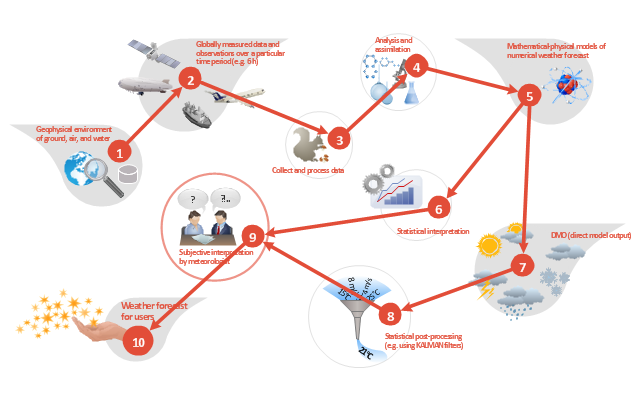
"(1) The weather is predicted for a particular geological area. Hence, the workflow is fed with a model of the geophysical environment of ground, air and water for a requested area.
(2) Over a specified period of time (e.g. 6 hours) several different variables are measured and observed. Ground stations, ships, airplanes, weather balloons, satellites and buoys measure the air pressure, air/ water temperature, wind velocity, air humidity, vertical temperature profiles, cloud velocity, rain fall, and more.
(3) This data needs to be collected from the different sources and stored for later access.
(4) The collected data is analyzed and transformed into a common format (e.g. Fahrenheit to Celsius scale). The normalized values are used to create the current state of the atmosphere.
(5) Then, a numerical weather forecast is made based on mathematical-physical models (e.g. GFS - Global Forecast System, UKMO - United Kingdom MOdel, GME - global model of Deutscher Wetterdienst). The environmental area needs to be discretized beforehand using grid cells. The physical parameters measured in Step 2 are exposed in 3D space as timely function. This leads to a system of partial differential equations reflecting the physical relations that is solved numerically.
(6) The results of the numerical models are complemented with a statistical interpretation (e.g. with MOS - Model-Output-Statistics). That means the forecast result of the numerical models is compared to statistical weather data. Known forecast failures are corrected.
(7) The numerical post-processing is done with DMO (Direct Model Output): the numerical results are interpolated for specific geological locations.
(8) Additionally, a statistical post-processing step removes failures of measuring devices (e.g. using KALMAN filters).
(9) The statistical interpretation and the numerical results are then observed and interpreted by meteorologists based on their subjective experiences.
(10) Finally, the weather forecast is visualized and presented to interested people." [iaas.uni-stuttgart.de/ forschung/ projects/ simtech/ sim-workflows.php]
The example "Workflow diagram - Weather forecast" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Workflow Diagrams solution from the Business Processes area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[iaas.uni-stuttgart.de/ forschung/ projects/ simtech/ sim-workflows.php]
"(1) The weather is predicted for a particular geological area. Hence, the workflow is fed with a model of the geophysical environment of ground, air and water for a requested area.
(2) Over a specified period of time (e.g. 6 hours) several different variables are measured and observed. Ground stations, ships, airplanes, weather balloons, satellites and buoys measure the air pressure, air/ water temperature, wind velocity, air humidity, vertical temperature profiles, cloud velocity, rain fall, and more.
(3) This data needs to be collected from the different sources and stored for later access.
(4) The collected data is analyzed and transformed into a common format (e.g. Fahrenheit to Celsius scale). The normalized values are used to create the current state of the atmosphere.
(5) Then, a numerical weather forecast is made based on mathematical-physical models (e.g. GFS - Global Forecast System, UKMO - United Kingdom MOdel, GME - global model of Deutscher Wetterdienst). The environmental area needs to be discretized beforehand using grid cells. The physical parameters measured in Step 2 are exposed in 3D space as timely function. This leads to a system of partial differential equations reflecting the physical relations that is solved numerically.
(6) The results of the numerical models are complemented with a statistical interpretation (e.g. with MOS - Model-Output-Statistics). That means the forecast result of the numerical models is compared to statistical weather data. Known forecast failures are corrected.
(7) The numerical post-processing is done with DMO (Direct Model Output): the numerical results are interpolated for specific geological locations.
(8) Additionally, a statistical post-processing step removes failures of measuring devices (e.g. using KALMAN filters).
(9) The statistical interpretation and the numerical results are then observed and interpreted by meteorologists based on their subjective experiences.
