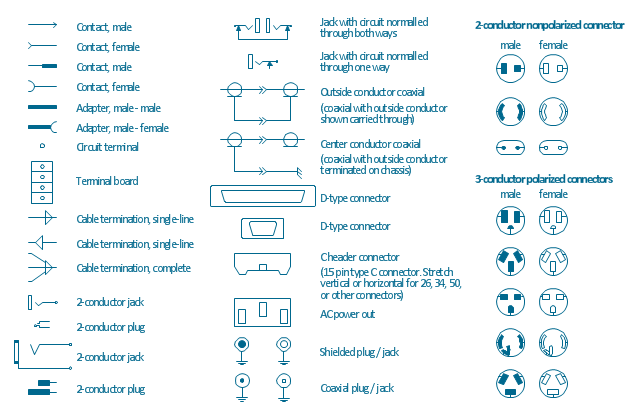
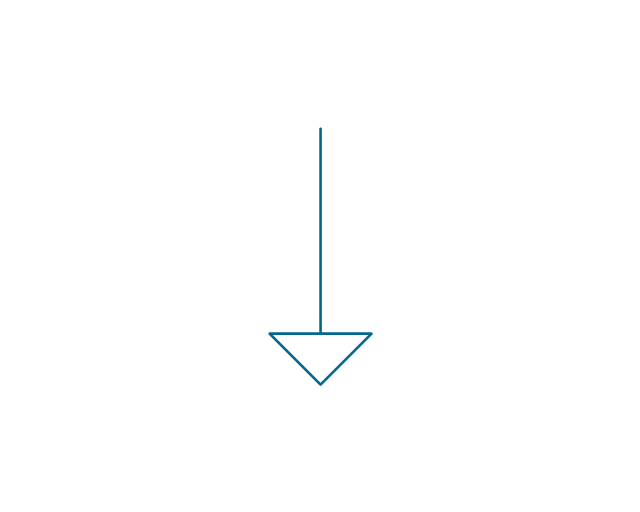
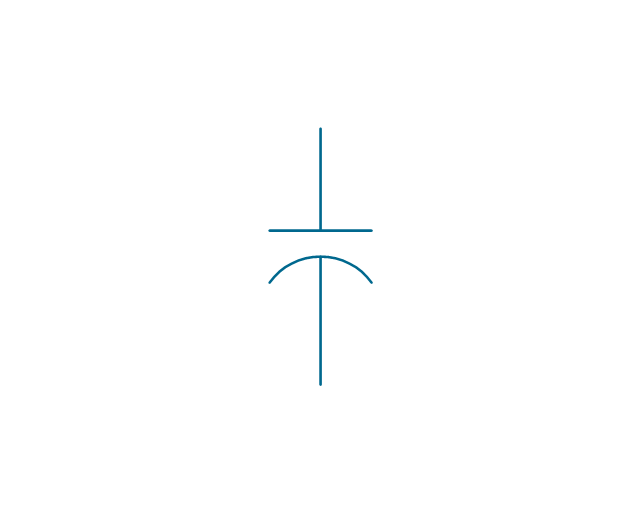
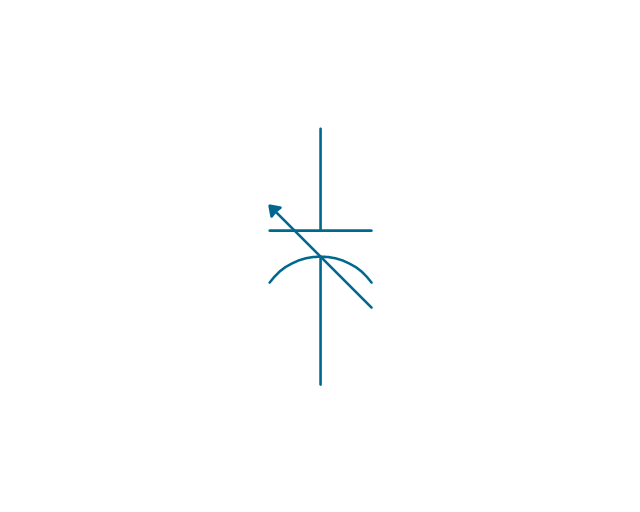
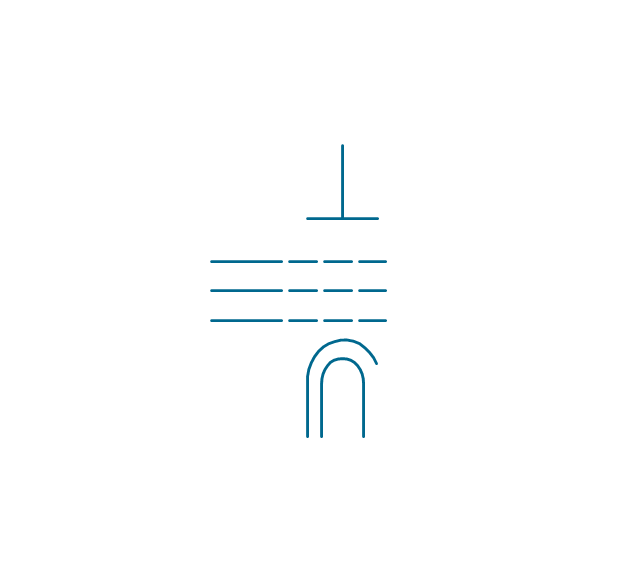
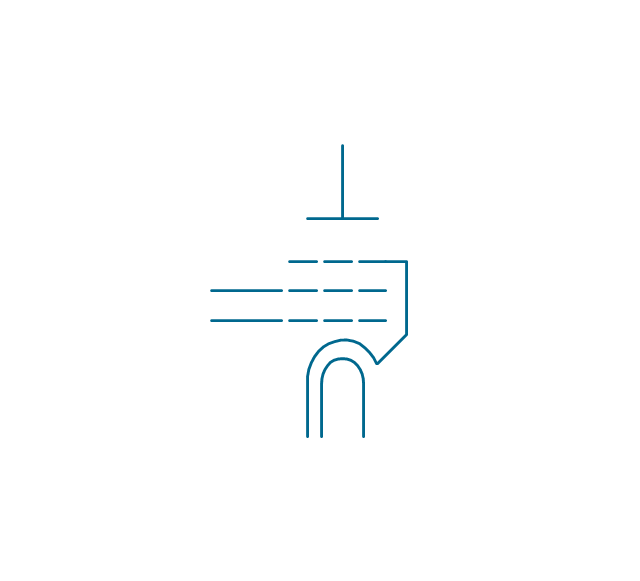
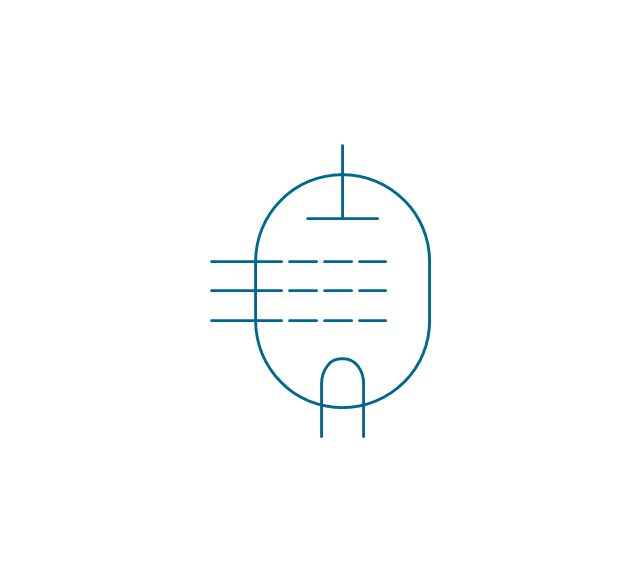
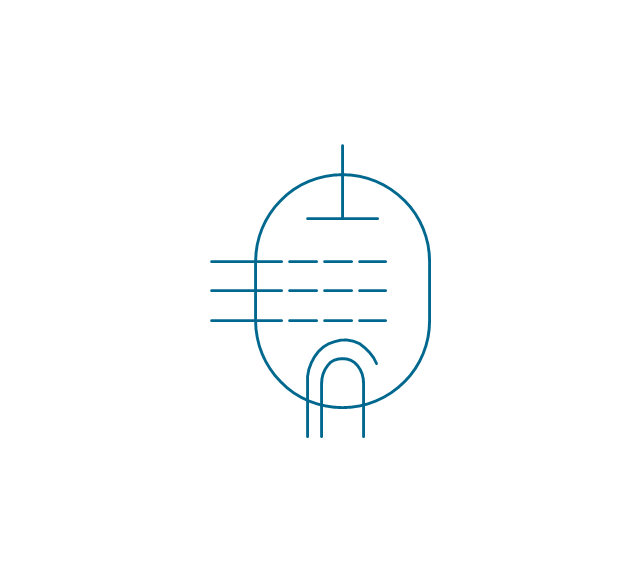
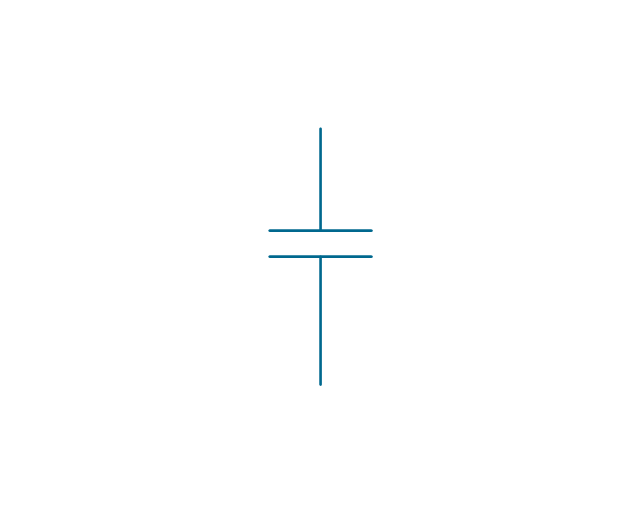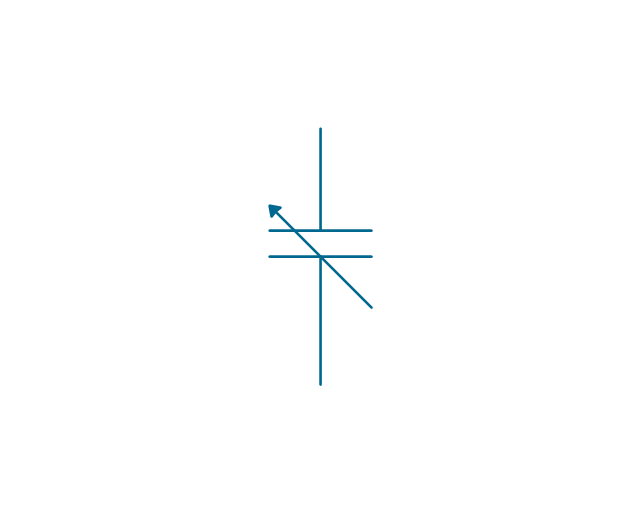The vector stencils library "Terminals and connectors" contains 43 element symbols of terminals, connectors, plugs, polarized connectors, jacks, coaxial cables, and conductors.
