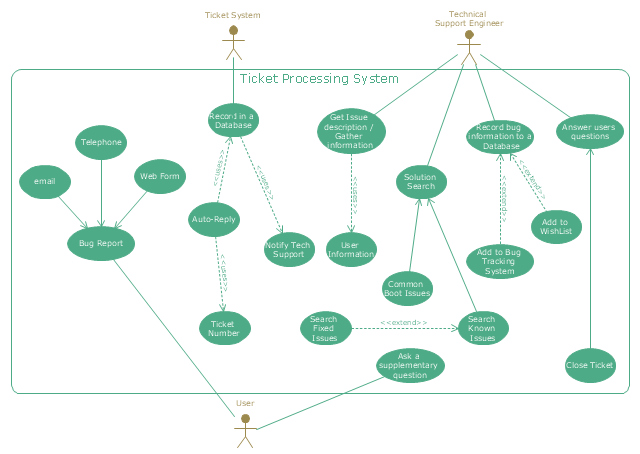
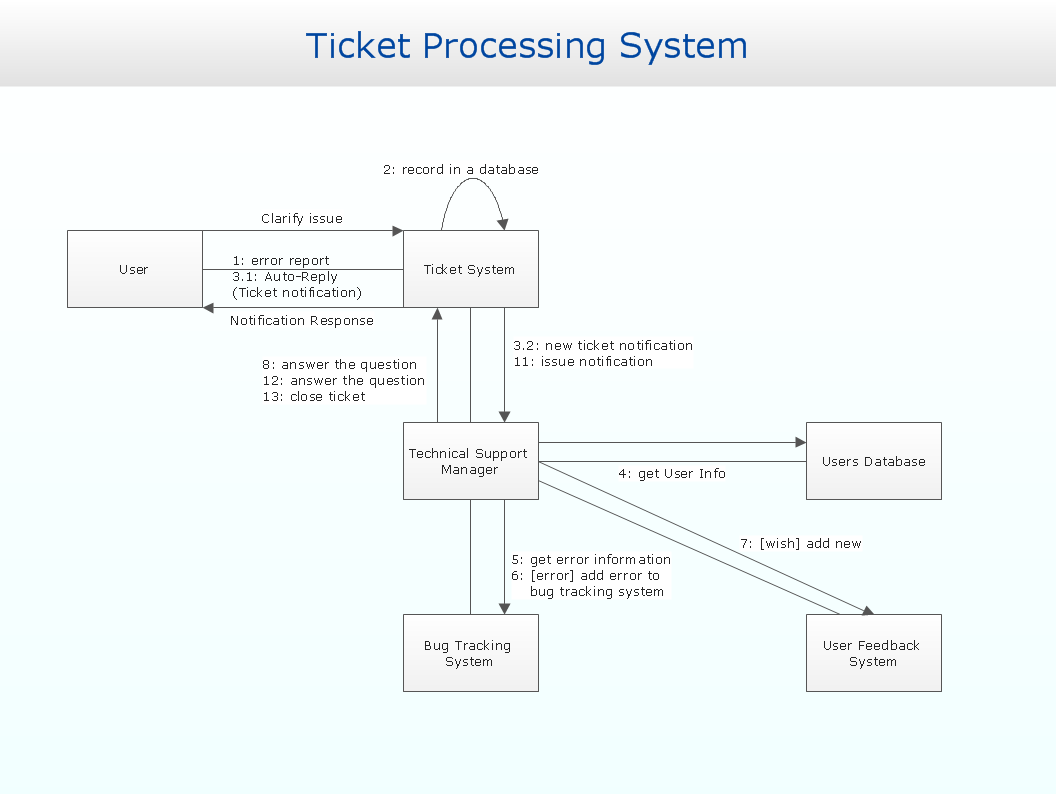
"An example scenario is presented to demonstrate how a common issue tracking system would work:
(1) A customer service technician receives a telephone call, email, or other communication from a customer about a problem. Some applications provide built-in messaging system and automatic error reporting from exception handling blocks.
