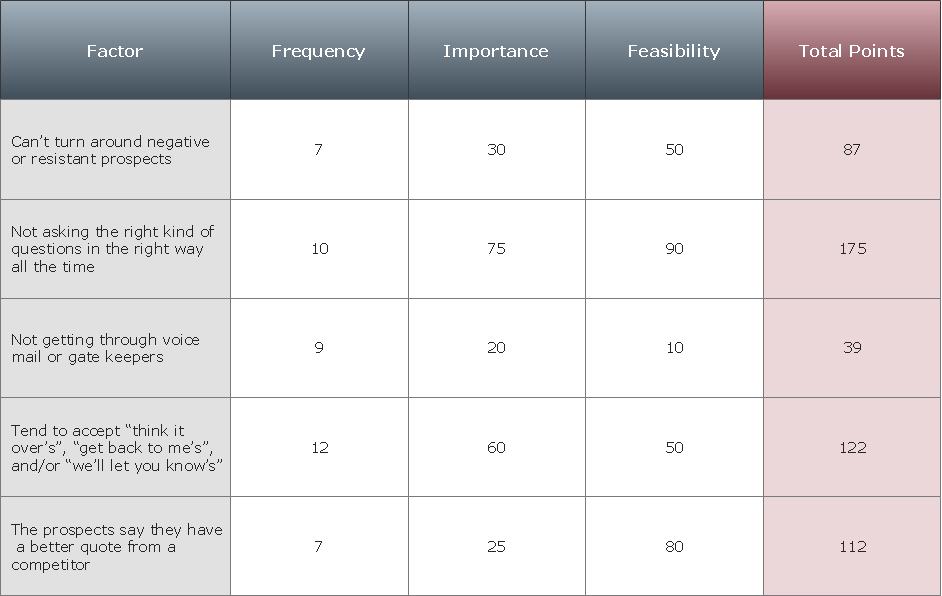
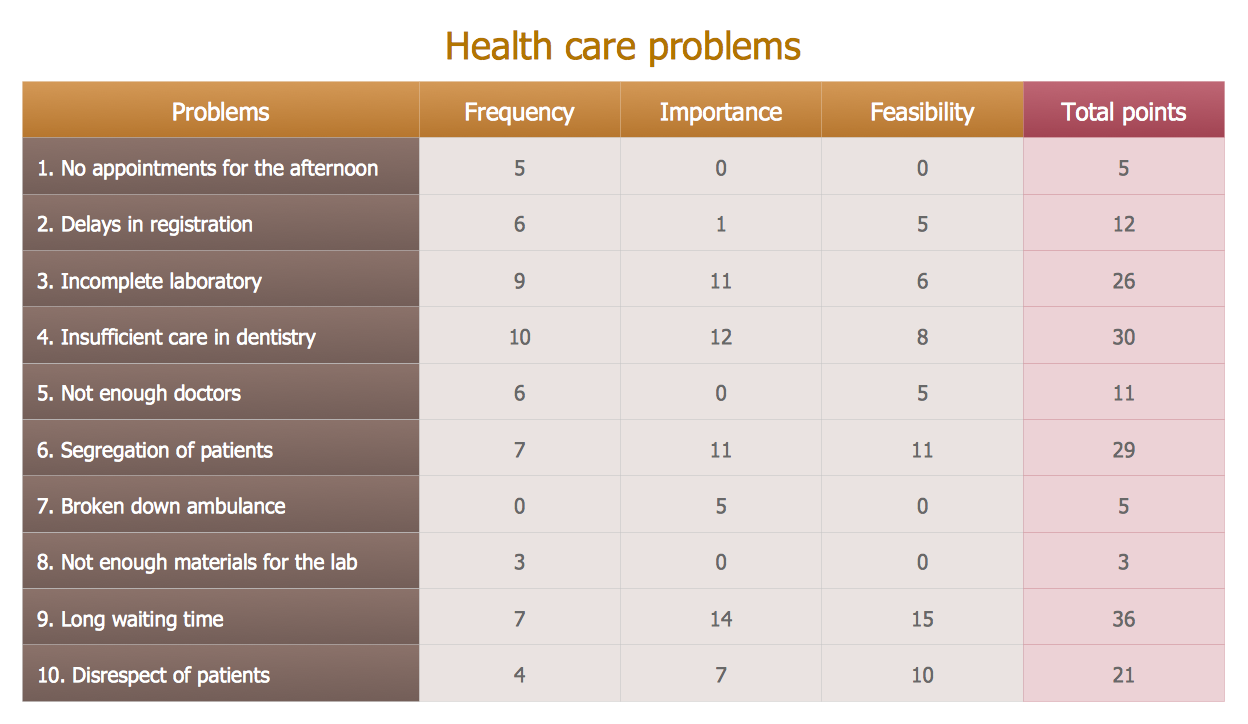
PROBLEM ANALYSIS. Prioritization Matrix
ConceptDraw Office suite is a software for Prioritization Matrix diagram making. This diagram ranks the drivers’ factors to determine priority. It identifies the factors of the first priority for analysis of possible corrective actions. It assesses the weight of each factor for each criterion and specifies it in the Prioritization Matrix. The total sum of weights for a factor’s criteria indicates its priority.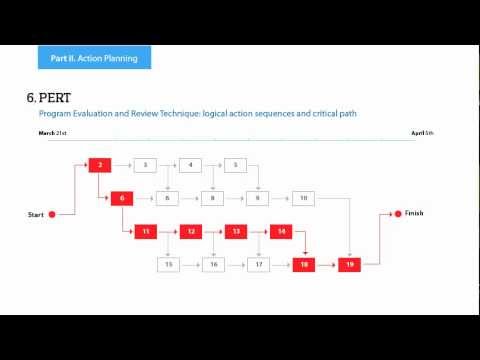
Prioritization Matrix
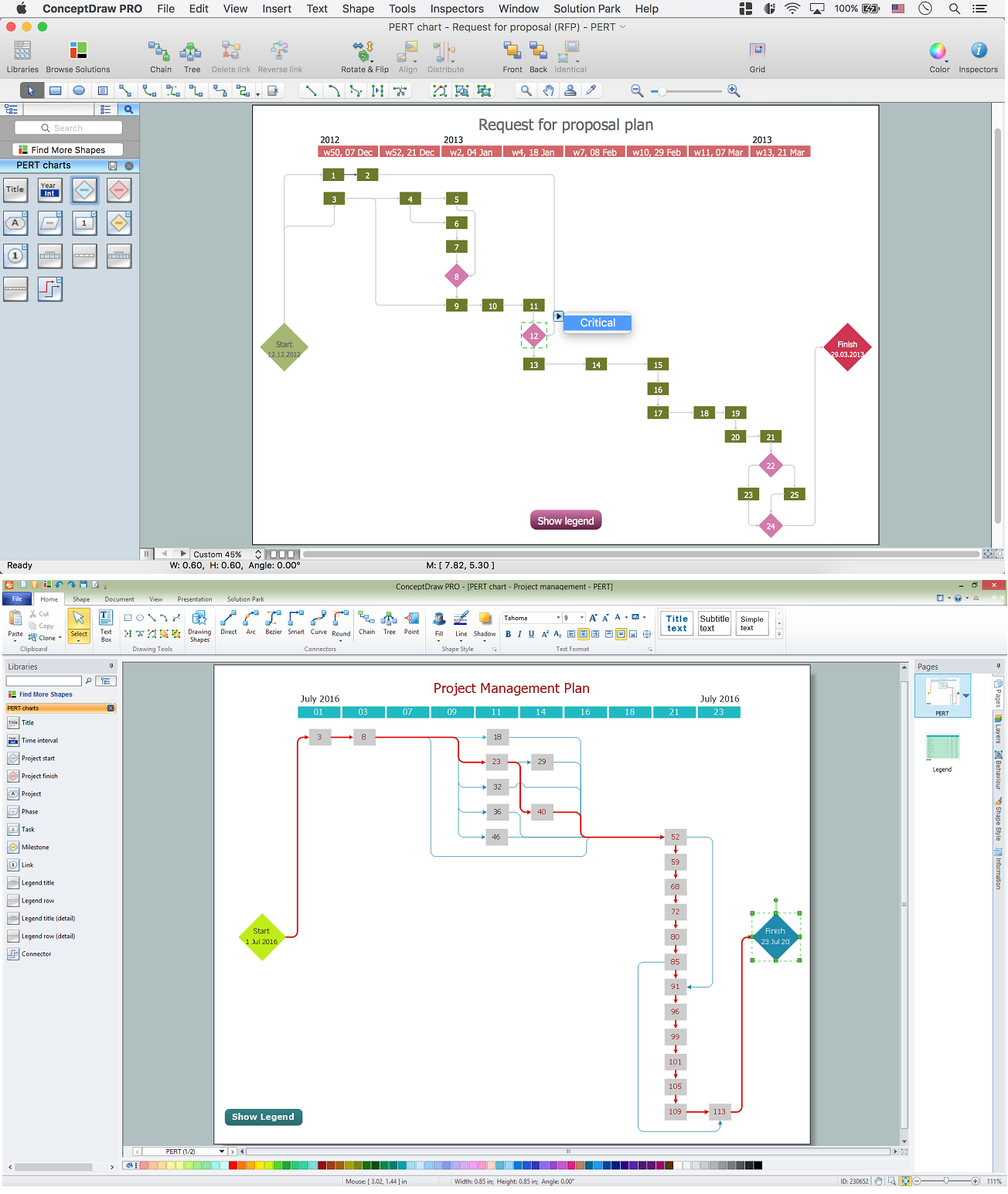
You can design the Prioritization Matrix by hand on the paper, but we offer you the most easier way - to use the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Seven Management and Planning Tools Solution from the Management Area.Activity on Node Network Diagramming Tool
Activity on Node Network Diagramming Tool - Activity Network and Project Evaluation and Review Technique, or PERT, charts are a way of documenting and analyzing the tasks in a project.This sample shows the Activity on