Use it for drawing the wiring diagrams, electrical layouts, electronic schematics, and circuit diagrams.
"An electrical connector is an electro-mechanical device for joining electrical circuits as an interface using a mechanical assembly. Connectors consist of plugs (male-ended) and jacks (female-ended). The connection may be temporary, as for portable equipment, require a tool for assembly and removal, or serve as a permanent electrical joint between two wires or devices. An adapter can be used to effectively bring together dissimilar connectors.
There are hundreds of types of electrical connectors. Connectors may join two lengths of flexible copper wire or cable, or connect a wire or cable or optical interface to an electrical terminal.
In computing, an electrical connector can also be known as a physical interface... Cable glands, known as cable connectors in the US, connect wires to devices mechanically rather than electrically and are distinct from quick-disconnects performing the latter." [Electrical connector. Wikipedia]
"A terminal is the point at which a conductor from an electrical component, device or network comes to an end and provides a point of connection to external circuits. A terminal may simply be the end of a wire or it may be fitted with a connector or fastener. In network analysis, terminal means a point at which connections can be made to a network in theory and does not necessarily refer to any real physical object. In this context, especially in older documents, it is sometimes called a "pole".
The connection may be temporary, as seen in portable equipment, may require a tool for assembly and removal, or may be a permanent electrical joint between two wires or devices.
All electric cell have two terminals. The first is the positive terminal and the second is the negative terminal. The positive terminal looks like a metal cap and the negative terminal looks like a metal disc. The current flows from the positive terminal, and out through the negative terminal, replicative of current flow (positive (+) to negative (-) flow)." [Terminal (electronics). Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Terminals and connectors" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it for drawing the wiring diagrams, electrical layouts, electronic schematics, and circuit diagrams.
"An electrical connector is an electro-mechanical device for joining electrical circuits as an interface using a mechanical assembly. Connectors consist of plugs (male-ended) and jacks (female-ended). The connection may be temporary, as for portable equipment, require a tool for assembly and removal, or serve as a permanent electrical joint between two wires or devices. An adapter can be used to effectively bring together dissimilar connectors.
There are hundreds of types of electrical connectors. Connectors may join two lengths of flexible copper wire or cable, or connect a wire or cable or optical interface to an electrical terminal.
In computing, an electrical connector can also be known as a physical interface... Cable glands, known as cable connectors in the US, connect wires to devices mechanically rather than electrically and are distinct from quick-disconnects performing the latter." [Electrical connector. Wikipedia]
"A terminal is the point at which a conductor from an electrical component, device or network comes to an end and provides a point of connection to external circuits. A terminal may simply be the end of a wire or it may be fitted with a connector or fastener. In network analysis, terminal means a point at which connections can be made to a network in theory and does not necessarily refer to any real physical object. In this context, especially in older documents, it is sometimes called a "pole".
The connection may be temporary, as seen in portable equipment, may require a tool for assembly and removal, or may be a permanent electrical joint between two wires or devices.
All electric cell have two terminals. The first is the positive terminal and the second is the negative terminal. The positive terminal looks like a metal cap and the negative terminal looks like a metal disc. The current flows from the positive terminal, and out through the negative terminal, replicative of current flow (positive (+) to negative (-) flow)." [Terminal (electronics). Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Terminals and connectors" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
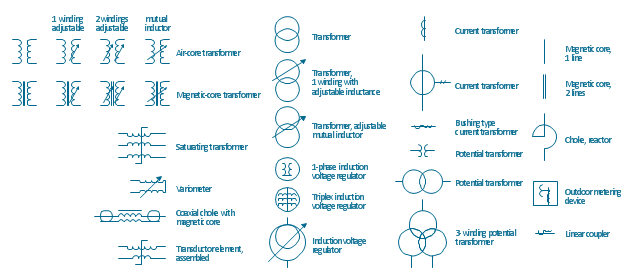
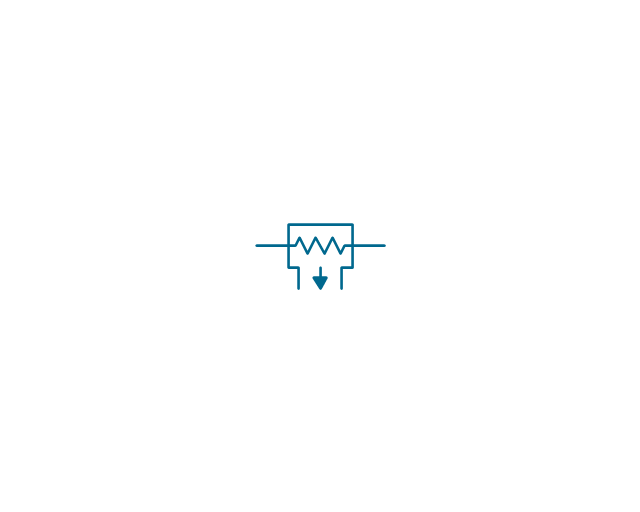
The vector stencils library "Transformers and windings" contains 29 element symbols of transformers, windings, couplers, metering devices, transductors, magnetic cores, chokes, and a variometer.
Use it to design the electromechanical device schematics and electronic circuit diagrams.
"A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. Transformers may be used in step-up or step-down voltage conversion, which 'transforms' an AC voltage from one voltage level on the input of the device to another level at the output terminals. This special function of transformers can provide control of specified requirements of current level as an alternating current source, or it may be used for impedance matching between mismatched electrical circuits to effect maximum power transfer between the circuits.
A transformer most commonly consists of two windings of wire that are wound around a common core to induce tight electromagnetic coupling between the windings. The core material is often a laminated iron core. The coil that receives the electrical input energy is referred to as the primary winding, while the output coil is called the secondary winding.
An alternating electric current flowing through the primary winding (coil) of a transformer generates an electromagnetic field in its surroundings and a varying magnetic flux in the core of the transformer. By electromagnetic induction this magnetic flux generates a varying electromotive force in the secondary winding, resulting in a voltage across the output terminals. If a load impedance is connected across the secondary winding, a current flows through the secondary winding drawing power from the primary winding and its power source." [Transformer. Wikipedia]
"An electromagnetic coil (or simply a "coil") is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet. When electricity is passed through a coil, it generates a magnetic field. One loop of wire is usually referred to as a turn or a winding, and a coil consists of one or more turns. For use in an electronic circuit, electrical connection terminals called taps are often connected to a coil. Coils are often coated with varnish or wrapped with insulating tape to provide additional insulation and secure them in place. A completed coil assembly with one or more set of coils and taps is often called the windings.
Windings are used in transformers, electric motors, inductors, solenoids, loudspeakers, and many other applications." [Electromagnetic coil. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transformers and windings" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it to design the electromechanical device schematics and electronic circuit diagrams.
"A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. Transformers may be used in step-up or step-down voltage conversion, which 'transforms' an AC voltage from one voltage level on the input of the device to another level at the output terminals. This special function of transformers can provide control of specified requirements of current level as an alternating current source, or it may be used for impedance matching between mismatched electrical circuits to effect maximum power transfer between the circuits.
A transformer most commonly consists of two windings of wire that are wound around a common core to induce tight electromagnetic coupling between the windings. The core material is often a laminated iron core. The coil that receives the electrical input energy is referred to as the primary winding, while the output coil is called the secondary winding.