(2) The technician verifies that the problem is real, and not just perceived. The technician will also ensure that enough information about the problem is obtained from the customer. This information generally includes the environment of the customer, when and how the issue occurs, and all other relevant circumstances.
(3) The technician creates the issue in the system, entering all relevant data, as provided by the customer.
(4) As work is done on that issue, the system is updated with new data by the technician. Any attempt at fixing the problem should be noted in the issue system. Ticket status most likely will be changed from open to pending.
(5) After the issue has been fully addressed, it is marked as resolved in the issue tracking system.
If the problem is not fully resolved, the ticket will be reopened once the technician receives new information from the customer. A Run Book Automation process that implements best practices for these workflows and increases IT personnel effectiveness is becoming very common." [Issue tracking system. Wikipedia]
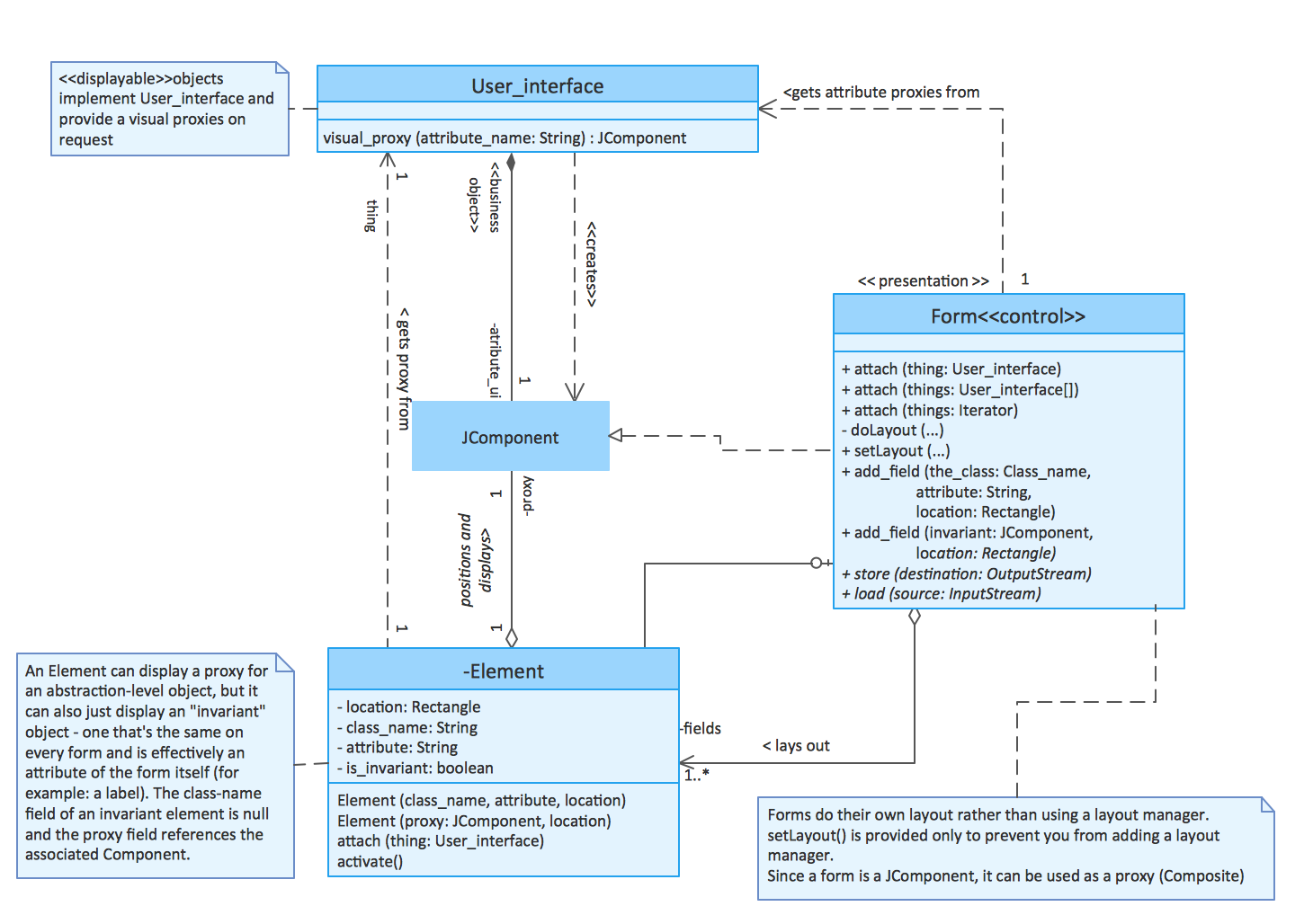
The UML use case diagram example "Ticket processing system" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
(1) A customer service technician receives a telephone call, email, or other communication from a customer about a problem. Some applications provide built-in messaging system and automatic error reporting from exception handling blocks.