node network diagramming method. It was created in ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software using the Seven Management and Planning Tools solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Business process improvement (BPI) is a systematic approach to help an organization optimize its underlying processes to achieve more efficient results. ...
An organization is only as good as its processes. To be able to make the necessary changes in an organization, one needs to understand the key processes of the company. Rummler and Brache suggested a model for running a Process Improvement and Management project (PI&M), containing the following steps:
1. Identify the process to be improved (based on a critical business issue): The identification of key processes can be a formal or informal exercise. The management team might select processes by applying a set of criteria derived from strategic and tactical priorities, or process selection is based on obvious performance gaps. It is important is to select the process(es) which have the greatest impact on a competitive advantage or customer requirement.
2. Develop the objective(s) for the project based on the requirements of the process: The focus might be on quality improvement, productivity, cost, customer service or cycle time. The goal is however always the same; to get the key process under control.
3. Select the members of the cross-functional team: A horizontal (cross-functional) analysis is carried out by a team composed of representatives of all functions involved in the process. While a consultant or in-house staff person can do the job, the quality of the analysis and the commitment to change is far greater with a cross-functional team.
4. Document the current process by creating a flowchart or "organization map": Describe the process regarding the Organizational level, the Process level and the Job/ Performer level according to Rummler. Develop a cross-functional process map for the process.
5. Identify "disconnects" in the process: “Disconnections” are everything that inhibit the efficiency and effectiveness of the process. The identification should be categorized into the three levels: The Organizational level, the Process level and the Job/ Performer level.