An alternating electric current flowing through the primary winding (coil) of a transformer generates an electromagnetic field in its surroundings and a varying magnetic flux in the core of the transformer. By electromagnetic induction this magnetic flux generates a varying electromotive force in the secondary winding, resulting in a voltage across the output terminals. If a load impedance is connected across the secondary winding, a current flows through the secondary winding drawing power from the primary winding and its power source." [Transformer. Wikipedia]
"An electromagnetic coil (or simply a "coil") is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet. When electricity is passed through a coil, it generates a magnetic field. One loop of wire is usually referred to as a turn or a winding, and a coil consists of one or more turns. For use in an electronic circuit, electrical connection terminals called taps are often connected to a coil. Coils are often coated with varnish or wrapped with insulating tape to provide additional insulation and secure them in place. A completed coil assembly with one or more set of coils and taps is often called the windings.
Windings are used in transformers, electric motors, inductors, solenoids, loudspeakers, and many other applications." [Electromagnetic coil. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transformers and windings" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
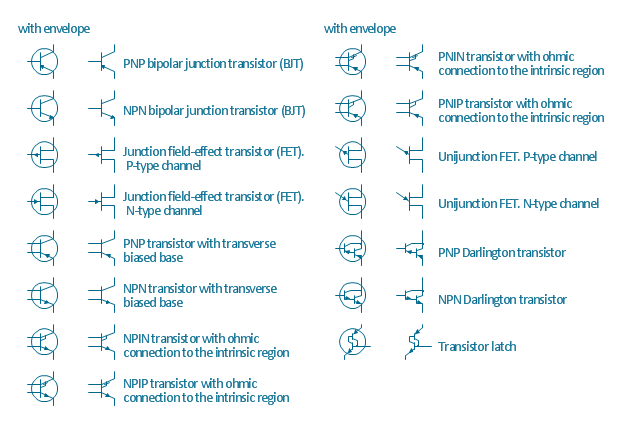
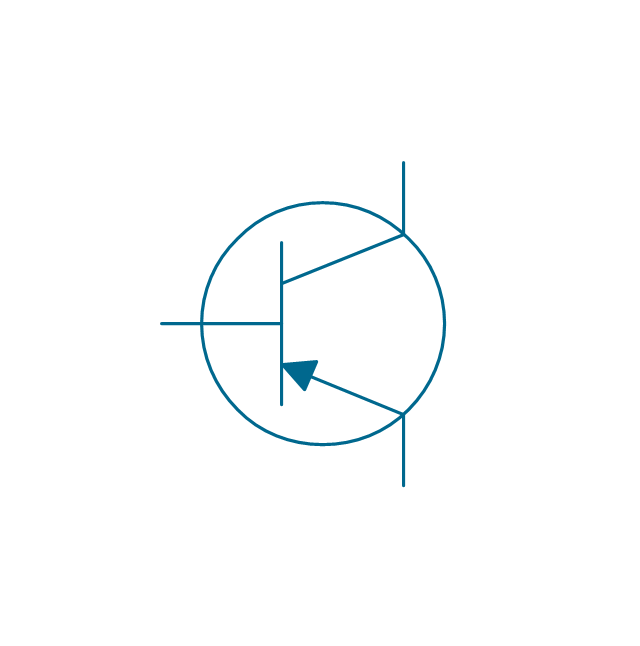
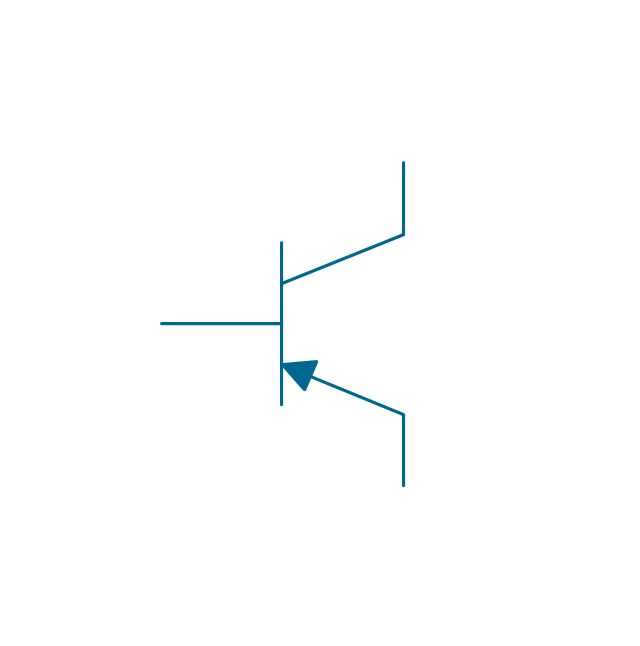
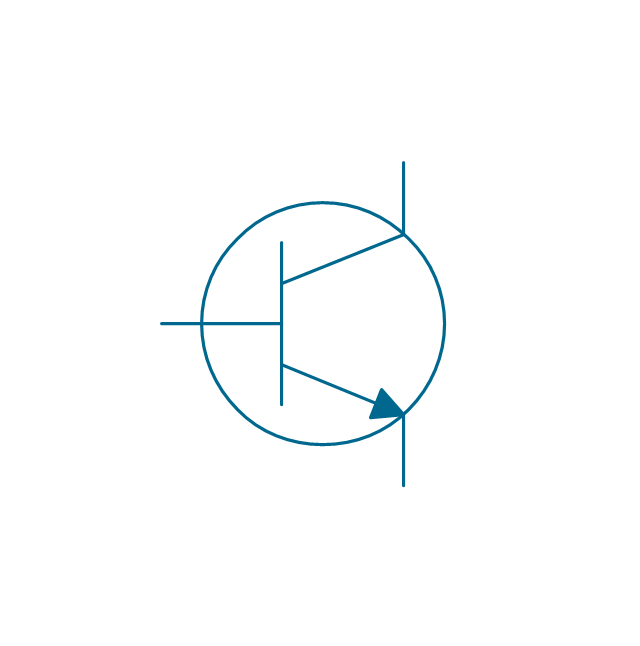
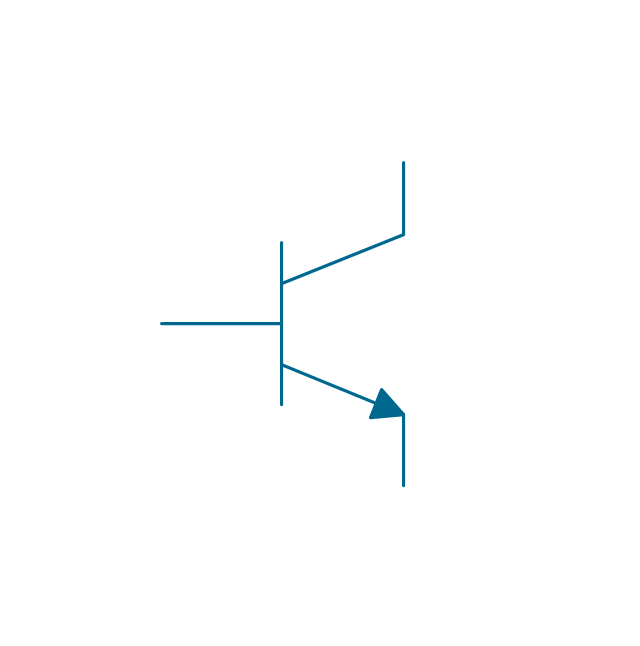
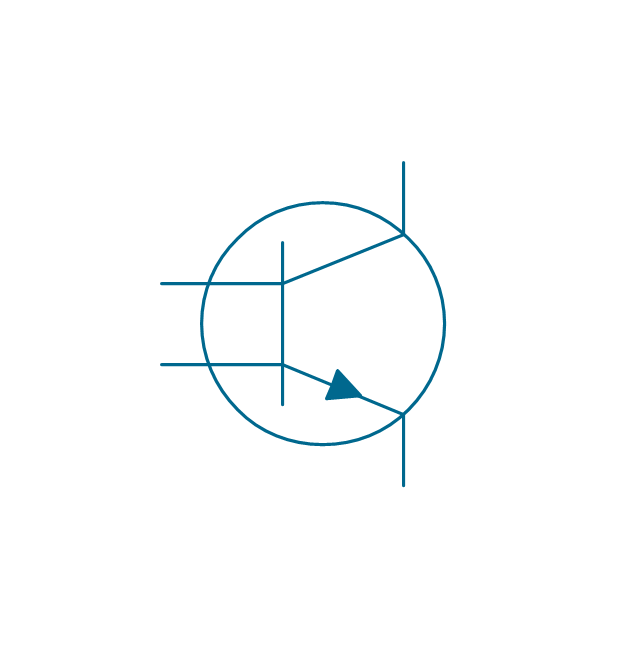
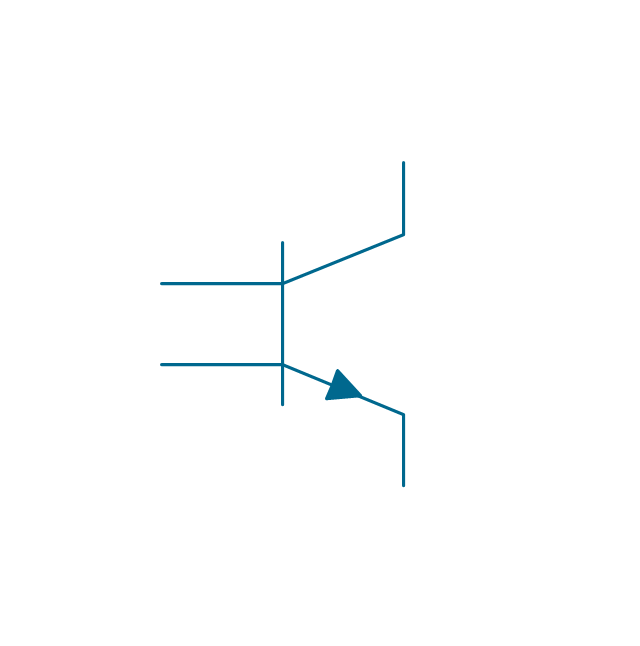
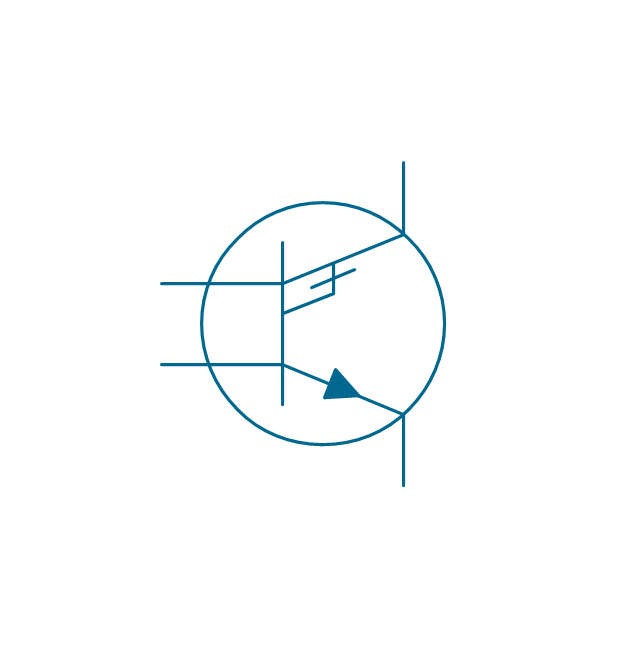
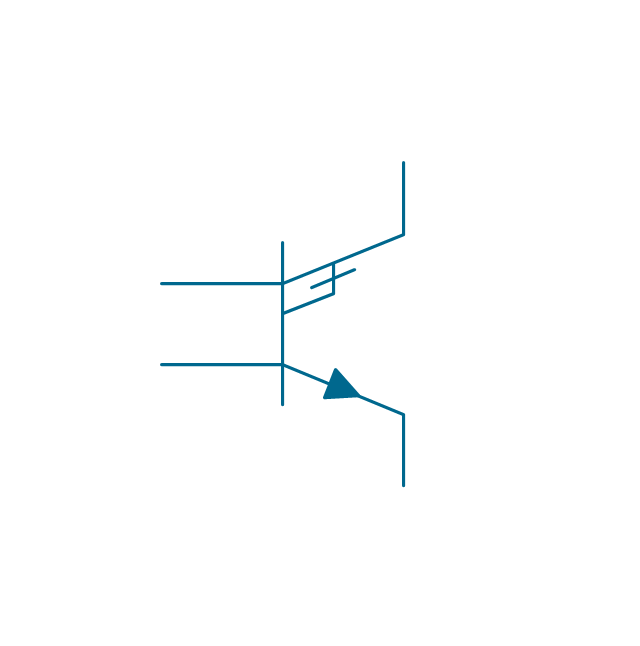
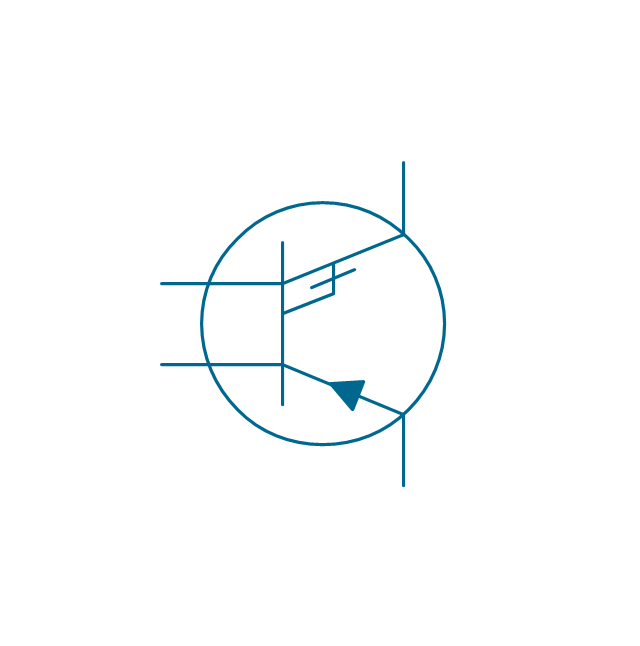
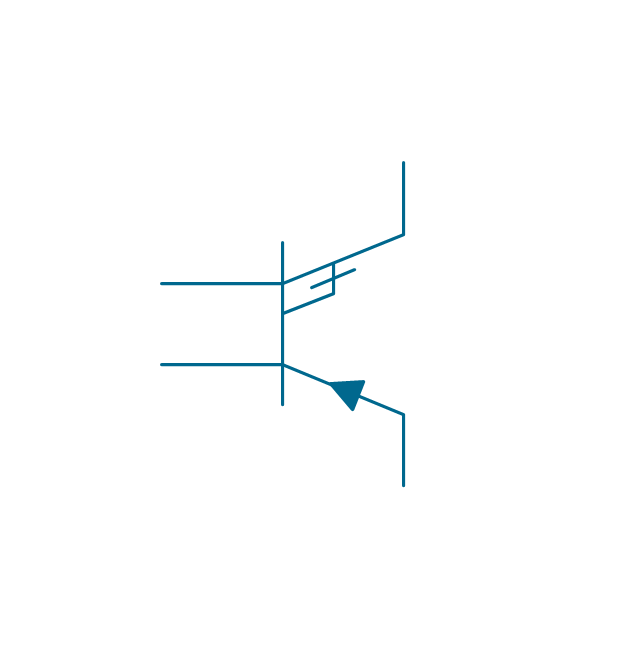
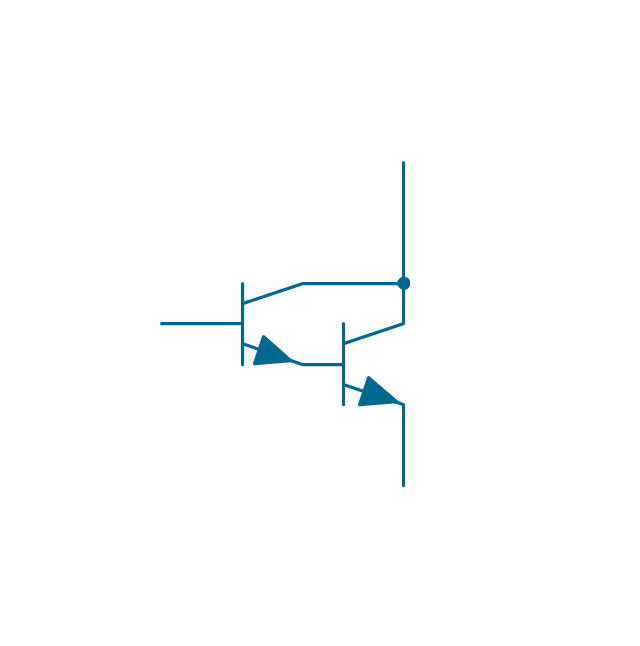
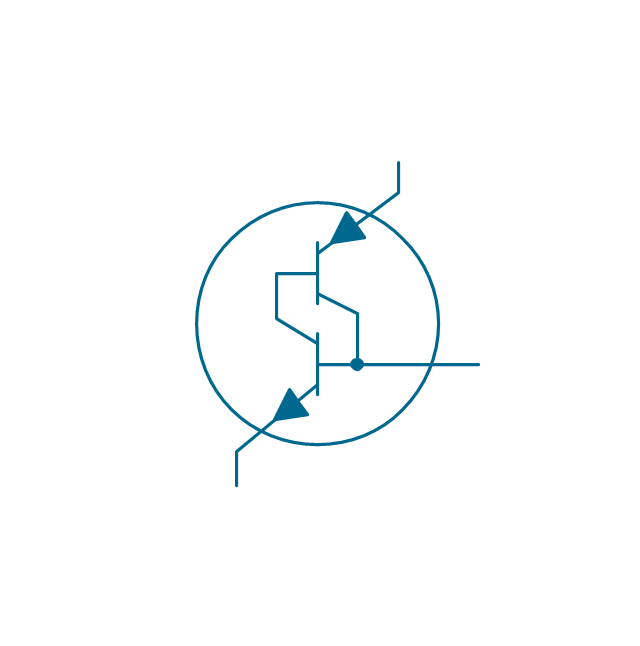
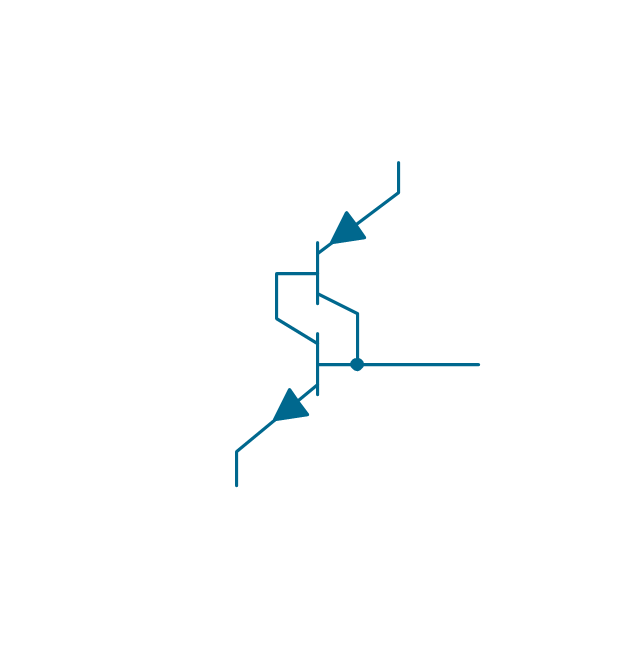
The vector stencils library "Transistors" contains 30 symbols of transistors drawing electronic schematics and circuit diagrams.