(2) The technician verifies that the problem is real, and not just perceived. The technician will also ensure that enough information about the problem is obtained from the customer. This information generally includes the environment of the customer, when and how the issue occurs, and all other relevant circumstances.
(3) The technician creates the issue in the system, entering all relevant data, as provided by the customer.
(4) As work is done on that issue, the system is updated with new data by the technician. Any attempt at fixing the problem should be noted in the issue system. Ticket status most likely will be changed from open to pending.
(5) After the issue has been fully addressed, it is marked as resolved in the issue tracking system.
If the problem is not fully resolved, the ticket will be reopened once the technician receives new information from the customer. A Run Book Automation process that implements best practices for these workflows and increases IT personnel effectiveness is becoming very common." [Issue tracking system. Wikipedia]
The UML use case diagram example "Ticket processing system" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
UML Tool & UML Diagram Examples
The Unified Modeling Language (abbr. UML) is a general-purpose modeling language widely used in the field of software development, software engineering, education, science, industry, business. In 1997 the UML was approved as a standard by the OMG (Object Management Group) and in 2005 was published as ISO standard by the International Organization for Standardization. UML is widely and succesfully applied for optimization the process of software systems development and business systems analysis. There are used 14 types of UML diagrams, 7 from them depict structural information, another 7 types represent different types of behavior and aspects of interactions. Design of any automated process is easy with ConceptDraw DIAGRAM and unique Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area, which provides numerous UML examples, templates and vector stencils libraries for drawing all types of UML 1.x and UML 2.x diagrams. Use of predesigned UML diagram examples and templates lets you quickly start drawing your own UML diagrams in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software.UML Use Case Diagrams
ConceptDraw has several examples that help you to start using software for designing UML Use Case Diagrams.
Diagramming Software for Design UML Use Case Diagrams
Use Case Diagrams describes the functionality provided by a system in terms of actors, their goals represented as use cases, and any dependencies among those use cases.
 Rapid UML
Rapid UML
Rapid UML solution extends ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software with templates, samples and libraries of vector stencils for quick drawing the UML diagrams using Rapid Draw technology.
