HelpDesk
How to Draw Geometric Shapes
Knowledge of geometry grants people good logic, abstract and spatial thinking skills. The object of study of geometry is the size, shape and position, the 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional shapes. Geometry is related to many other areas in math and is used daily by engineers, architects, designers, and many other professionals. Today, the objects of geometry are not only shapes and solids. It deals with properties and relationships and looks much more about analysis and reasoning. Geometry drawings can be helpful when you study geometry or need to illustrate some investigation related to geometry. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM allows you to draw plane and solid geometry shapes quickly and easily.The vector stencils library "Solid geometry" contains 15 shapes of solid geometric figures.
Use these shapes to draw your geometrical diagrams and illustrations in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these shapes to draw your geometrical diagrams and illustrations in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics solution extends ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software with templates, samples and libraries of vector stencils for drawing the mathematical illustrations, diagrams and charts.
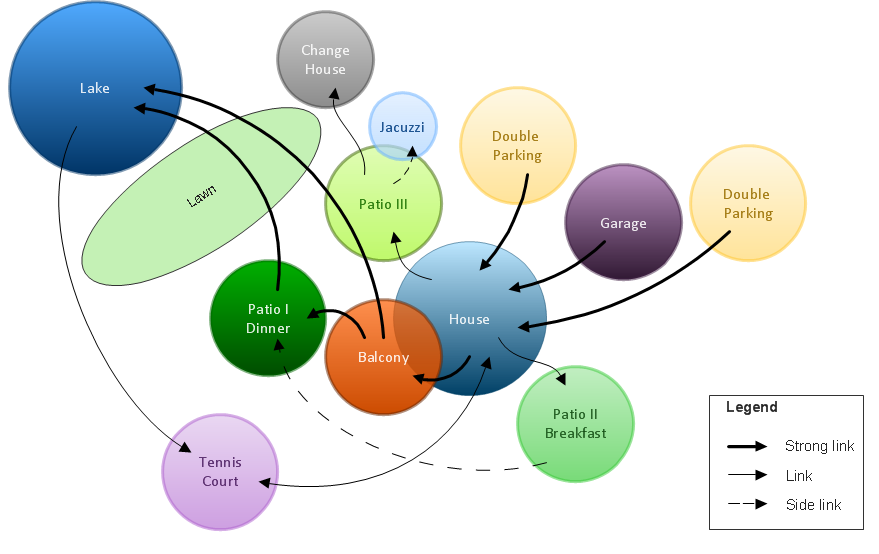
Bubble diagrams in Landscape Design with ConceptDraw DIAGRAM
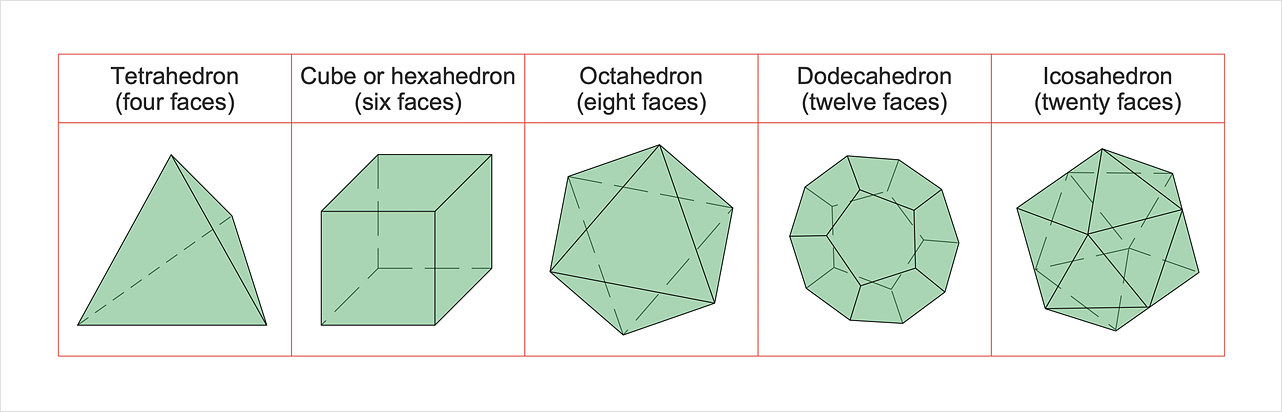
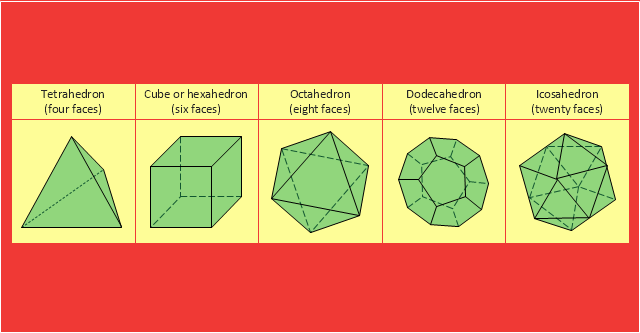
Bubble Diagrams are the charts with a bubble presentation of data with obligatory consideration of bubble's sizes. They are analogs of Mind Maps and find their application at many fields, and even in landscape design. At this case the bubbles are applied to illustrate the arrangement of different areas of future landscape design, such as lawns, flowerbeds, playgrounds, pools, recreation areas, etc. Bubble Diagram helps to see instantly the whole project, it is easy for design and quite informative, in most cases it reflects all needed information. Often Bubble