"A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.
The transistor is the fundamental building block of modern electronic devices, and is ubiquitous in modern electronic systems. ...
Transistors are categorized by:
(1) Semiconductor material...: the metalloids germanium ... and silicon ... in amorphous, polycrystalline and monocrystalline form; the compounds gallium arsenide ... and silicon carbide ..., the alloy silicon-germanium ..., the allotrope of carbon graphene ...
(2) Structure: BJT, JFET, IGFET (MOSFET), insulated-gate bipolar transistor, "other types"
(3) Electrical polarity (positive and negative): n–p–n, p–n–p (BJTs); n-channel, p-channel (FETs)
(4) Maximum power rating: low, medium, high
(5) Maximum operating frequency: low, medium, high, radio (RF), microwave frequency...
(6) Application: switch, general purpose, audio, high voltage, super-beta, matched pair
(7) Physical packaging: through-hole metal, through-hole plastic, surface mount, ball grid array, power modules...
(8) Amplification factor..." [Transistor. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transistors" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.
The transistor is the fundamental building block of modern electronic devices, and is ubiquitous in modern electronic systems. ...
Transistors are categorized by:
(1) Semiconductor material...: the metalloids germanium ... and silicon ... in amorphous, polycrystalline and monocrystalline form; the compounds gallium arsenide ... and silicon carbide ..., the alloy silicon-germanium ..., the allotrope of carbon graphene ...
(2) Structure: BJT, JFET, IGFET (MOSFET), insulated-gate bipolar transistor, "other types"
(3) Electrical polarity (positive and negative): n–p–n, p–n–p (BJTs); n-channel, p-channel (FETs)
(4) Maximum power rating: low, medium, high
(5) Maximum operating frequency: low, medium, high, radio (RF), microwave frequency...
(6) Application: switch, general purpose, audio, high voltage, super-beta, matched pair
(7) Physical packaging: through-hole metal, through-hole plastic, surface mount, ball grid array, power modules...
(8) Amplification factor..." [Transistor. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transistors" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Electrical circuits" contains 49 element symbols of electrical and electronic devices, including ignitors, starters, transmitters, circuit protectors, transducers, radio and audio equipment.
Use it for drawing electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
Use it for drawing electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
HelpDesk
How to Draw an Electrical Scheme Using ConceptDraw Solution Park
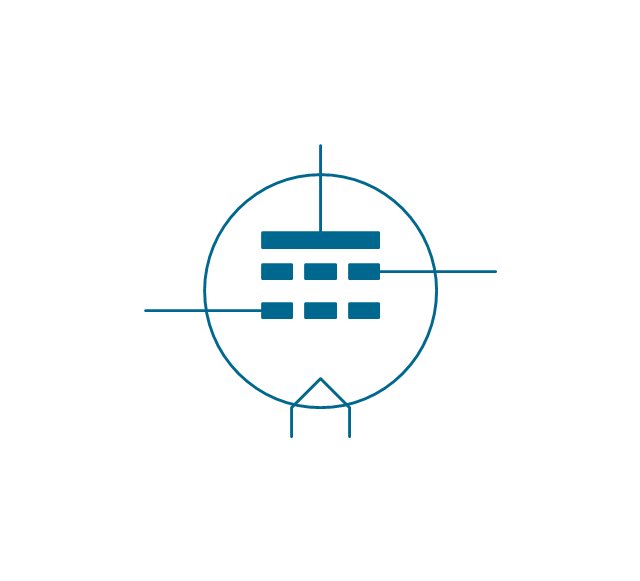
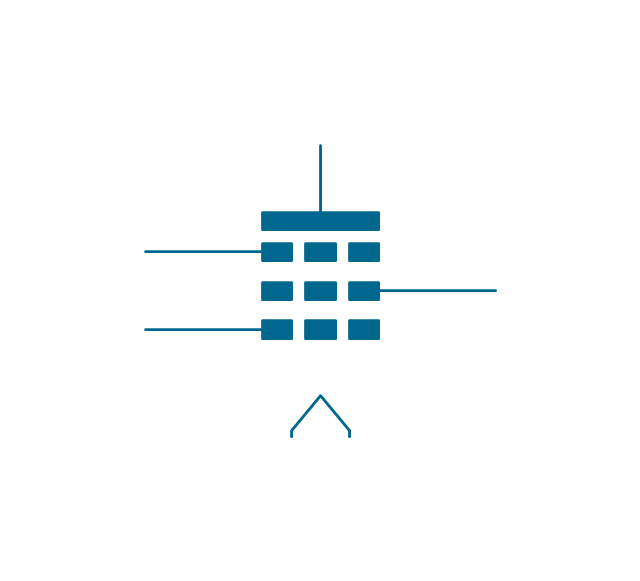
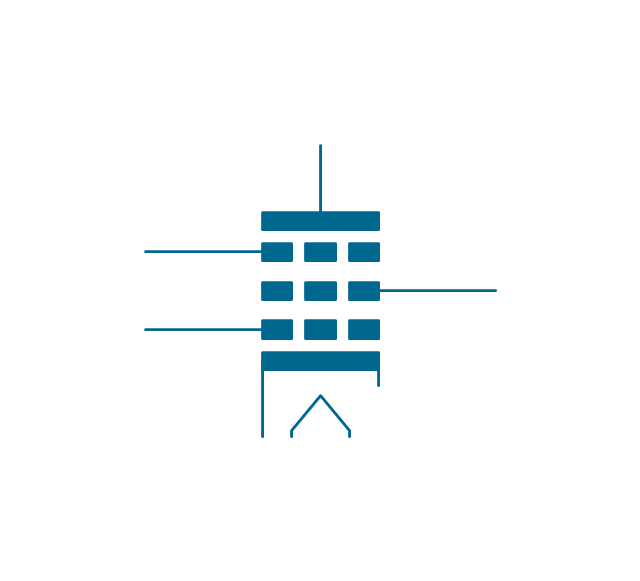
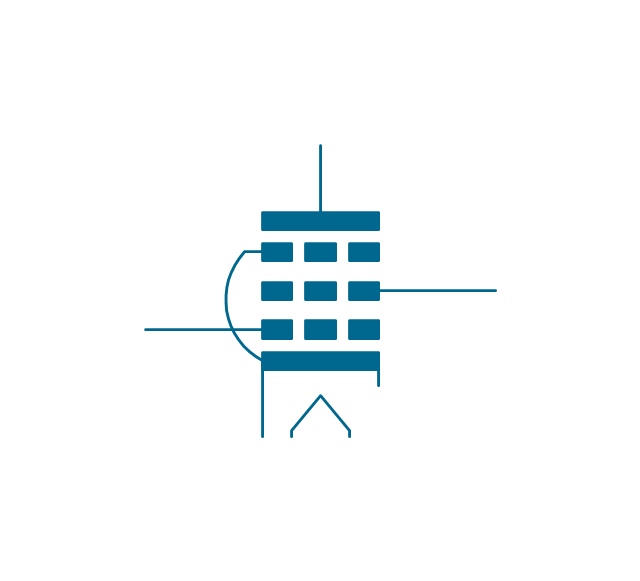
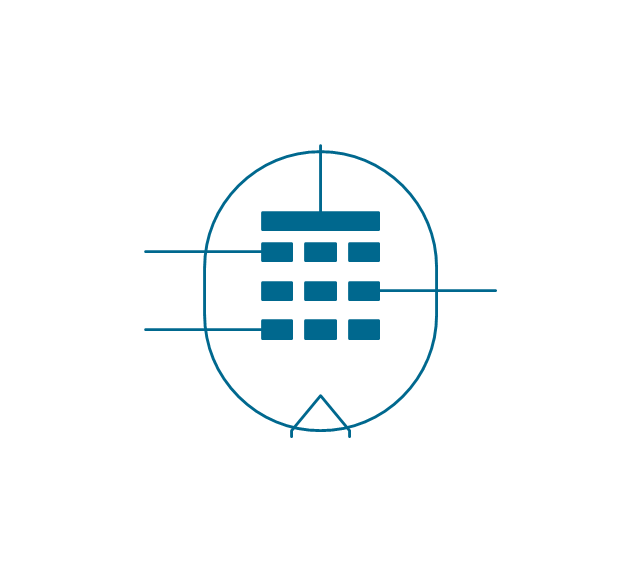
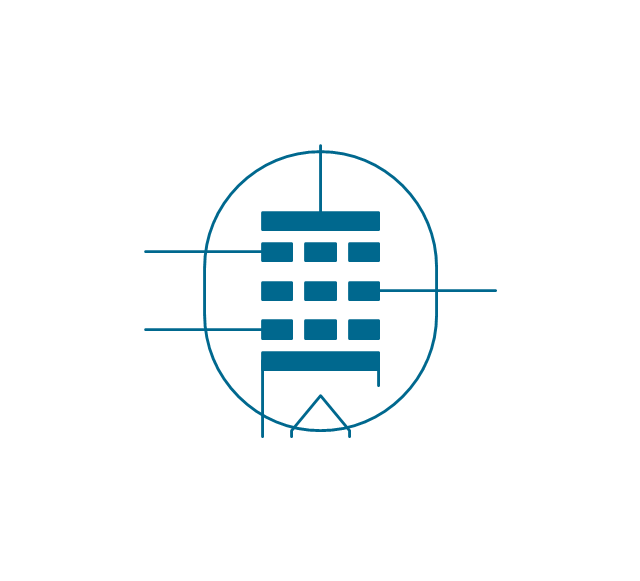
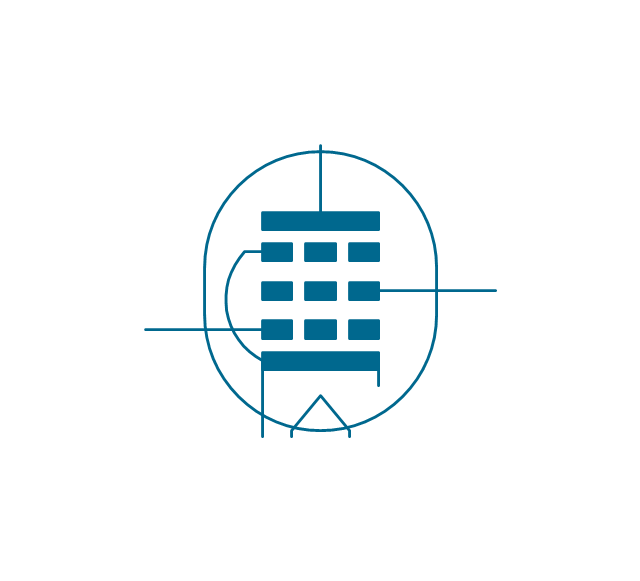
The ability to visualize industrial systems in electronics, electrical, chemical, process, and mechanical engineering is delivered by the ConceptDraw Engineering solution.The vector stencils library "Electron tubes" contains 36 element symbols of electron tubes.
