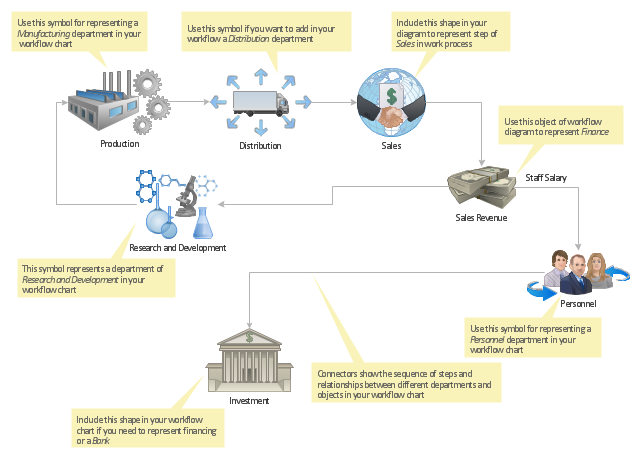
LLNL Flow Charts
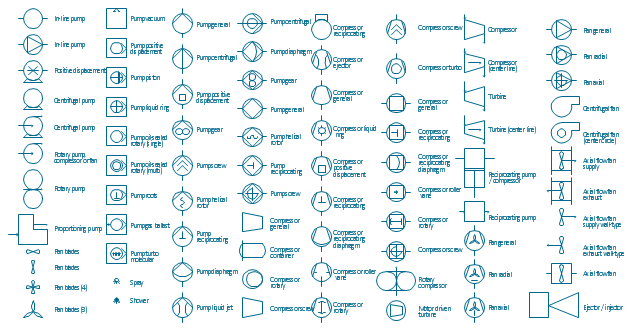
These flow charts help scientists analysts and other decision makers to visualize the complex interrelationships involved in managing our nation x2019.The vector stencils library "Pumps" contains 82 symbols of pumps, compressors, fans, turbines, and power generators.
Use these icons to design pumping systems, air and fluid compression systems, and industrial process diagrams.
"A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they use to move the fluid: direct lift, displacement, and gravity pumps.
Pumps operate by some mechanism (typically reciprocating or rotary), and consume energy to perform mechanical work by moving the fluid. Pumps operate via many energy sources, including manual operation, electricity, engines, or wind power, come in many sizes, from microscopic for use in medical applications to large industrial pumps.
Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of applications such as pumping water from wells, aquarium filtering, pond filtering and aeration, in the car industry for water-cooling and fuel injection, in the energy industry for pumping oil and natural gas or for operating cooling towers. In the medical industry, pumps are used for biochemical processes in developing and manufacturing medicine, and as artificial replacements for body parts, in particular the artificial heart and penile prosthesis.
In biology, many different types of chemical and bio-mechanical pumps have evolved, and biomimicry is sometimes used in developing new types of mechanical pumps." [Pump. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Pumps" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these icons to design pumping systems, air and fluid compression systems, and industrial process diagrams.
"A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they use to move the fluid: direct lift, displacement, and gravity pumps.
Pumps operate by some mechanism (typically reciprocating or rotary), and consume energy to perform mechanical work by moving the fluid. Pumps operate via many energy sources, including manual operation, electricity, engines, or wind power, come in many sizes, from microscopic for use in medical applications to large industrial pumps.
Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of applications such as pumping water from wells, aquarium filtering, pond filtering and aeration, in the car industry for water-cooling and fuel injection, in the energy industry for pumping oil and natural gas or for operating cooling towers. In the medical industry, pumps are used for biochemical processes in developing and manufacturing medicine, and as artificial replacements for body parts, in particular the artificial heart and penile prosthesis.
In biology, many different types of chemical and bio-mechanical pumps have evolved, and biomimicry is sometimes used in developing new types of mechanical pumps." [Pump. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Pumps" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
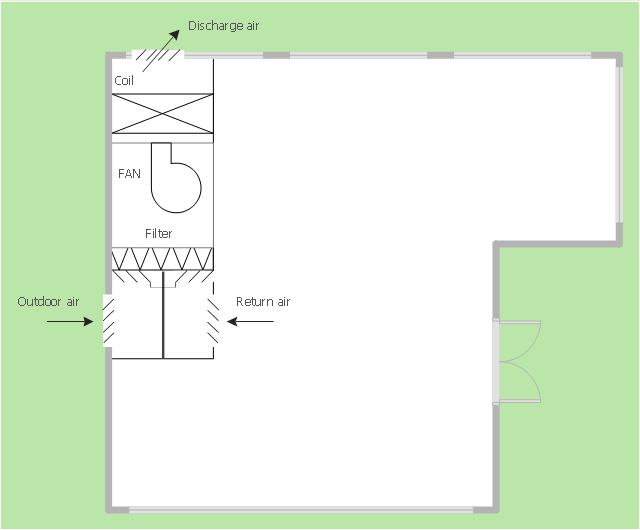
This mechanical room HVAC plan sample shows the layout of air handler (air handling unit, AHU) equipment: mixing chamber, air filter, fan (blower), heat exchanger coil, diffusers.