Diagram is used as a draft for the future landscape project, on the first stage of its design, and in case of approval of chosen design concept is created advanced detailed landscape plan with specification of plants and used materials. Creation of Bubble Diagrams for landscape in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software is an easy task thanks to the Bubble Diagrams solution from "Diagrams" area. You can use the ready scanned location plan as the base or create it easy using the special ConceptDraw libraries and templates."In Euclidean geometry, a Platonic solid is a regular, convex polyhedron with congruent faces of regular polygons and the same number of faces meeting at each vertex. Five solids meet those criteria, and each is named after its number of faces.
Geometers have studied the mathematical beauty and symmetry of the Platonic solids for thousands of years. They are named for the ancient Greek philosopher Plato who theorized in his dialogue, the Timaeus, that the classical elements were made of these regular solids." [Platonic solid. Wikipedia]
The geometry diagram example "Platonic solid" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Geometers have studied the mathematical beauty and symmetry of the Platonic solids for thousands of years. They are named for the ancient Greek philosopher Plato who theorized in his dialogue, the Timaeus, that the classical elements were made of these regular solids." [Platonic solid. Wikipedia]
The geometry diagram example "Platonic solid" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Bank UML sequence diagram" contains 34 shapes for drawing UML sequence diagrams.
Use it for object-oriented modeling of your bank information system.
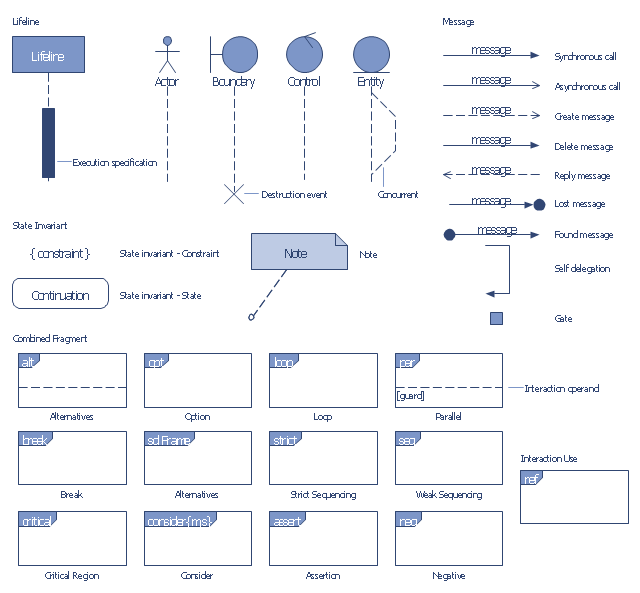
"A sequence diagram shows, as parallel vertical lines (lifelines), different processes or objects that live simultaneously, and, as horizontal arrows, the messages exchanged between them, in the order in which they occur. This allows the specification of simple runtime scenarios in a graphical manner.
