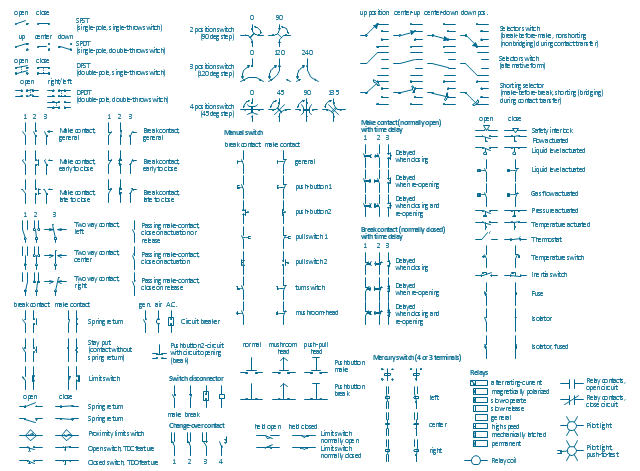
The vector stencils library "Switches and relays" contains 58 symbols of electrical contacts, switches, relays, circuit breakers, selectors, connectors, disconnect devices, switching circuits, current regulators, and thermostats for electrical devices.
"In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another.
The most familiar form of switch is a manually operated electromechanical device with one or more sets of electrical contacts, which are connected to external circuits. Each set of contacts can be in one of two states: either "closed" meaning the contacts are touching and electricity can flow between them, or "open", meaning the contacts are separated and the switch is nonconducting. The mechanism actuating the transition between these two states (open or closed) can be either a "toggle" (flip switch for continuous "on" or "off") or "momentary" (push-for "on" or push-for "off") type.
A switch may be directly manipulated by a human as a control signal to a system, such as a computer keyboard button, or to control power flow in a circuit, such as a light switch. Automatically operated switches can be used to control the motions of machines, for example, to indicate that a garage door has reached its full open position or that a machine tool is in a position to accept another workpiece. Switches may be operated by process variables such as pressure, temperature, flow, current, voltage, and force, acting as sensors in a process and used to automatically control a system. ... A switch that is operated by another electrical circuit is called a relay. Large switches may be remotely operated by a motor drive mechanism. Some switches are used to isolate electric power from a system, providing a visible point of isolation that can be padlocked if necessary to prevent accidental operation of a machine during maintenance, or to prevent electric shock." [Switch. Wikipedia]
"A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to mechanically operate a switch, but other operating principles are also used, such as solid-state relays. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal (with complete electrical isolation between control and controlled circuits), or where several circuits must be controlled by one signal. The first relays were used in long distance telegraph circuits as amplifiers: they repeated the signal coming in from one circuit and re-transmitted it on another circuit. Relays were used extensively in telephone exchanges and early computers to perform logical operations.
A type of relay that can handle the high power required to directly control an electric motor or other loads is called a contactor. Solid-state relays control power circuits with no moving parts, instead using a semiconductor device to perform switching. Relays with calibrated operating characteristics and sometimes multiple operating coils are used to protect electrical circuits from overload or faults; in modern electric power systems these functions are performed by digital instruments still called "protective relays"." [Relay. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Switches and relays" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another.
The most familiar form of switch is a manually operated electromechanical device with one or more sets of electrical contacts, which are connected to external circuits. Each set of contacts can be in one of two states: either "closed" meaning the contacts are touching and electricity can flow between them, or "open", meaning the contacts are separated and the switch is nonconducting. The mechanism actuating the transition between these two states (open or closed) can be either a "toggle" (flip switch for continuous "on" or "off") or "momentary" (push-for "on" or push-for "off") type.
A switch may be directly manipulated by a human as a control signal to a system, such as a computer keyboard button, or to control power flow in a circuit, such as a light switch. Automatically operated switches can be used to control the motions of machines, for example, to indicate that a garage door has reached its full open position or that a machine tool is in a position to accept another workpiece. Switches may be operated by process variables such as pressure, temperature, flow, current, voltage, and force, acting as sensors in a process and used to automatically control a system. ... A switch that is operated by another electrical circuit is called a relay. Large switches may be remotely operated by a motor drive mechanism. Some switches are used to isolate electric power from a system, providing a visible point of isolation that can be padlocked if necessary to prevent accidental operation of a machine during maintenance, or to prevent electric shock." [Switch. Wikipedia]
"A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to mechanically operate a switch, but other operating principles are also used, such as solid-state relays. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal (with complete electrical isolation between control and controlled circuits), or where several circuits must be controlled by one signal. The first relays were used in long distance telegraph circuits as amplifiers: they repeated the signal coming in from one circuit and re-transmitted it on another circuit. Relays were used extensively in telephone exchanges and early computers to perform logical operations.