"Ventilating (the V in HVAC) is the process of "changing" or replacing air in any space to provide high indoor air quality (i.e. to control temperature, replenish oxygen, or remove moisture, odors, smoke, heat, dust, airborne bacteria, and carbon dioxide). Ventilation is used to remove unpleasant smells and excessive moisture, introduce outside air, to keep interior building air circulating, and to prevent stagnation of the interior air.
Ventilation includes both the exchange of air to the outside as well as circulation of air within the building. It is one of the most important factors for maintaining acceptable indoor air quality in buildings. Methods for ventilating a building may be divided into mechanical/ forced and natural types.
"Mechanical" or "forced" ventilation is used to control indoor air quality. Excess humidity, odors, and contaminants can often be controlled via dilution or replacement with outside air. However, in humid climates much energy is required to remove excess moisture from ventilation air.
Ventilation increases the energy needed for heating or cooling, however heat recovery ventilation can be used to mitigate the energy consumption. This involves heat exchange between incoming and outgoing air. Energy recovery ventilation additionally includes exchange of humidity." [Ventilation (architecture). Wikipedia]
The HVAC floor plan example "Ventilation system layout" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the HVAC Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Ventilating (the V in HVAC) is the process of "changing" or replacing air in any space to provide high indoor air quality (i.e. to control temperature, replenish oxygen, or remove moisture, odors, smoke, heat, dust, airborne bacteria, and carbon dioxide). Ventilation is used to remove unpleasant smells and excessive moisture, introduce outside air, to keep interior building air circulating, and to prevent stagnation of the interior air.
Ventilation includes both the exchange of air to the outside as well as circulation of air within the building. It is one of the most important factors for maintaining acceptable indoor air quality in buildings. Methods for ventilating a building may be divided into mechanical/ forced and natural types.
"Mechanical" or "forced" ventilation is used to control indoor air quality. Excess humidity, odors, and contaminants can often be controlled via dilution or replacement with outside air. However, in humid climates much energy is required to remove excess moisture from ventilation air.
Ventilation increases the energy needed for heating or cooling, however heat recovery ventilation can be used to mitigate the energy consumption. This involves heat exchange between incoming and outgoing air. Energy recovery ventilation additionally includes exchange of humidity." [Ventilation (architecture). Wikipedia]
The HVAC floor plan example "Ventilation system layout" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the HVAC Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
HelpDesk
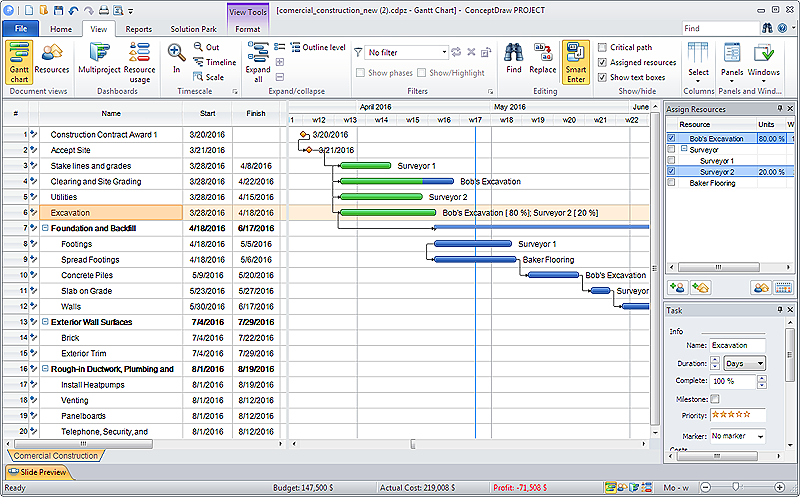
How to Plan and Allocate Resources in Your Project with ConceptDraw PROJECT for Windows
Effective resource management is a key factor in the successful project implementation. The common types of resources for which the project manager has an impact, include material resources (materials, energy), staff (work) and equipment. CoceptDraw PROJECT provides easy ways to project Resources Management: Create a list of project resources and assign the right human resource, as well as the necessary material, or equipment to be used."Carbohydrate catabolism is the breakdown of carbohydrates into smaller units. Carbohydrates literally undergo combustion to retrieve the large amounts of energy in their bonds. Energy is secured by mitochondria in the form of ATP.