Use it for drawing electrical schematics and electronic circuit diagrams in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
Use it for drawing electrical schematics and electronic circuit diagrams in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
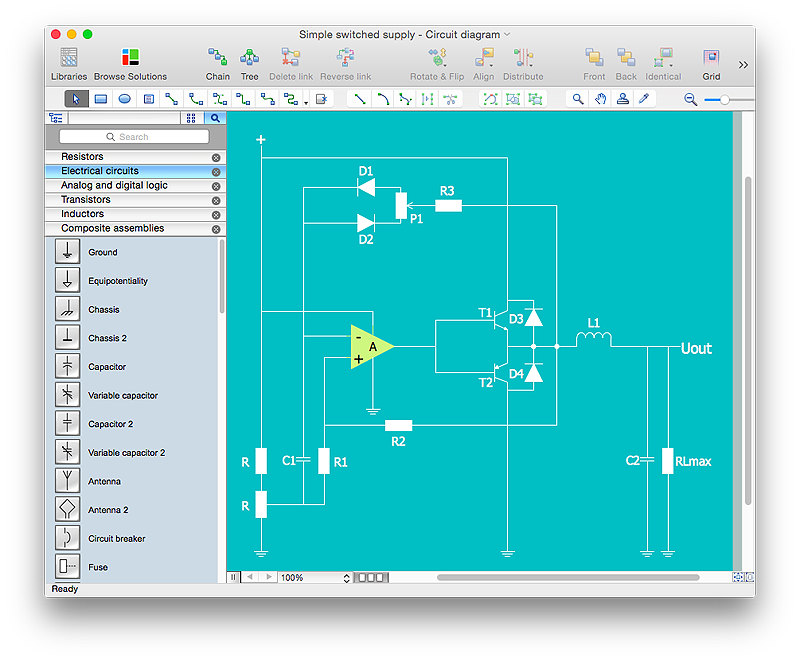
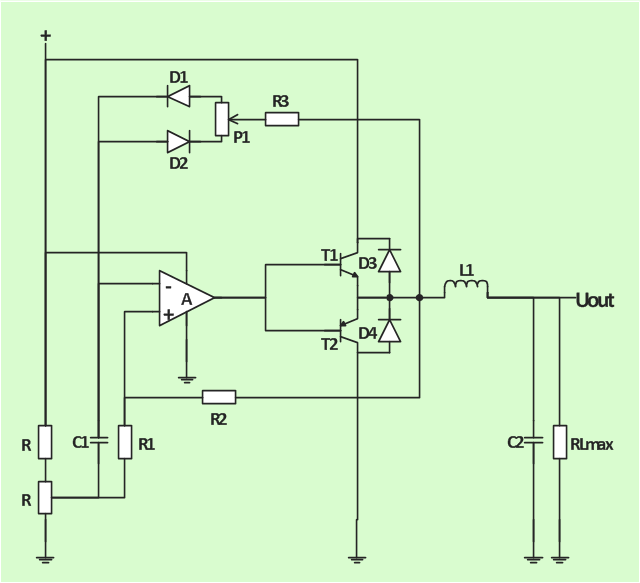
The analogue electronics diagram "Simple switched supply" was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: Switchat.png.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Switchat.png]
"Analogue electronics (or analog in American English) are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two different levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal." [Analogue electronics. Wikipedia]
The circuit diagram example "Simple switched supply" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Switchat.png]
"Analogue electronics (or analog in American English) are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two different levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal." [Analogue electronics. Wikipedia]
The circuit diagram example "Simple switched supply" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
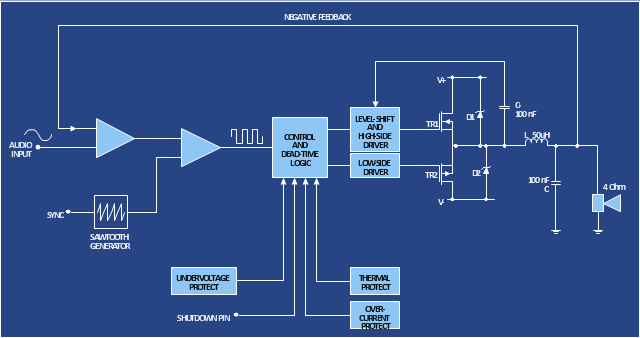
The circuit diagram example "Amplifier" was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: Slika br.5.JPG.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Slika_ br.5.JPG]
This file is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 1.0 Universal Public Domain Dedication. [creativecommons.org/ publicdomain/ zero/ 1.0/ deed.en]
"An electronic amplifier, amplifier, or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal. It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply.
There are four basic types of electronic amplifier: the voltage amplifier, the current amplifier, the transconductance amplifier, and the transresistance amplifier. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain." [Amplifier. Wikipedia]
The circuit diagram example "Amplifier" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Slika_ br.5.JPG]
This file is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 1.0 Universal Public Domain Dedication. [creativecommons.org/ publicdomain/ zero/ 1.0/ deed.en]
"An electronic amplifier, amplifier, or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal. It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply.
There are four basic types of electronic amplifier: the voltage amplifier, the current amplifier, the transconductance amplifier, and the transresistance amplifier. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain." [Amplifier. Wikipedia]
The circuit diagram example "Amplifier" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Transistors" contains 30 symbols of transistors.