A type of relay that can handle the high power required to directly control an electric motor or other loads is called a contactor. Solid-state relays control power circuits with no moving parts, instead using a semiconductor device to perform switching. Relays with calibrated operating characteristics and sometimes multiple operating coils are used to protect electrical circuits from overload or faults; in modern electric power systems these functions are performed by digital instruments still called "protective relays"." [Relay. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Switches and relays" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
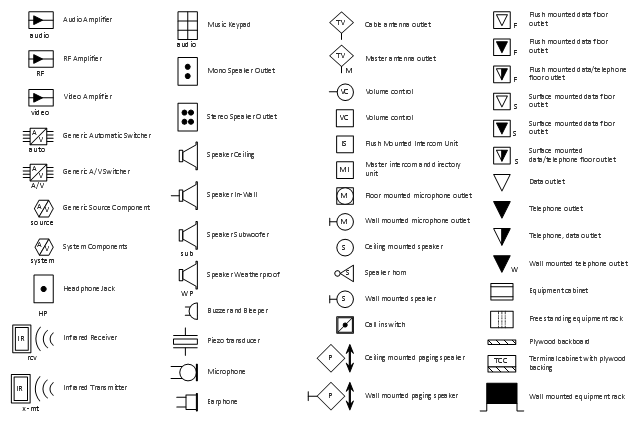
The vector stencils library "Video and audio" contains 50 symbols of audio and video devices and equipment.
Use the design elements library "Video and audio" for drawing audio and video system layouts, cabling floor plans, electrical circuit schematics and wiring diagrams of video and sound reproduction systems using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
Using the "Video and audio" library you can create video and audio engineering drawings and layout plans of your digital and analog, stereophonic (stereo), high fidelity (Hi-Fi, or hifi), quadraphonic, surround-sound, and home audio systems, home entertainment systems, home cinema (home theater, or home theatre), high-definition television (HDTV) and 3D television systems.
The shapes library "Video and audio" is included in the Electric and Telecom Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use the design elements library "Video and audio" for drawing audio and video system layouts, cabling floor plans, electrical circuit schematics and wiring diagrams of video and sound reproduction systems using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
Using the "Video and audio" library you can create video and audio engineering drawings and layout plans of your digital and analog, stereophonic (stereo), high fidelity (Hi-Fi, or hifi), quadraphonic, surround-sound, and home audio systems, home entertainment systems, home cinema (home theater, or home theatre), high-definition television (HDTV) and 3D television systems.
The shapes library "Video and audio" is included in the Electric and Telecom Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
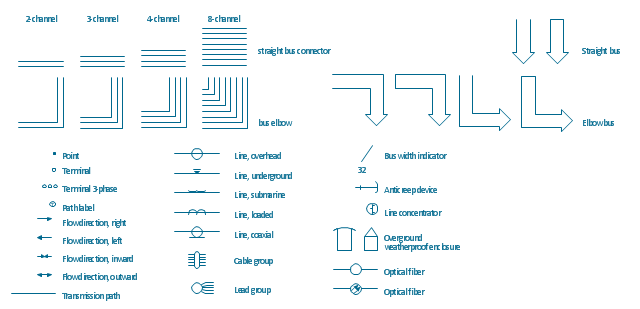
The vector stencils library "Transmission paths" contains 43 symbols of power transmission paths, electronic circuits, bus connectors and elbows, terminals, junctions, and concentrators.
Use it to annotate electrical diagrams, electronic schematics and circuit diagrams.
"A physical medium in data communications is the transmission path over which a signal propagates.
Many transmission media are used as communications channel.
For telecommunications purposes in the United States, Federal Standard 1037C, transmission media are classified as one of the following:
(1) Guided (or bounded) - waves are guided along a solid medium such as a transmission line.
(2) Wireless (or unguided) - transmission and reception are achieved by means of an antenna.
One of the most common physical medias used in networking is copper wire. Copper wire to carry signals to long distances using relatively low amounts of power. The unshielded twisted pair (UTP) is eight strands of copper wire, organized into four pairs.
Another example of a physical medium is optical fiber, which has emerged as the most commonly used transmission medium for long-distance communications. Optical fiber is a thin strand of glass that guides light along its length.
Multimode and single mode are two types of commonly used optical fiber. Multimode fiber uses LEDs as the light source and can carry signals over shorter distances, about 2 kilometers. Single mode can carry signals over distances of tens of miles.