There are several different types of carbohydrates: polysaccharides (e.g., starch, amylopectin, glycogen, cellulose), monosaccharides (e.g., glucose, galactose, fructose, ribose) and the disaccharides (e.g., maltose, lactose).
Glucose reacts with oxygen in the following redox reaction, C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O, the carbon dioxide and water is a waste product and the chemical reaction is exothermic.
The breakdown of glucose into energy in the form of molecules of ATP is therefore one of the most important biochemical pathways found in living organisms." [Carbohydrate catabolism. Wikipedia]
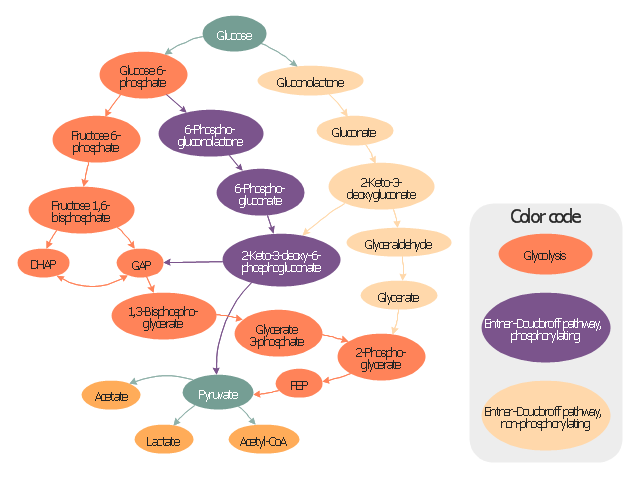
This glucose catabolism pathways map shows glycolysis by orange color, Entner-Doudoroff phosphorylating pathway by green color, Entner-Doudoroff non-phosphorylating pathway by Yellow color.
This methabolic pathway map was redesigned from Wikimedia file: Glucose catabolism pathways.svg. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Glucose_ catabolism_ pathways.svg]
The biochemical diagram example "Glucose catabolism pathways map" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
There are several different types of carbohydrates: polysaccharides (e.g., starch, amylopectin, glycogen, cellulose), monosaccharides (e.g., glucose, galactose, fructose, ribose) and the disaccharides (e.g., maltose, lactose).
Glucose reacts with oxygen in the following redox reaction, C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O, the carbon dioxide and water is a waste product and the chemical reaction is exothermic.
The breakdown of glucose into energy in the form of molecules of ATP is therefore one of the most important biochemical pathways found in living organisms." [Carbohydrate catabolism. Wikipedia]
This glucose catabolism pathways map shows glycolysis by orange color, Entner-Doudoroff phosphorylating pathway by green color, Entner-Doudoroff non-phosphorylating pathway by Yellow color.
This methabolic pathway map was redesigned from Wikimedia file: Glucose catabolism pathways.svg. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Glucose_ catabolism_ pathways.svg]
The biochemical diagram example "Glucose catabolism pathways map" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Workflow components.
A workflow can usually be described using formal or informal flow diagramming techniques, showing directed flows between processing steps. Single processing steps or components of a workflow can basically be defined by three parameters:
(1) input description: the information, material and energy required to complete the step,
(2) transformation rules, algorithms, which may be carried out by associated human roles or machines, or a combination,
(3) output description: the information, material and energy produced by the step and provided as input to downstream steps.
Components can only be plugged together if the output of one previous (set of) component(s) is equal to the mandatory input requirements of the following component. Thus, the essential description of a component actually comprises only in- and output that are described fully in terms of data types and their meaning (semantics). The algorithms' or rules' description need only be included when there are several alternative ways to transform one type of input into one type of output – possibly with different accuracy, speed, etc.
When the components are non-local services that are invoked remotely via a computer network, such as Web services, additional descriptors (such as QoS and availability) also must be considered." [Workflow. Wikipedia]
The workflow diagram template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Workflow Diagrams solution from the Business Processes area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
A workflow can usually be described using formal or informal flow diagramming techniques, showing directed flows between processing steps. Single processing steps or components of a workflow can basically be defined by three parameters:
(1) input description: the information, material and energy required to complete the step,
(2) transformation rules, algorithms, which may be carried out by associated human roles or machines, or a combination,
(3) output description: the information, material and energy produced by the step and provided as input to downstream steps.
Components can only be plugged together if the output of one previous (set of) component(s) is equal to the mandatory input requirements of the following component. Thus, the essential description of a component actually comprises only in- and output that are described fully in terms of data types and their meaning (semantics). The algorithms' or rules' description need only be included when there are several alternative ways to transform one type of input into one type of output – possibly with different accuracy, speed, etc.