Use these shapes for drawing electronic schematics and circuit diagrams in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
Use these shapes for drawing electronic schematics and circuit diagrams in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
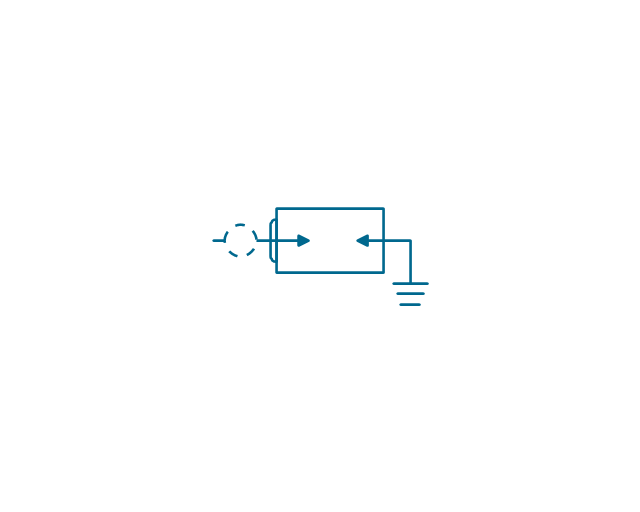
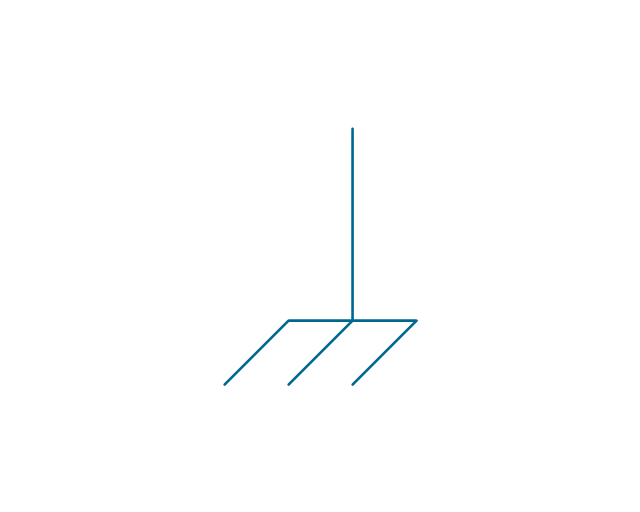
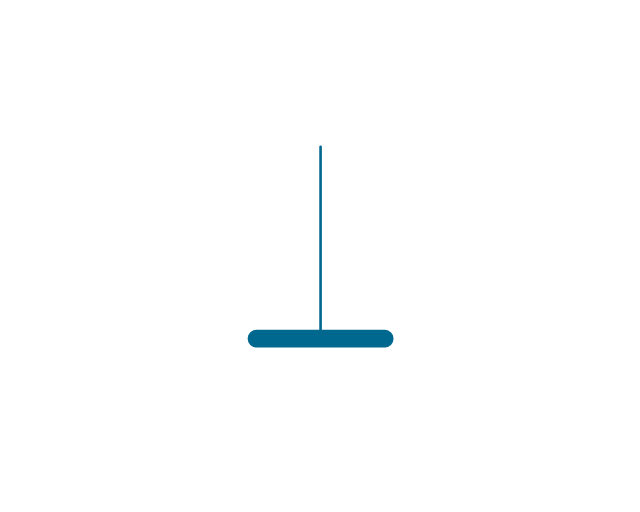
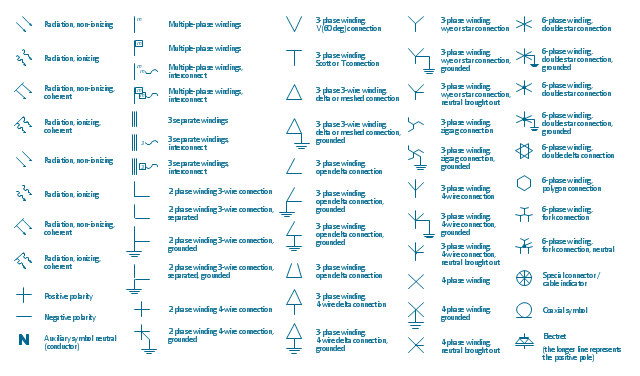
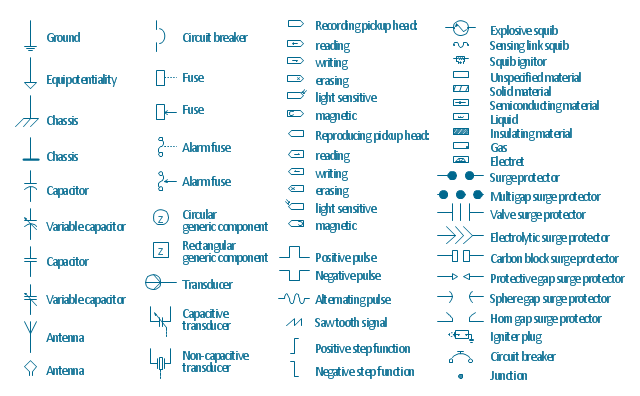
The vector stencils library "Qualifying" contains 56 qualifying symbols of radiation, polarity, phase, windings, wire, ground, connection, connector, coaxial, electret.
Use these signs to annotate or specify characteristics of objects in electrical drawings, electronic schematics, circuit diagrams, electromechanical drawings, and wiring diagrams, cabling layout diagrams.
"An electrical drawing, is a type of technical drawing that shows information about power, lighting, and communication for an engineering or architectural project. Any electrical working drawing consists of "lines, symbols, dimensions, and notations to accurately convey an engineering's design to the workers, who install the electrical system on the job".
A complete set of working drawings for the average electrical system in large projects usually consists of:
(1) A plot plan showing the building's location and outside electrical wiring.
(2) Floor plans showing the location of electrical systems on every floor.
(3) Power-riser diagrams showing panel boards.
(4) Control wiring diagrams.
(5) Schedules and other information in combination with construction drawings.
Electrical drafters prepare wiring and layout diagrams used by workers who erect, install, and repair electrical equipment and wiring in communication centers, power plants, electrical distribution systems, and buildings." [Electrical drawing. Wikipedia]
The signs example "Design elements - Qualifying" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these signs to annotate or specify characteristics of objects in electrical drawings, electronic schematics, circuit diagrams, electromechanical drawings, and wiring diagrams, cabling layout diagrams.
"An electrical drawing, is a type of technical drawing that shows information about power, lighting, and communication for an engineering or architectural project. Any electrical working drawing consists of "lines, symbols, dimensions, and notations to accurately convey an engineering's design to the workers, who install the electrical system on the job".
A complete set of working drawings for the average electrical system in large projects usually consists of:
(1) A plot plan showing the building's location and outside electrical wiring.
(2) Floor plans showing the location of electrical systems on every floor.
(3) Power-riser diagrams showing panel boards.
(4) Control wiring diagrams.
(5) Schedules and other information in combination with construction drawings.
Electrical drafters prepare wiring and layout diagrams used by workers who erect, install, and repair electrical equipment and wiring in communication centers, power plants, electrical distribution systems, and buildings." [Electrical drawing. Wikipedia]
The signs example "Design elements - Qualifying" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
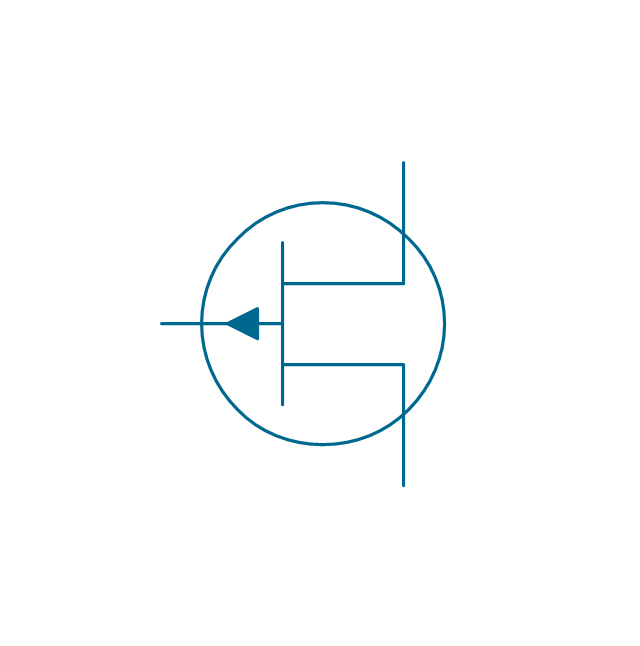
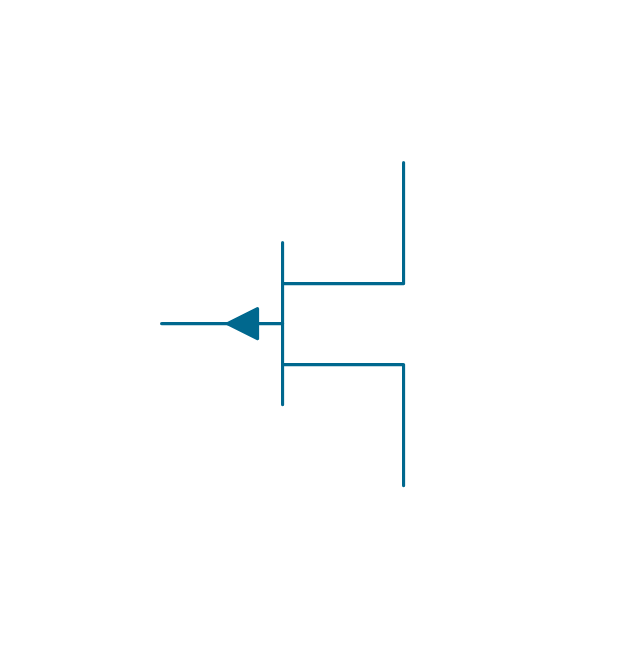
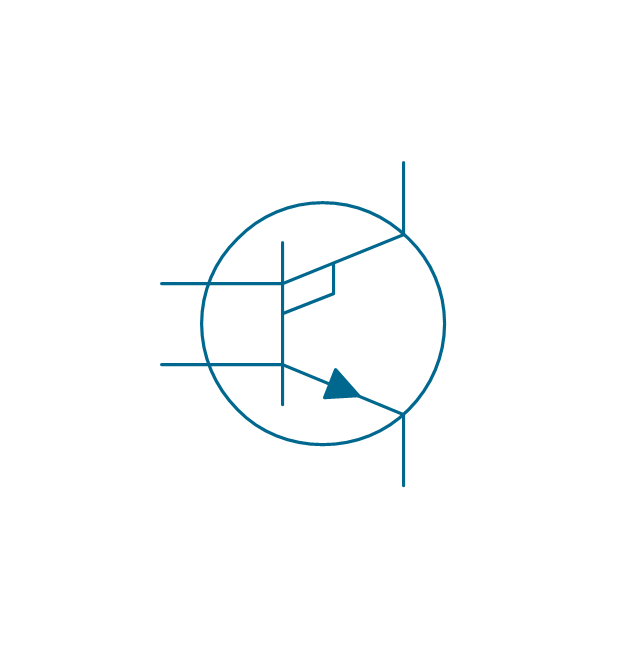
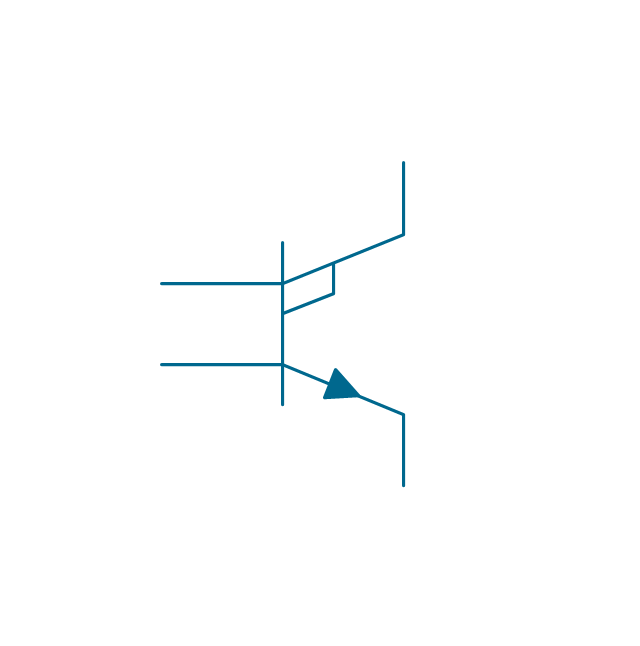
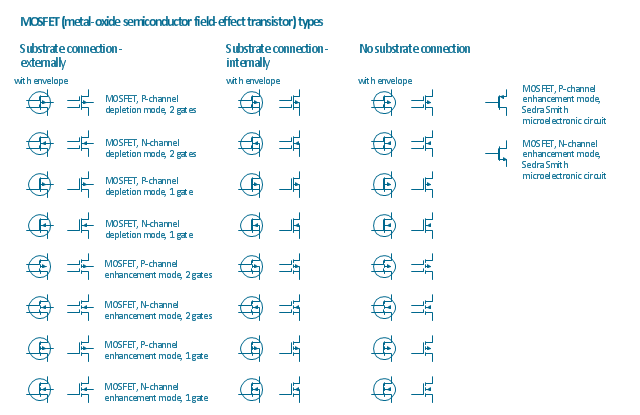
The vector stencils library "MOSFET" contains 18 symbols of MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor) elements for drawing electronic circuits diagrams.