HelpDesk
How to Create a Bank ATM Use Case Diagram
UML diagrams are often used in banking management for documenting a banking system. In particular, the interaction of bank customers with an automated teller machine (ATM) can be represented in a Use Case diagram. Before the software code for an ATM, or any other system design, is written, it is necessary to create a visual representation of any object-oriented processes. This is done most effectively by creating a Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagram, using object-oriented modeling. UML works as a general purpose modeling language for software engineers or system analysts, offering a number of different diagram styles with which to visually depict all aspects of a software system. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming software, enhanced and expanded with the ATM UML Diagrams solution, offers the full range of icons, templates and design elements needed to faithfully represent ATM and banking information system architecture using UML standards. The ATM UML Diagrams solution is useful for beginner and advanced users alike. More experienced users will appreciate a full range of vector stencil libraries and ConceptDraw DIAGRAM 's powerful software, that allows you to create your ATM UML diagram in a matter of moments."An issue tracking system (also ITS, trouble ticket system, support ticket, request management or incident ticket system) is a computer software package that manages and maintains lists of issues, as needed by an organization. Issue tracking systems are commonly used in an organization's customer support call center to create, update, and resolve reported customer issues, or even issues reported by that organization's other employees. An issue tracking system often also contains a knowledge base containing information on each customer, resolutions to common problems, and other such data. An issue tracking system is similar to a "bugtracker", and often, a software company will sell both, and some bugtrackers are capable of being used as an issue tracking system, and vice versa. Consistent use of an issue or bug tracking system is considered one of the "hallmarks of a good software team".
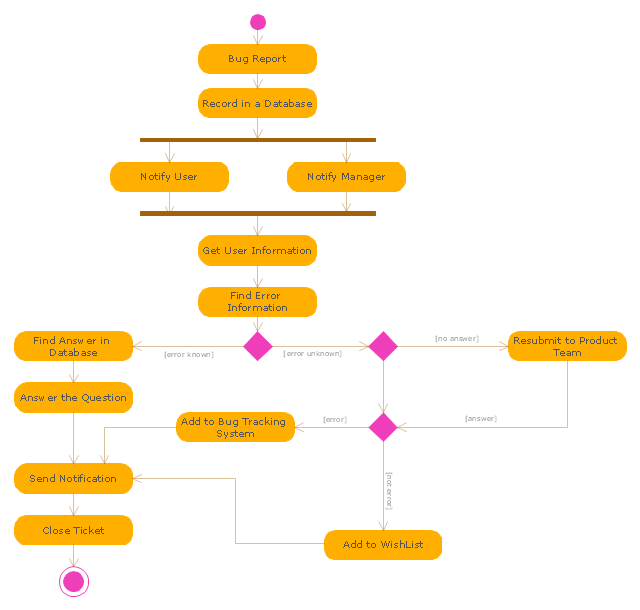
A ticket element, within an issue tracking system, is a running report on a particular problem, its status, and other relevant data. They are commonly created in a help desk or call center environment and almost always have a unique reference number, also known as a case, issue or call log number which is used to allow the user or help staff to quickly locate, add to or communicate the status of the user's issue or request.
These tickets are so called because of their origin as small cards within a traditional wall mounted work planning system when this kind of support started. Operators or staff receiving a call or query from a user would fill out a small card with the user's details and a brief summary of the request and place it into a position (usually the last) in a column of pending slots for an appropriate engineer, so determining the staff member who would deal with the query and the priority of the request." [Issue tracking system. Wikipedia]
The UML activity diagram example "Ticket processing system" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
A ticket element, within an issue tracking system, is a running report on a particular problem, its status, and other relevant data. They are commonly created in a help desk or call center environment and almost always have a unique reference number, also known as a case, issue or call log number which is used to allow the user or help staff to quickly locate, add to or communicate the status of the user's issue or request.