Wireless media may carry surface waves or skywaves, either longitudinally or transversely, and are so classified.
In both communications, communication is in the form of electromagnetic waves. With guided transmission media, the waves are guided along a physical path; examples of guided media include phone lines, twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, and optical fibers. Unguided transmission media are methods that allow the transmission of data without the use of physical means to define the path it takes. Examples of this include microwave, radio or infrared. Unguided media provide a means for transmitting electromagnetic waves but do not guide them; examples are propagation through air, vacuum and seawater.
The term direct link is used to refer to the transmission path between two devices in which signals propagate directly from transmitters to receivers with no intermediate devices, other than amplifiers or repeaters used to increase signal strength. This term can apply to both guided and unguided media.
A transmission may be simplex, half-duplex, or full-duplex.
In simplex transmission, signals are transmitted in only one direction; one station is a transmitter and the other is the receiver. In the half-duplex operation, both stations may transmit, but only one at a time. In full duplex operation, both stations may transmit simultaneously. In the latter case, the medium is carrying signals in both directions at same time." [Transmission medium. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transmission paths" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it to annotate electrical diagrams, electronic schematics and circuit diagrams.
"A physical medium in data communications is the transmission path over which a signal propagates.
Many transmission media are used as communications channel.
For telecommunications purposes in the United States, Federal Standard 1037C, transmission media are classified as one of the following:
(1) Guided (or bounded) - waves are guided along a solid medium such as a transmission line.
(2) Wireless (or unguided) - transmission and reception are achieved by means of an antenna.
One of the most common physical medias used in networking is copper wire. Copper wire to carry signals to long distances using relatively low amounts of power. The unshielded twisted pair (UTP) is eight strands of copper wire, organized into four pairs.
Another example of a physical medium is optical fiber, which has emerged as the most commonly used transmission medium for long-distance communications. Optical fiber is a thin strand of glass that guides light along its length.
Multimode and single mode are two types of commonly used optical fiber. Multimode fiber uses LEDs as the light source and can carry signals over shorter distances, about 2 kilometers. Single mode can carry signals over distances of tens of miles.
Wireless media may carry surface waves or skywaves, either longitudinally or transversely, and are so classified.
In both communications, communication is in the form of electromagnetic waves. With guided transmission media, the waves are guided along a physical path; examples of guided media include phone lines, twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, and optical fibers. Unguided transmission media are methods that allow the transmission of data without the use of physical means to define the path it takes. Examples of this include microwave, radio or infrared. Unguided media provide a means for transmitting electromagnetic waves but do not guide them; examples are propagation through air, vacuum and seawater.
The term direct link is used to refer to the transmission path between two devices in which signals propagate directly from transmitters to receivers with no intermediate devices, other than amplifiers or repeaters used to increase signal strength. This term can apply to both guided and unguided media.
A transmission may be simplex, half-duplex, or full-duplex.
In simplex transmission, signals are transmitted in only one direction; one station is a transmitter and the other is the receiver. In the half-duplex operation, both stations may transmit, but only one at a time. In full duplex operation, both stations may transmit simultaneously. In the latter case, the medium is carrying signals in both directions at same time." [Transmission medium. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transmission paths" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Event-driven Process Chain Diagrams
Event-driven Process Chain Diagrams
Event-driven Process Chain (EPC) Diagram is a type of flowchart widely used for modeling in business engineering and reengineering, business process improvement, and analysis. EPC method was developed within the Architecture of Integrated Information Systems (ARIS) framework.
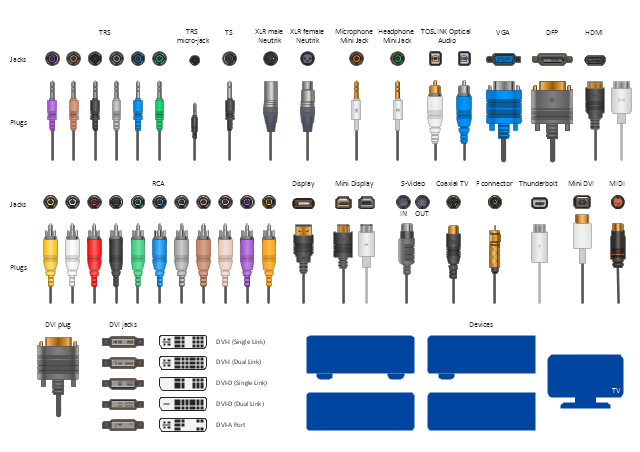
The vector stencils library "Audio and video connectors" contains 94 symbols of audio and video connectors (TRS, TS, XLR, microphone, headphone, TOSLINK, DVI, VGA, DFP, S-Video, RCA, display port, HDMI, Thunderbolt, coaxial TV, F connector, MIDI) and device silhouettes.