Diagram building blocks.
If the lifeline is that of an object, it demonstrates a role. Leaving the instance name blank can represent anonymous and unnamed instances.
Messages, written with horizontal arrows with the message name written above them, display interaction. Solid arrow heads represent synchronous calls, open arrow heads represent asynchronous messages, and dashed lines represent reply messages. ...
Activation boxes, or method-call boxes, are opaque rectangles drawn on top of lifelines to represent that processes are being performed in response to the message (ExecutionSpecifications in UML).
Objects calling methods on themselves use messages and add new activation boxes on top of any others to indicate a further level of processing.
When an object is destroyed (removed from memory), an X is drawn on top of the lifeline, and the dashed line ceases to be drawn below it ...
A message sent from outside the diagram can be represented by a message originating from a filled-in circle (found message in UML) or from a border of the sequence diagram (gate in UML)." [Sequence diagram. Wikipedia]
This example of UML sequence diagram symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it for object-oriented modeling of your bank information system.
"A sequence diagram shows, as parallel vertical lines (lifelines), different processes or objects that live simultaneously, and, as horizontal arrows, the messages exchanged between them, in the order in which they occur. This allows the specification of simple runtime scenarios in a graphical manner.
Diagram building blocks.
If the lifeline is that of an object, it demonstrates a role. Leaving the instance name blank can represent anonymous and unnamed instances.
Messages, written with horizontal arrows with the message name written above them, display interaction. Solid arrow heads represent synchronous calls, open arrow heads represent asynchronous messages, and dashed lines represent reply messages. ...
Activation boxes, or method-call boxes, are opaque rectangles drawn on top of lifelines to represent that processes are being performed in response to the message (ExecutionSpecifications in UML).
Objects calling methods on themselves use messages and add new activation boxes on top of any others to indicate a further level of processing.
When an object is destroyed (removed from memory), an X is drawn on top of the lifeline, and the dashed line ceases to be drawn below it ...
A message sent from outside the diagram can be represented by a message originating from a filled-in circle (found message in UML) or from a border of the sequence diagram (gate in UML)." [Sequence diagram. Wikipedia]
This example of UML sequence diagram symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Sequence diagram" contains 32 SysML symbols.
Use it to design your sequence diagrams using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
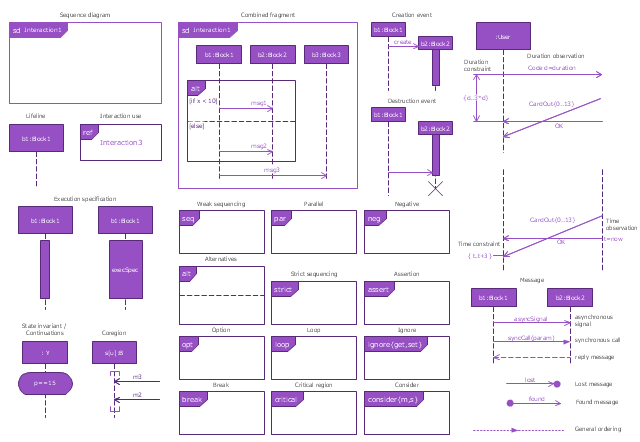
"A sequence diagram shows, as parallel vertical lines (lifelines), different processes or objects that live simultaneously, and, as horizontal arrows, the messages exchanged between them, in the order in which they occur. This allows the specification of simple runtime scenarios in a graphical manner. ...