These tickets are so called because of their origin as small cards within a traditional wall mounted work planning system when this kind of support started. Operators or staff receiving a call or query from a user would fill out a small card with the user's details and a brief summary of the request and place it into a position (usually the last) in a column of pending slots for an appropriate engineer, so determining the staff member who would deal with the query and the priority of the request." [Issue tracking system. Wikipedia]
The UML activity diagram example "Ticket processing system" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
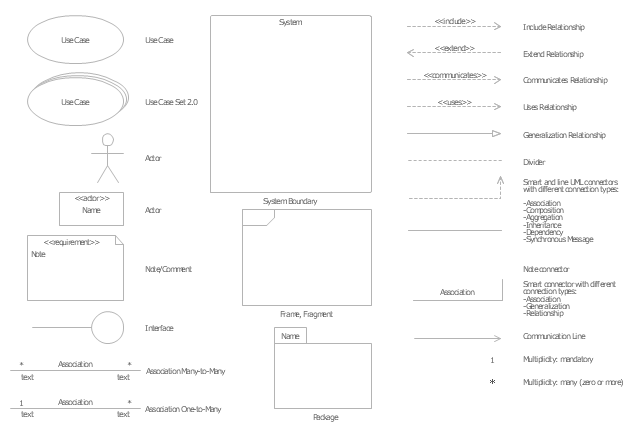
UML Flowchart Symbols
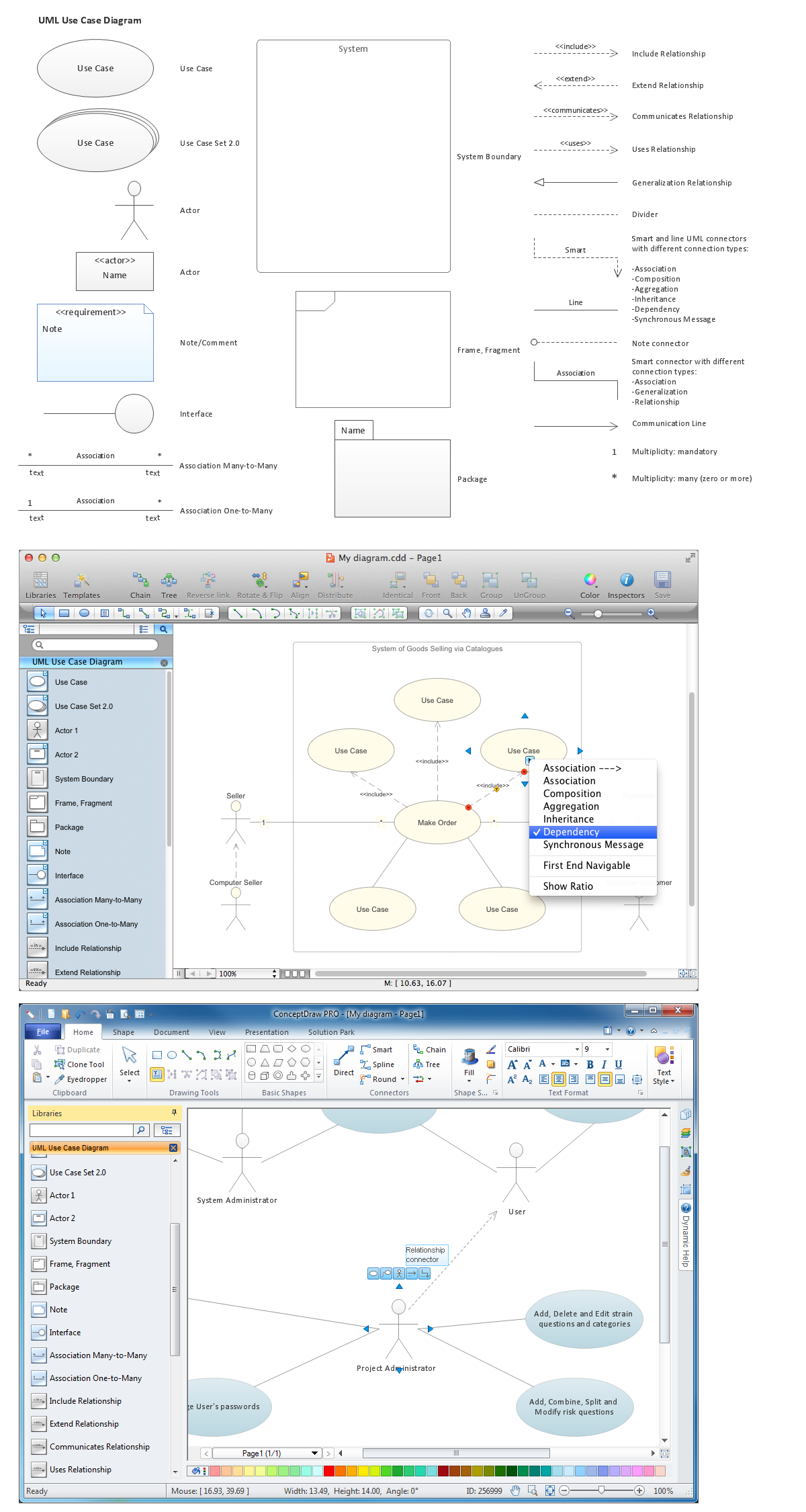
The UML diagram is a powerful tool which lets visually represent all system's components, the interactions between them and relationships with external user interface. The Rapid UML solution for ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software offers diversity of UML flowchart symbols for drawing all types of UML diagrams.The vector stencils library "UML use case diagrams" contains 25 symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"Use case diagrams are usually referred to as behavior diagrams used to describe a set of actions (use cases) that some system or systems (subject) should or can perform in collaboration with one or more external users of the system (actors). Each use case should provide some observable and valuable result to the actors or other stakeholders of the system. ...