(10) Finally, the weather forecast is visualized and presented to interested people." [iaas.uni-stuttgart.de/ forschung/ projects/ simtech/ sim-workflows.php]
The example "Workflow diagram - Weather forecast" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Workflow Diagrams solution from the Business Processes area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
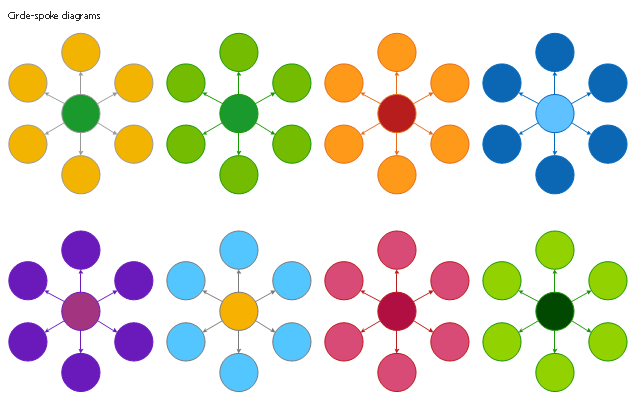
The vector stencils library "Circle-spoke diagram" contains 8 templates for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
Circle-Spoke Diagrams (Spoke charts) have a central item surrounded by other items in a circle. The circle-spoke diagram is a diagram meant to illustrate that each spoke has equal value. Circle-spoke diagrams are used to show the relationships between a single main element and several satellites.
The circle-spoke diagrams are used to show the features or components of a central item in marketing, management documents and presentations.
The example "Design elements - Circle-spoke diagram" is included in the Circle-Spoke Diagrams solution from the area "What is a Diagram" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Circle-Spoke Diagrams (Spoke charts) have a central item surrounded by other items in a circle. The circle-spoke diagram is a diagram meant to illustrate that each spoke has equal value. Circle-spoke diagrams are used to show the relationships between a single main element and several satellites.
The circle-spoke diagrams are used to show the features or components of a central item in marketing, management documents and presentations.
The example "Design elements - Circle-spoke diagram" is included in the Circle-Spoke Diagrams solution from the area "What is a Diagram" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
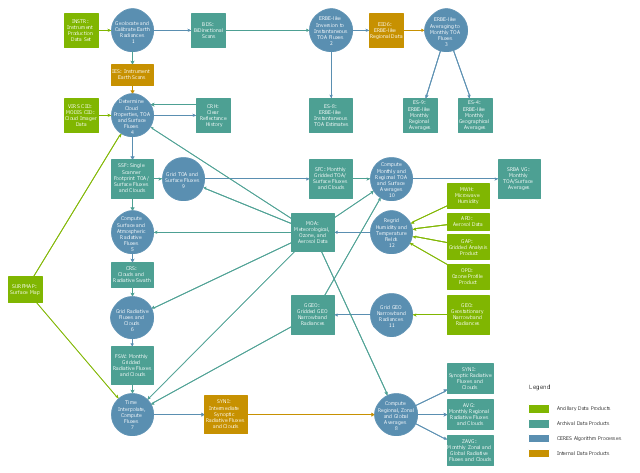
This DFD sample was created on the base of the figure from the NASA website. [asd-www.larc.nasa.gov/ ATBD/ DFD.html]
"Clouds and the Earth's Radiant Energy System (CERES).
EOS-Terra: Understanding Earth's Clouds and Climate.
The Clouds and the Earth's Radiant Energy System (CERES) instrument is one of several that will be flown aboard the Earth Observing System's Terra spacecraft, scheduled for launch in late1999. The data from the CERES instrument will be used to study the energy exchanged between the Sun; the Earth's atmosphere, surface and clouds; and outer space.
The CERES EOS-Terra instrument will be the second CERES instrument in Earth orbit. The first CERES instrument is currently orbiting the Earth aboard the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission observatory, which was launched in November 1997. Early results of the TRMM mission show that the first CERES has provided better measurement capabilities than any previous satellite instrument of its kind.
What CERES Will Measure.
CERES will measure the energy at the top of the atmosphere, as well as estimate energy levels in the atmosphere and at the Earth's surface. Using information from very high resolution cloud imaging instruments on the same spacecraft, CERES also will determine cloud properties, including cloud amount, altitude, thickness, and the size of the cloud particles. All of these measurements are critical for advancing our understanding of the Earth's total climate system and further improving climate prediction models.