If the lifeline is that of an object, it demonstrates a role. Leaving the instance name blank can represent anonymous and unnamed instances.
Messages, written with horizontal arrows with the message name written above them, display interaction. Solid arrow heads represent synchronous calls, open arrow heads represent asynchronous messages, and dashed lines represent reply messages. If a caller sends a synchronous message, it must wait until the message is done, such as invoking a subroutine. If a caller sends an asynchronous message, it can continue processing and doesn’t have to wait for a response. Asynchronous calls are present in multithreaded applications and in message-oriented middleware. Activation boxes, or method-call boxes, are opaque rectangles drawn on top of lifelines to represent that processes are being performed in response to the message (ExecutionSpecifications in UML).
Objects calling methods on themselves use messages and add new activation boxes on top of any others to indicate a further level of processing.
When an object is destroyed (removed from memory), an X is drawn on top of the lifeline, and the dashed line ceases to be drawn below it (this is not the case in the first example though). It should be the result of a message, either from the object itself, or another.
A message sent from outside the diagram can be represented by a message originating from a filled-in circle (found message in UML) or from a border of the sequence diagram (gate in UML)." [Sequence diagram. Wikipedia]
The SysML shapes example "Design elements - Sequence diagram" is included in the SysML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it to design your sequence diagrams using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"A sequence diagram shows, as parallel vertical lines (lifelines), different processes or objects that live simultaneously, and, as horizontal arrows, the messages exchanged between them, in the order in which they occur. This allows the specification of simple runtime scenarios in a graphical manner. ...
If the lifeline is that of an object, it demonstrates a role. Leaving the instance name blank can represent anonymous and unnamed instances.
Messages, written with horizontal arrows with the message name written above them, display interaction. Solid arrow heads represent synchronous calls, open arrow heads represent asynchronous messages, and dashed lines represent reply messages. If a caller sends a synchronous message, it must wait until the message is done, such as invoking a subroutine. If a caller sends an asynchronous message, it can continue processing and doesn’t have to wait for a response. Asynchronous calls are present in multithreaded applications and in message-oriented middleware. Activation boxes, or method-call boxes, are opaque rectangles drawn on top of lifelines to represent that processes are being performed in response to the message (ExecutionSpecifications in UML).
Objects calling methods on themselves use messages and add new activation boxes on top of any others to indicate a further level of processing.
When an object is destroyed (removed from memory), an X is drawn on top of the lifeline, and the dashed line ceases to be drawn below it (this is not the case in the first example though). It should be the result of a message, either from the object itself, or another.
A message sent from outside the diagram can be represented by a message originating from a filled-in circle (found message in UML) or from a border of the sequence diagram (gate in UML)." [Sequence diagram. Wikipedia]
The SysML shapes example "Design elements - Sequence diagram" is included in the SysML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Diagram Of Flat And Solid Shapes In Mathematics
- Diagram Of Solid Shape
- Solid Figures And Their Diagrams
- Design elements - Solid geometry | How to Draw Geometric Shapes ...
- Diagram Of Solid In Mathematics
- Detailed Sketches Of Pyramids Solid Shapes
- Design elements - Solid geometry | Entity Relationship Diagram ...
- Solid Shapes Images
- Solid geometry - Vector stencils library | Mathematics Symbols ...
- Design elements - Solid geometry | Solid geometry - Vector stencils ...
- Pyramid Diagram | Design elements - Solid geometry | Solid ...
- Solid Mathematical Shapes
- How To Draw Solid Shapes
- Solid Diagram Symbols
- Solid Figures Diagram
- Design elements - Solid geometry | Solid Shape Examples Of Cuboid
- Rapid UML | Example 0 F Cuboid Shape
- The Diagram Of Plane Shapes
- Mathematical Diagrams | Mathematics | Mathematics Symbols ...