Use case diagrams are in fact twofold - they are both behavior diagrams, because they describe behavior of the system, and they are also structure diagrams - as a special case of class diagrams where classifiers are restricted to be either actors or use cases related to each other with associations. ...
Use case is usually shown as an ellipse containing the name of the use case. ...
Name of the use case could also be placed below the ellipse. ...
If a subject (or system boundary) is displayed, the use case ellipse is visually located inside the system boundary rectangle. Note, that this does not necessarily mean that the subject classifier owns the contained use cases, but merely that the use case applies to that classifier. ...
A list of use case properties - operations and attributes - could be shown in a compartment within the use case oval below the use case name. ...
Use case with extension points may be listed in a compartment of the use case with the heading extension points. ...
A use case can also be shown using the standard rectangle notation for classifiers with an ellipse icon in the upper right-hand corner of the rectangle and with optional separate list compartments for its features. ...
Subject (sometimes called a system boundary) is presented by a rectangle with subject's name, associated keywords and stereotypes in the upper left corner. Use cases applicable to the subject are located inside the rectangle and actors - outside of the system boundary. ...
Standard UML notation for actor is "stick man" icon with the name of the actor above or below of the icon. Actor names should follow the capitalization and punctuation guidelines for classes. The names of abstract actors should be shown in italics. ...
Custom icons that convey the kind of actor may also be used to denote an actor, such as using a separate icon(s) for non-human actors. ...
An actor may also be shown as a class rectangle with the standard keyword «actor», having usual notation for class compartments ...
An actor can only have binary associations to use cases, components, and classes. ...
An association between an actor and a use case indicates that the actor and the use case somehow interact or communicate with each other.
Only binary associations are allowed between actors and use cases.
An actor could be associated to one or several use cases. ...
A use case may have one or several associated actors." [uml-diagrams.org/ use-case-diagrams.html]
The example "Design elements - UML use case diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Use case diagrams are usually referred to as behavior diagrams used to describe a set of actions (use cases) that some system or systems (subject) should or can perform in collaboration with one or more external users of the system (actors). Each use case should provide some observable and valuable result to the actors or other stakeholders of the system. ...
Use case diagrams are in fact twofold - they are both behavior diagrams, because they describe behavior of the system, and they are also structure diagrams - as a special case of class diagrams where classifiers are restricted to be either actors or use cases related to each other with associations. ...
Use case is usually shown as an ellipse containing the name of the use case. ...
Name of the use case could also be placed below the ellipse. ...
If a subject (or system boundary) is displayed, the use case ellipse is visually located inside the system boundary rectangle. Note, that this does not necessarily mean that the subject classifier owns the contained use cases, but merely that the use case applies to that classifier. ...
A list of use case properties - operations and attributes - could be shown in a compartment within the use case oval below the use case name. ...
Use case with extension points may be listed in a compartment of the use case with the heading extension points. ...
