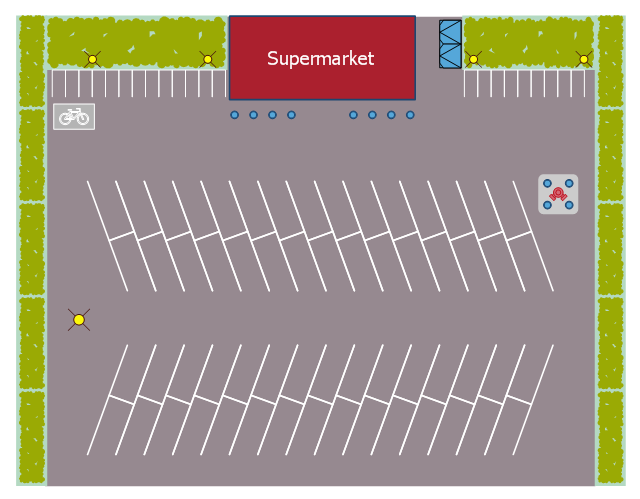
"Site planning in landscape architecture and architecture refers to the organizational stage of the landscape design process. It involves the organization of land use zoning, access, circulation, privacy, security, shelter, land drainage, and other factors. This is done by arranging the compositional elements of landform, planting, water, buildings and paving in site plans.
Site planning generally begins by assessing a potential site for development through site analysis. Information about slope, soils, hydrology, vegetation, parcel ownership, orientation, etc. are assessed and mapped. By determining areas that are poor for development (such as floodplain or steep slopes) and better for development, the planner or architect can assess optimal location and design a structure that works within this space.
Site planning is also one part of the Architect Registration Examination (ARE) in the United States and Canada." [Site planning. Wikipedia]
The site plan example "Supermarket parking" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Site Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ building-site-plans
Site planning generally begins by assessing a potential site for development through site analysis. Information about slope, soils, hydrology, vegetation, parcel ownership, orientation, etc. are assessed and mapped. By determining areas that are poor for development (such as floodplain or steep slopes) and better for development, the planner or architect can assess optimal location and design a structure that works within this space.
Site planning is also one part of the Architect Registration Examination (ARE) in the United States and Canada." [Site planning. Wikipedia]
The site plan example "Supermarket parking" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Site Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ building-site-plans
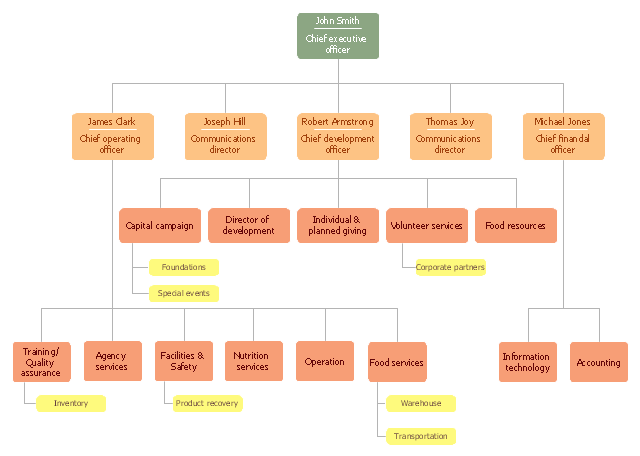
"A food bank or foodbank is a non-profit, charitable organization that distributes food to those who have difficulty purchasing enough food to avoid hunger.
In the United States and Australia, food banks usually operate on the "warehouse" model. They act as food storage and distribution depots for smaller front line agencies; and usually do not themselves give out food directly to the hungry. After the food is collected, sorted, and reviewed for quality, these food banks distribute it to non-profit community or government agencies, including food pantries, food closets, soup kitchens, homeless shelters, orphanages, and schools.
Outside North America and Australia, the "front line" model is often found. Such food banks give out most or all of their food directly to the end users. For both models, the largest sources of food include for-profit growers, manufacturers, distributors and retailers who in the normal course of business have excess food that they cannot sell. Some foodbanks receive a substantial proportion of their food from individual donors, including their volunteer workers. There is considerable overlap with food salvage, food rescue and gleaning, although not with freeganism or dumpster-diving." [Food bank. Wikipedia]
The organization chart example "Foodbank" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Organizational Charts solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ management-org-charts
In the United States and Australia, food banks usually operate on the "warehouse" model. They act as food storage and distribution depots for smaller front line agencies; and usually do not themselves give out food directly to the hungry. After the food is collected, sorted, and reviewed for quality, these food banks distribute it to non-profit community or government agencies, including food pantries, food closets, soup kitchens, homeless shelters, orphanages, and schools.
Outside North America and Australia, the "front line" model is often found. Such food banks give out most or all of their food directly to the end users. For both models, the largest sources of food include for-profit growers, manufacturers, distributors and retailers who in the normal course of business have excess food that they cannot sell. Some foodbanks receive a substantial proportion of their food from individual donors, including their volunteer workers. There is considerable overlap with food salvage, food rescue and gleaning, although not with freeganism or dumpster-diving." [Food bank. Wikipedia]
The organization chart example "Foodbank" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Organizational Charts solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ management-org-charts
- Supermarket parking - Site plan | Site plan | Secure parking |
- Organization chart - Foodbank | Examples of Flowcharts, Org Charts ...
- Create Sophisticated Professional Diagrams - Simply | Organization ...
- How to Draw an Organization Chart | ConceptDraw PRO ...
- Supermarket parking - Site plan | Advertising creation process ...
- Examples of Flowcharts, Org Charts and More - Conceptdraw.com
- Organizational Structure | How to Draw an Organization Chart ...
- ConceptDraw PRO - Organizational chart software | Organizational ...
- How to Draw an Organization Chart | Organizational Charts ...
- Examples of Flowcharts, Org Charts and More | IDEF1X Standard ...
- Six Markets Model Chart Template - Conceptdraw.com
- ConceptDraw PRO - Organizational chart software | Business ...
- Examples of Flowcharts, Org Charts and More | ConceptDraw PRO ...
- Company's organizational chart
- Site Plans
- Arrow graph - Total value of manufacturers' shipments | Flowchart by ...