"A variety of symbols are used for the MOSFET. The basic design is generally a line for the channel with the source and drain leaving it at right angles and then bending back at right angles into the same direction as the channel. Sometimes three line segments are used for enhancement mode and a solid line for depletion mode. ... Another line is drawn parallel to the channel for the gate.
The "bulk" or "body" connection, if shown, is shown connected to the back of the channel with an arrow indicating PMOS or NMOS. Arrows always point from P to N, so an NMOS (N-channel in P-well or P-substrate) has the arrow pointing in (from the bulk to the channel). If the bulk is connected to the source (as is generally the case with discrete devices) it is sometimes angled to meet up with the source leaving the transistor. If the bulk is not shown (as is often the case in IC design as they are generally common bulk) an inversion symbol is sometimes used to indicate PMOS, alternatively an arrow on the source may be used in the same way as for bipolar transistors (out for nMOS, in for pMOS). ...
For the symbols in which the bulk, or body, terminal is shown, it is here shown internally connected to the source... This is a typical configuration, but by no means the only important configuration. In general, the MOSFET is a four-terminal device, and in integrated circuits many of the MOSFETs share a body connection, not necessarily connected to the source terminals of all the transistors." [MOSFET. Wikipedia]
The symbols example "Design elements - MOSFET" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A variety of symbols are used for the MOSFET. The basic design is generally a line for the channel with the source and drain leaving it at right angles and then bending back at right angles into the same direction as the channel. Sometimes three line segments are used for enhancement mode and a solid line for depletion mode. ... Another line is drawn parallel to the channel for the gate.
The "bulk" or "body" connection, if shown, is shown connected to the back of the channel with an arrow indicating PMOS or NMOS. Arrows always point from P to N, so an NMOS (N-channel in P-well or P-substrate) has the arrow pointing in (from the bulk to the channel). If the bulk is connected to the source (as is generally the case with discrete devices) it is sometimes angled to meet up with the source leaving the transistor. If the bulk is not shown (as is often the case in IC design as they are generally common bulk) an inversion symbol is sometimes used to indicate PMOS, alternatively an arrow on the source may be used in the same way as for bipolar transistors (out for nMOS, in for pMOS). ...
For the symbols in which the bulk, or body, terminal is shown, it is here shown internally connected to the source... This is a typical configuration, but by no means the only important configuration. In general, the MOSFET is a four-terminal device, and in integrated circuits many of the MOSFETs share a body connection, not necessarily connected to the source terminals of all the transistors." [MOSFET. Wikipedia]
The symbols example "Design elements - MOSFET" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This AV connector pinout diagram example was redesigned from the file: DVI pinout.svg. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:DVI_ pinout.svg]
"In electronics, a pinout (sometimes written "pin-out") is a cross-reference between the contacts, or pins, of an electrical connector or electronic component, and their functions. ...
The functions of contacts in electrical connectors, be they power- or signaling-related, must be specified in order for connectors to be interchangeable. When connected, each contact of a connector must mate with the contact on the other connector that has the same function. If contacts of disparate functions are allowed to make contact, the connection may fail and damage may result. Therefore, pinouts are a vital reference when building and testing connectors, cables, and adapters." [Pinout. Wikipedia]
The example "DVI pinout diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Audio and Video Connectors solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In electronics, a pinout (sometimes written "pin-out") is a cross-reference between the contacts, or pins, of an electrical connector or electronic component, and their functions. ...
The functions of contacts in electrical connectors, be they power- or signaling-related, must be specified in order for connectors to be interchangeable. When connected, each contact of a connector must mate with the contact on the other connector that has the same function. If contacts of disparate functions are allowed to make contact, the connection may fail and damage may result. Therefore, pinouts are a vital reference when building and testing connectors, cables, and adapters." [Pinout. Wikipedia]
The example "DVI pinout diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Audio and Video Connectors solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Electrical circuits" contains 49 element symbols of electrical and electronic devices, including ignitors, starters, transmitters, circuit protectors, transducers, radio and audio equipment.
Use it for drawing electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics.
"An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a network consisting of a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. Linear electrical networks, a special type consisting only of sources (voltage or current), linear lumped elements (resistors, capacitors, inductors), and linear distributed elements (transmission lines), have the property that signals are linearly superimposable. They are thus more easily analyzed, using powerful frequency domain methods such as Laplace transforms, to determine DC response, AC response, and transient response.
A resistive circuit is a circuit containing only resistors and ideal current and voltage sources. Analysis of resistive circuits is less complicated than analysis of circuits containing capacitors and inductors. If the sources are constant (DC) sources, the result is a DC circuit.
A network that contains active electronic components is known as an electronic circuit. Such networks are generally nonlinear and require more complex design and analysis tools." [Electrical network. Wikipedia]
The symbils example "Design elements - Electrical circuits" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it for drawing electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics.
"An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a network consisting of a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. Linear electrical networks, a special type consisting only of sources (voltage or current), linear lumped elements (resistors, capacitors, inductors), and linear distributed elements (transmission lines), have the property that signals are linearly superimposable. They are thus more easily analyzed, using powerful frequency domain methods such as Laplace transforms, to determine DC response, AC response, and transient response.
A resistive circuit is a circuit containing only resistors and ideal current and voltage sources. Analysis of resistive circuits is less complicated than analysis of circuits containing capacitors and inductors. If the sources are constant (DC) sources, the result is a DC circuit.
A network that contains active electronic components is known as an electronic circuit. Such networks are generally nonlinear and require more complex design and analysis tools." [Electrical network. Wikipedia]
The symbils example "Design elements - Electrical circuits" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Design elements - Electrical and telecom
- Wiring Diagrams with ConceptDraw PRO | Electrical Diagram ...
- Standard Universal Audio & Video Connection Types | Audio and ...
- Electrical Drawing Software | How To use House Electrical Plan ...
- Design elements - Switches and relays
- Symbol Of The Elements Of Electronic
- Design elements - Semiconductors | Design elements - Electrical ...
- Electronic Schematic
- Bipolar current mirror - Circuit diagram | Amplifier - Circuit diagram ...
- Design elements - Composite assemblies | Design elements ...
- Design elements - Electrical circuits | Electrical circuits - Vector ...
- Wiring Diagram Floor Software | Electrical Drawing Software | Wiring ...
- Electrical Schematic Symbols | Electrical Diagram Symbols ...
- Hotel Network Topology Diagram. Hotel Guesthouse WiFi Network ...
- How To use House Electrical Plan Software | Electrical Drawing ...
- Audio video hook up diagram template
- Electrical Drawing Software | Technical Drawing Software | How To ...
- How To use Electrical and Telecom Plan Software | Circuits and ...
- All Basic Symbols Of Electronics Hd
- Electronic Tube Drawings