When the components are non-local services that are invoked remotely via a computer network, such as Web services, additional descriptors (such as QoS and availability) also must be considered." [Workflow. Wikipedia]
The workflow diagram template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Workflow Diagrams solution from the Business Processes area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
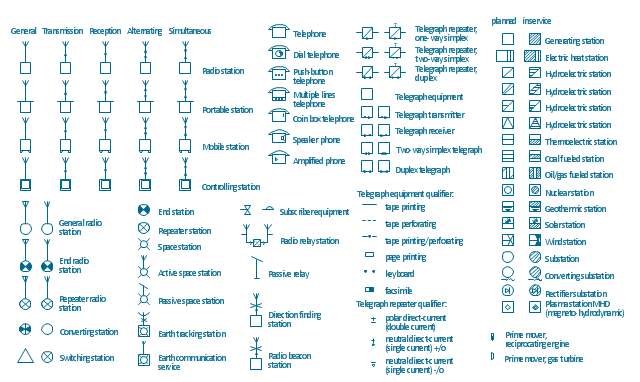
The vector stencils library "Stations" contains 110 symbols of communications equipment, generating, transmitting and receiving stations; substations; satellites; and power plants for power generation and distribution and radio relay systems.
"A power station (also referred to as a generating station, power plant, powerhouse or generating plant) is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. At the center of nearly all power stations is a generator, a rotating machine that converts mechanical power into electrical power by creating relative motion between a magnetic field and a conductor. The energy source harnessed to turn the generator varies widely. It depends chiefly on which fuels are easily available, cheap enough and on the types of technology that the power company has access to. Most power stations in the world burn fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas to generate electricity, and some use nuclear power, but there is an increasing use of cleaner renewable sources such as solar, wind, wave and hydroelectric." [Power station. Wikipedia]
"Radio broadcasting is a one-way wireless transmission over radio waves intended to reach a wide audience. Stations can be linked in radio networks to broadcast a common radio format, either in broadcast syndication or simulcast or both. Audio broadcasting also can be done via cable radio, local wire television networks, satellite radio, and internet radio via streaming media on the Internet.
The signal types can be either analog audio or digital audio." [Radio broadcasting. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Stations" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A power station (also referred to as a generating station, power plant, powerhouse or generating plant) is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. At the center of nearly all power stations is a generator, a rotating machine that converts mechanical power into electrical power by creating relative motion between a magnetic field and a conductor. The energy source harnessed to turn the generator varies widely. It depends chiefly on which fuels are easily available, cheap enough and on the types of technology that the power company has access to. Most power stations in the world burn fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas to generate electricity, and some use nuclear power, but there is an increasing use of cleaner renewable sources such as solar, wind, wave and hydroelectric." [Power station. Wikipedia]
"Radio broadcasting is a one-way wireless transmission over radio waves intended to reach a wide audience. Stations can be linked in radio networks to broadcast a common radio format, either in broadcast syndication or simulcast or both. Audio broadcasting also can be done via cable radio, local wire television networks, satellite radio, and internet radio via streaming media on the Internet.
The signal types can be either analog audio or digital audio." [Radio broadcasting. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Stations" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Energy resources diagram | Types of Flowcharts | Resources and ...
- Bar Graph Of Different Types Of Energy
- Electrical Symbols — Power Sources | Types of Flowcharts | Design ...
- Types of Flowcharts | Resources and energy - Vector stencils library ...
- Types of Flowcharts | Ecology pictograms - Vector stencils library ...
- Types of Flowcharts | Process Flow Diagram | Energy resources ...
- Types of Flowcharts | Energy resources diagram | Pie Charts | Solar ...
- Energy Pyramid Diagram | Resources and energy - Vector stencils ...
- Energy resources diagram | Types of Flowcharts | Manufacturing ...
- Energy resources diagram | Types of Flowcharts | Pyramid Diagram ...
- Energy resources diagram | Types of Flowcharts | Pie Charts ...
- Types of Flowcharts | Arrow Diagram For The Wind Energy
- LLNL Flow Charts | Manufacturing and Maintenance | Types of ...
- Types of Flowcharts | Divided Bar Diagrams | Target and Circular ...
- Geo Map - United States of America Map | U.S. primary energy ...
- LLNL Flow Charts | Types of Flowcharts | Chart Examples | Energy ...
- Types of Flowcharts | Energy resources diagram | Wind Power Flow ...
- LLNL Flow Charts | Types of Flowcharts | Energy Pyramid Diagram ...
- Energy resources diagram | Types of Flowcharts | Landscape ...
- Types of Flowcharts | Diagram of a Pyramid | Energy Pyramid ...
.jpg)