A use case can also be shown using the standard rectangle notation for classifiers with an ellipse icon in the upper right-hand corner of the rectangle and with optional separate list compartments for its features. ...
Subject (sometimes called a system boundary) is presented by a rectangle with subject's name, associated keywords and stereotypes in the upper left corner. Use cases applicable to the subject are located inside the rectangle and actors - outside of the system boundary. ...
Standard UML notation for actor is "stick man" icon with the name of the actor above or below of the icon. Actor names should follow the capitalization and punctuation guidelines for classes. The names of abstract actors should be shown in italics. ...
Custom icons that convey the kind of actor may also be used to denote an actor, such as using a separate icon(s) for non-human actors. ...
An actor may also be shown as a class rectangle with the standard keyword «actor», having usual notation for class compartments ...
An actor can only have binary associations to use cases, components, and classes. ...
An association between an actor and a use case indicates that the actor and the use case somehow interact or communicate with each other.
Only binary associations are allowed between actors and use cases.
An actor could be associated to one or several use cases. ...
A use case may have one or several associated actors." [uml-diagrams.org/ use-case-diagrams.html]
The example "Design elements - UML use case diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
UML Diagram
The accepted open standard that is used in software engineering and system design, when modeling object-oriented systems and business processes is known as Unified Modeling Language (UML). UML was created for definition, visualization, design and documentation software systems. It isn't a programming language, but on the base of UML model can be generated code. UML uses generic set of graphic notations for creation an abstract model of the system called UML-model. The UML notation lets visually represent requirements, subsystems, structural and behavioral patterns, logical and physical elements, etc. UML defines 13 types of diagrams: Class (Package), Use Case, Sequence, Object, Collaboration, Component, Timing, Interaction Overview, State Machine, Composite Structure, Activity, and Deployment. All these types of UML Diagrams can be fast and easy created with powerful ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software extended with special Rapid UML solution from Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.This example of bank ATM UML activity diagram was created on the base of UML use case diagram of automated teller machine from the course "Thinking in Java, 2nd edition, Revision 9" by Bruce Eckel published on the website of the Computer Science and Electrical Engineering Department of the University of Maryland, Baltimore (UMBC).
"If you are designing an auto-teller, for example, the use case for a particular aspect of the functionality of the system is able to describe what the auto-teller does in every possible situation. Each of these “situations” is referred to as a scenario, and a use case can be considered a collection of scenarios. You can think of a scenario as a question that starts with: “What does the system do if...?” For example, “What does the auto-teller do if a customer has just deposited a check within the last 24 hours, and there’s not enough in the account without the check having cleared to provide a desired withdrawal?”
Use case diagrams are intentionally simple to prevent you from getting bogged down in system implementation details prematurely...
Each stick person represents an “actor,” which is typically a human or some other kind of free agent. (These can even be other computer systems, as is the case with “ATM.”) The box represents the boundary of your system. The ellipses represent the use cases, which are descriptions of valuable work that can be performed with the system. The lines between the actors and the use cases represent the interactions.
It doesn’t matter how the system is actually implemented, as long as it looks like this to the user."
[csee.umbc.edu/ courses/ 331/ resources/ tij/ text/ TIJ213.gif]
This automated teller machine (ATM) UML use case diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"If you are designing an auto-teller, for example, the use case for a particular aspect of the functionality of the system is able to describe what the auto-teller does in every possible situation. Each of these “situations” is referred to as a scenario, and a use case can be considered a collection of scenarios. You can think of a scenario as a question that starts with: “What does the system do if...?” For example, “What does the auto-teller do if a customer has just deposited a check within the last 24 hours, and there’s not enough in the account without the check having cleared to provide a desired withdrawal?”
Use case diagrams are intentionally simple to prevent you from getting bogged down in system implementation details prematurely...
