IDEF3 Standard
Use Case Diagrams technology. IDEF3 Standard is intended for description and further analysis of technological processes of an enterprise. Using IDEF3 standard it is possible to examine and model scenarios of technological processes.IDEF1X Standard
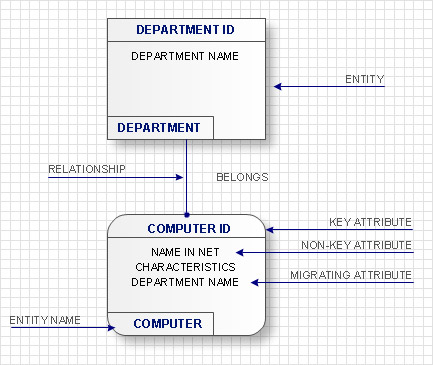
Use Case Diagrams technology. IDEF1x standard - for work with relational data bases. IDEF1x standard is meant for constructing of conceptual schemes which represent the structure of data in the context of the concerned system, for example, a commercial organization.This bank account UML package diagram was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: Package diagram1.jpg.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Package_ diagram1.jpg]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"A very important concept in object-oriented design, inheritance, refers to the ability of one class (child class) to inherit the identical functionality of another class (super class), and then add new functionality of its own. (In a very non-technical sense, imagine that I inherited my mother's general musical abilities, but in my family I'm the only one who plays electric guitar.) To model inheritance on a class diagram, a solid line is drawn from the child class (the class inheriting the behavior) with a closed, unfilled arrowhead (or triangle) pointing to the super class. Consider types of bank accounts: Figure 4 shows how both CheckingAccount and SavingsAccount classes inherit from the BankAccount class.
Figure 4: Inheritance is indicated by a solid line with a closed, unfilled arrowhead pointing at the super class." [ibm.com/ developerworks/ rational/ library/ content/ RationalEdge/ sep04/ bell/ index.html]
This bank account UML package diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Package_ diagram1.jpg]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"A very important concept in object-oriented design, inheritance, refers to the ability of one class (child class) to inherit the identical functionality of another class (super class), and then add new functionality of its own. (In a very non-technical sense, imagine that I inherited my mother's general musical abilities, but in my family I'm the only one who plays electric guitar.) To model inheritance on a class diagram, a solid line is drawn from the child class (the class inheriting the behavior) with a closed, unfilled arrowhead (or triangle) pointing to the super class. Consider types of bank accounts: Figure 4 shows how both CheckingAccount and SavingsAccount classes inherit from the BankAccount class.
Figure 4: Inheritance is indicated by a solid line with a closed, unfilled arrowhead pointing at the super class." [ibm.com/ developerworks/ rational/ library/ content/ RationalEdge/ sep04/ bell/ index.html]
This bank account UML package diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
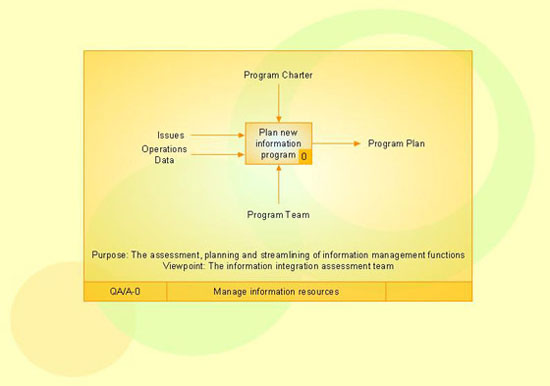
The vector stencils library "IDEF0 diagrams" contains 18 symbols for drawing IDEF0 function modeling diagrams using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"The IDEF0 model ... is based on a simple syntax. Each activity is described by a verb-based label placed in a box. Inputs are shown as arrows entering the left side of the activity box while output are shown as exiting arrows on the right side of the box. Controls are displayed as arrows entering the top of the box and mechanisms are displayed as arrows entering from the bottom of the box. Inputs, Controls, Outputs, and Mechanisms are all referred to as concepts.
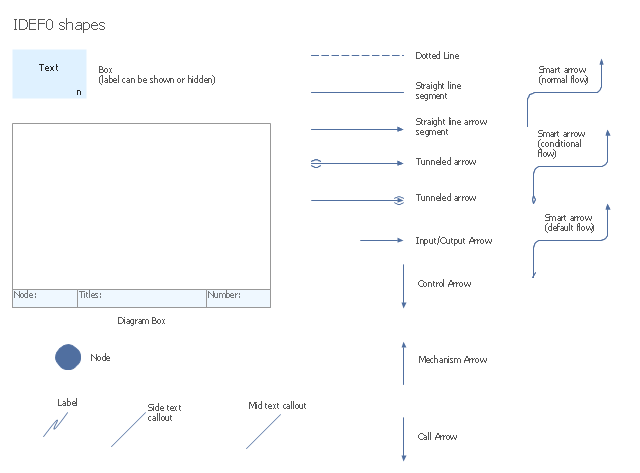
- Arrow : A directed line, composed of one or more arrow segments, that models an open channel or conduit conveying data or objects from source (no arrowhead) to use (with arrowhead). There are 4 arrow classes: Input Arrow, Output Arrow, Control Arrow, and Mechanism Arrow (includes Call Arrow). See Arrow Segment, Boundary Arrow, Internal Arrow.
- Box : A rectangle, containing a name and number, used to represent a function.
- Context : The immediate environment in which a function (or set of functions on a diagram) operates.
- Decomposition : The partitioning of a modeled function into its component functions.