The CERES instrument is based on NASA Langley's highly successful Earth Radiation Budget Experiment (ERBE) which used three satellites to provide global energy budget measurements from 1984 to 1990." [nasa.gov/ centers/ langley/ news/ factsheets/ CERES.html]
The DFD example "CERES data flow diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Data Flow Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Clouds and the Earth's Radiant Energy System (CERES).
EOS-Terra: Understanding Earth's Clouds and Climate.
The Clouds and the Earth's Radiant Energy System (CERES) instrument is one of several that will be flown aboard the Earth Observing System's Terra spacecraft, scheduled for launch in late1999. The data from the CERES instrument will be used to study the energy exchanged between the Sun; the Earth's atmosphere, surface and clouds; and outer space.
The CERES EOS-Terra instrument will be the second CERES instrument in Earth orbit. The first CERES instrument is currently orbiting the Earth aboard the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission observatory, which was launched in November 1997. Early results of the TRMM mission show that the first CERES has provided better measurement capabilities than any previous satellite instrument of its kind.
What CERES Will Measure.
CERES will measure the energy at the top of the atmosphere, as well as estimate energy levels in the atmosphere and at the Earth's surface. Using information from very high resolution cloud imaging instruments on the same spacecraft, CERES also will determine cloud properties, including cloud amount, altitude, thickness, and the size of the cloud particles. All of these measurements are critical for advancing our understanding of the Earth's total climate system and further improving climate prediction models.
The CERES instrument is based on NASA Langley's highly successful Earth Radiation Budget Experiment (ERBE) which used three satellites to provide global energy budget measurements from 1984 to 1990." [nasa.gov/ centers/ langley/ news/ factsheets/ CERES.html]
The DFD example "CERES data flow diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Data Flow Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
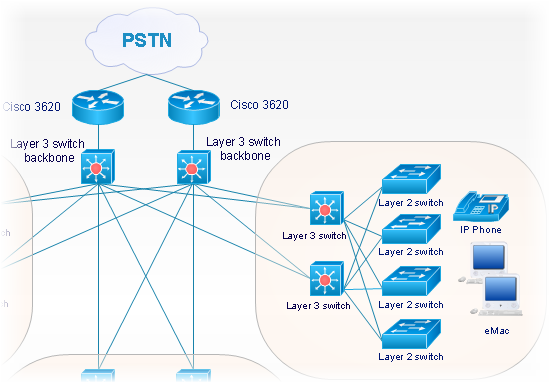
Cisco Network Objects in ConceptDraw PRO
ConceptDraw PRO is the only application on the Macintosh platform, supplied with a comprehensive Cisco icon set. For graphic solutions that support Windows, only Microsoft Visio has a library of Cisco shapes. ConceptDraw PRO is a valuable option to many network professionals that use Macintosh computers or work in a combined Mac and PC environment.
 Aerospace and Transport
Aerospace and Transport
This solution extends ConceptDraw PRO software with templates, samples and library of vector clipart for drawing the Aerospace and Transport Illustrations. It contains clipart of aerospace objects and transportation vehicles, office buildings and anci
- Satellite telecom network diagram | Hybrid satellite and common ...
- Satellite telecom network diagram | Mobile satellite communication ...
- Mobile satellite communication network diagram | Using Both Wired ...
- Mobile satellite communication network diagram ...
- Telecommunication Network Diagrams | Hybrid satellite and ...
- Satellite network diagram
- Mobile satellite communication network diagram ...
- Mobile satellite communication network diagram | Mobile satellite TV ...
- Hybrid satellite and common carrier network diagram | Satellite ...
- Drawing Of Satellite
- Hybrid satellite and common carrier network diagram | Satellite ...
- Satellite telecom network diagram | Hybrid satellite and common ...
- GPS operation diagram | Mobile satellite TV network diagram | Bar ...
- Satellite telecom network diagram | Computers and network ...
- Mobile satellite communication network diagram | Digital ...
- Satelite Diagram
- Wireless broadband network diagram | Mobile satellite TV network ...
- ConceptDraw PRO Network Diagram Tool | Mobile satellite ...
- Aerospace and Transport | Telecommunication Network Diagrams ...
- Network Architecture | Hybrid satellite and common carrier network ...