6. Recommend changes (organizational, in the process or in its execution): Categorize and prioritize the main problems and possibilities, evaluate alternative solutions. Develop a cross-functional process map for the recommended process.
7. Establish process and sub-process measures: The process measures should reflect the objectives of the project.
8. Implement the improvements." [Business process improvement. Wikipedia]
The opportunity flow chart example "Replacing engine oil" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Cross-Functional Flowcharts solution from the Business Processes area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
An organization is only as good as its processes. To be able to make the necessary changes in an organization, one needs to understand the key processes of the company. Rummler and Brache suggested a model for running a Process Improvement and Management project (PI&M), containing the following steps:
1. Identify the process to be improved (based on a critical business issue): The identification of key processes can be a formal or informal exercise. The management team might select processes by applying a set of criteria derived from strategic and tactical priorities, or process selection is based on obvious performance gaps. It is important is to select the process(es) which have the greatest impact on a competitive advantage or customer requirement.
2. Develop the objective(s) for the project based on the requirements of the process: The focus might be on quality improvement, productivity, cost, customer service or cycle time. The goal is however always the same; to get the key process under control.
3. Select the members of the cross-functional team: A horizontal (cross-functional) analysis is carried out by a team composed of representatives of all functions involved in the process. While a consultant or in-house staff person can do the job, the quality of the analysis and the commitment to change is far greater with a cross-functional team.
4. Document the current process by creating a flowchart or "organization map": Describe the process regarding the Organizational level, the Process level and the Job/ Performer level according to Rummler. Develop a cross-functional process map for the process.
5. Identify "disconnects" in the process: “Disconnections” are everything that inhibit the efficiency and effectiveness of the process. The identification should be categorized into the three levels: The Organizational level, the Process level and the Job/ Performer level.
6. Recommend changes (organizational, in the process or in its execution): Categorize and prioritize the main problems and possibilities, evaluate alternative solutions. Develop a cross-functional process map for the recommended process.
7. Establish process and sub-process measures: The process measures should reflect the objectives of the project.
8. Implement the improvements." [Business process improvement. Wikipedia]
The opportunity flow chart example "Replacing engine oil" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Cross-Functional Flowcharts solution from the Business Processes area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- PROBLEM ANALYSIS. Prioritization Matrix | How To Create a ...
- PROBLEM ANALYSIS. Prioritization Matrix | PROBLEM ANALYSIS ...
- PROBLEM ANALYSIS. Prioritization Matrix | Prioritization Matrix ...
- PROBLEM ANALYSIS Prioritization Matrix | Seven Management and ...
- Prioritization Matrix | Element Of Problem Prioritize
- Cause and Effect Analysis (Fishbone Diagrams) | Problem solving ...
- PROBLEM ANALYSIS Prioritization Matrix | Seven Management and ...
- PROBLEM ANALYSIS. Prioritization Matrix | Corrective Action ...
- PROBLEM ANALYSIS. Prioritization Matrix | PROBLEM ANALYSIS ...
- Seven Management and Planning Tools | PROBLEM ANALYSIS ...
- Cause and Effect Analysis | PROBLEM ANALYSIS. Root Cause ...
- Seven Management and Planning Tools | PROBLEM ANALYSIS ...
- How To Create a Prioritization Matrix | Prioritization Matrix | Design ...
- PROBLEM ANALYSIS. Prioritization Matrix | CORRECTIVE ...
- Activity Network (PERT) Chart | Prioritization Matrix | CORRECTIVE ...
- How To Create a Prioritization Matrix | Prioritization matrix ...
- Seven Management and Planning Tools | How to Manage Problem ...
- How To Create a Prioritization Matrix | Prioritization matrix ...
- Prioritization Matrix | How To Create a Prioritization Matrix ...
- PROBLEM ANALYSIS Identify and Structure Factors | Seven ...