- Fork : The junction at which an IDEF0 arrow segment (going from source to use) divides into two or more arrow segments. May denote unbundling of meaning.
- Function : An activity, process, or transformation (modeled by an IDEF0 box) identified by a verb or verb phrase that describes what must be accomplished.
- Join : The junction at which an IDEF0 arrow segment (going from source to use) merges with one or more other arrow segments to form a single arrow segment. May denote bundling of arrow segment meanings.
- Node : A box from which child boxes originate; a parent box. See Node Index, Node Tree, Node Number, Node Reference, Diagram Node Number." [IDEF0. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - IDEF0 diagram" is included in the IDEF0 Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"The IDEF0 model ... is based on a simple syntax. Each activity is described by a verb-based label placed in a box. Inputs are shown as arrows entering the left side of the activity box while output are shown as exiting arrows on the right side of the box. Controls are displayed as arrows entering the top of the box and mechanisms are displayed as arrows entering from the bottom of the box. Inputs, Controls, Outputs, and Mechanisms are all referred to as concepts.
- Arrow : A directed line, composed of one or more arrow segments, that models an open channel or conduit conveying data or objects from source (no arrowhead) to use (with arrowhead). There are 4 arrow classes: Input Arrow, Output Arrow, Control Arrow, and Mechanism Arrow (includes Call Arrow). See Arrow Segment, Boundary Arrow, Internal Arrow.
- Box : A rectangle, containing a name and number, used to represent a function.
- Context : The immediate environment in which a function (or set of functions on a diagram) operates.
- Decomposition : The partitioning of a modeled function into its component functions.
- Fork : The junction at which an IDEF0 arrow segment (going from source to use) divides into two or more arrow segments. May denote unbundling of meaning.
- Function : An activity, process, or transformation (modeled by an IDEF0 box) identified by a verb or verb phrase that describes what must be accomplished.
- Join : The junction at which an IDEF0 arrow segment (going from source to use) merges with one or more other arrow segments to form a single arrow segment. May denote bundling of arrow segment meanings.
- Node : A box from which child boxes originate; a parent box. See Node Index, Node Tree, Node Number, Node Reference, Diagram Node Number." [IDEF0. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - IDEF0 diagram" is included in the IDEF0 Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
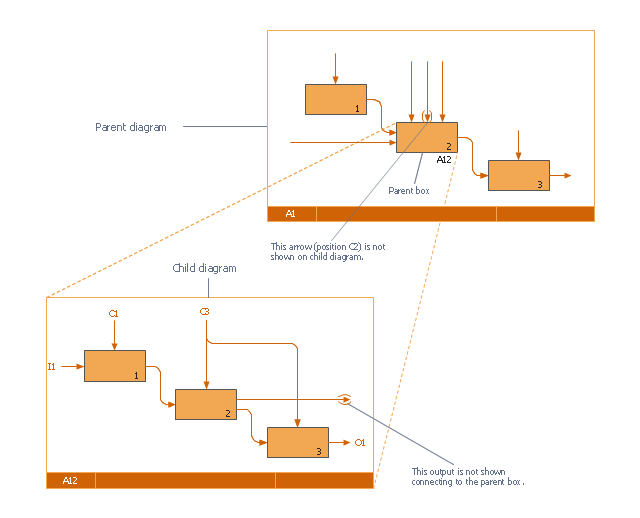
This IDEF0 diagram was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: 18 Example of Tunneled Arrows.svg.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:18_ Example_ of_ Tunneled_ Arrows.svg]
"Tunneled Arrows.
Arrows that provide information at one level of decomposition but are not needed at another (parent, child) level." [classes.engr.oregonstate.edu/ mime/ fall2013/ ie545-001/ Slides/ class%20 01-3b%20 IDEF0%20 1%20 revised.pdf]
The example "IDEF0 diagram - Tunneled arrows" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the solution "IDEF Business Process Diagrams" from the area "Business Processes" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:18_ Example_ of_ Tunneled_ Arrows.svg]
"Tunneled Arrows.
Arrows that provide information at one level of decomposition but are not needed at another (parent, child) level." [classes.engr.oregonstate.edu/ mime/ fall2013/ ie545-001/ Slides/ class%20 01-3b%20 IDEF0%20 1%20 revised.pdf]
The example "IDEF0 diagram - Tunneled arrows" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the solution "IDEF Business Process Diagrams" from the area "Business Processes" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- IDEF0 standard with ConceptDraw PRO | IDEF0 Diagrams | IDEF0 ...
- DFD - Process of account receivable | UML package diagram for ...
- UML package diagram for Bank account | About UML | Booch OOD ...
- UML package diagram for Bank account | UML Diagram | Design ...
- UML Class Diagram Generalization Example
- UML Deployment Diagram Example - ATM System | ATM UML ...
- Diagramming Software for Design UML Package Diagrams | UML ...
- Class UML Diagram for Bank Account System | UML package ...
- Diagram Of The Types Of Lines Im Basic Design
- UML class diagram - Bank account
- UML package diagram for Bank account
- ATM UML Diagrams | Design elements - Bank UML package ...
- Line Graphs | UML package diagram for Bank account | Design ...
- Process Flow Diagram For Account
- UML package diagram - Template | UML Deployment Diagram ...
- UML for Bank | ATM UML Diagrams | UML use case diagram ...
- UML Class Diagram Generalization Example | UML Sequence ...
- UML for Bank | UML use case diagram - Banking system | Class ...
- Class UML Diagram for Bank Account System | UML class diagram ...
- UML Class Diagram Generalization Example | UML Block Diagram ...