Use these jacks and plugs clipart icons for drawing hook up diagrams.
"Audio connectors and video connectors are electrical connectors (or optical connectors) for carrying audio signal and video signal, of either analog or digital format. Analog A/ V connectors often use shielded cables to inhibit radio frequency interference (RFI) and noise." [Audio and video connector. Wikipedia]
"The existence of many different audio and video standards necessitates the definition of hardware interfaces, which define the physical characteristics of the connections between electrical equipment. This includes the types and numbers of wires required along with the strength and frequency of the signal. It also includes the physical design of the plugs and sockets.
An interface may define a connector that is used only by that interface (e.g., DVI) or may define a connector that is also used by another interface; for example, RCA connectors are defined both by the composite video and component video interfaces.
Audio connectors and video connectors are electrical connectors (or optical connectors) for carrying audio signal and video signal, of either analog or digital format. Analog A/ V connectors often use shielded cables to inhibit radio frequency interference (RFI) and noise.
Since both analog and digital signals are used with some styles of connectors, knowledge of the interface used is necessary for a successful transfer of signals. Some interface types use only a distinctive connector or family of connectors, to ensure compatibility. Especially with analog interfaces, physically interchangeable connectors may not carry compatible signals.
Some of these connectors, and other types of connectors, are also used at radio frequency (RF) to connect a radio or television receiver to an antenna or to a cable system..." [Audio and video interfaces and connectors. Wikipedia]
The clipart icons example "Design elements - Audio and video connectors" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Audio and Video Connectors solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these jacks and plugs clipart icons for drawing hook up diagrams.
"Audio connectors and video connectors are electrical connectors (or optical connectors) for carrying audio signal and video signal, of either analog or digital format. Analog A/ V connectors often use shielded cables to inhibit radio frequency interference (RFI) and noise." [Audio and video connector. Wikipedia]
"The existence of many different audio and video standards necessitates the definition of hardware interfaces, which define the physical characteristics of the connections between electrical equipment. This includes the types and numbers of wires required along with the strength and frequency of the signal. It also includes the physical design of the plugs and sockets.
An interface may define a connector that is used only by that interface (e.g., DVI) or may define a connector that is also used by another interface; for example, RCA connectors are defined both by the composite video and component video interfaces.
Audio connectors and video connectors are electrical connectors (or optical connectors) for carrying audio signal and video signal, of either analog or digital format. Analog A/ V connectors often use shielded cables to inhibit radio frequency interference (RFI) and noise.
Since both analog and digital signals are used with some styles of connectors, knowledge of the interface used is necessary for a successful transfer of signals. Some interface types use only a distinctive connector or family of connectors, to ensure compatibility. Especially with analog interfaces, physically interchangeable connectors may not carry compatible signals.
Some of these connectors, and other types of connectors, are also used at radio frequency (RF) to connect a radio or television receiver to an antenna or to a cable system..." [Audio and video interfaces and connectors. Wikipedia]
The clipart icons example "Design elements - Audio and video connectors" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Audio and Video Connectors solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Computer and Networks Area
Computer and Networks Area
The solutions from Computer and Networks Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park collect samples, templates and vector stencils libraries for drawing computer and network diagrams, schemes and technical drawings.
 Audit Flowcharts
Audit Flowcharts
Audit flowcharts solution extends ConceptDraw PRO software with templates, samples and library of vector stencils for drawing the audit and fiscal flow charts.
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Process Flowchart ...
- Circuit Symbols
- Entity Relationship Diagram Symbols and Meaning ERD Symbols ...
- Block Diagram | Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning ...
- Design elements - Electrical circuits | Electrical Engineering ...
- Electrical Schematic Symbols | Design elements - IDEF3 object ...
- Entity Relationship Diagram Symbols and Meaning ERD Symbols ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Flowchart design ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | How To use House ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Algorithm flowchart ...
- Design elements - Chemical engineering | Mechanical Drawing ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Design elements ...
- Electrical Schematic Presentations Symbols
- How To use House Electrical Plan Software | Electrical Drawing ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Entity Relationship ...
- Process Flowchart | Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Rack ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Design elements ...
- Design elements - Switches | Network Glossary Definition | Symbols ...
- Symbols That Service Engineers Use In Circuit Diagrams
- Design elements - Qualifying | Process Flowchart | Basic Flowchart ...