Each stick person represents an “actor,” which is typically a human or some other kind of free agent. (These can even be other computer systems, as is the case with “ATM.”) The box represents the boundary of your system. The ellipses represent the use cases, which are descriptions of valuable work that can be performed with the system. The lines between the actors and the use cases represent the interactions.
It doesn’t matter how the system is actually implemented, as long as it looks like this to the user."
[csee.umbc.edu/ courses/ 331/ resources/ tij/ text/ TIJ213.gif]
This automated teller machine (ATM) UML use case diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
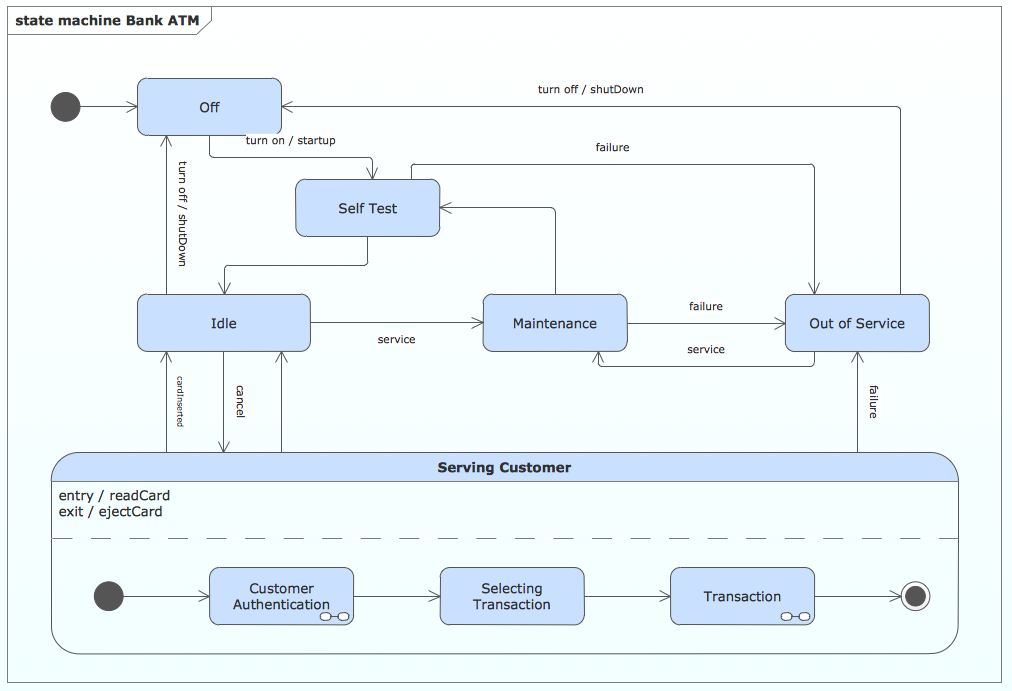
State Machine Diagram
UML state machine's goal is to overcome the main limitations of traditional finite-state machines while retaining their main benefits. ConceptDraw is ideal for software designers and software developers who need to draw UML State Machine Diagrams.
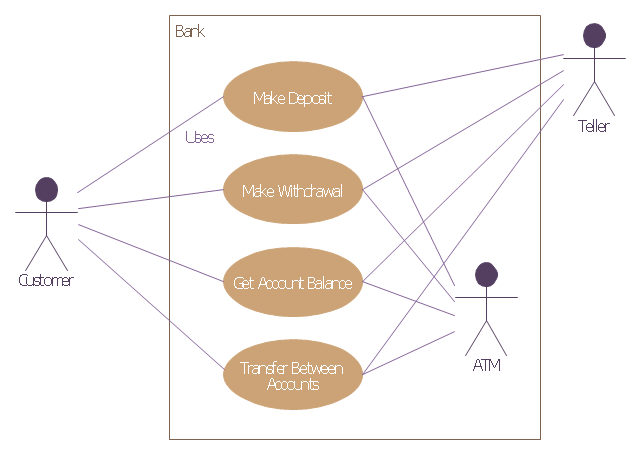
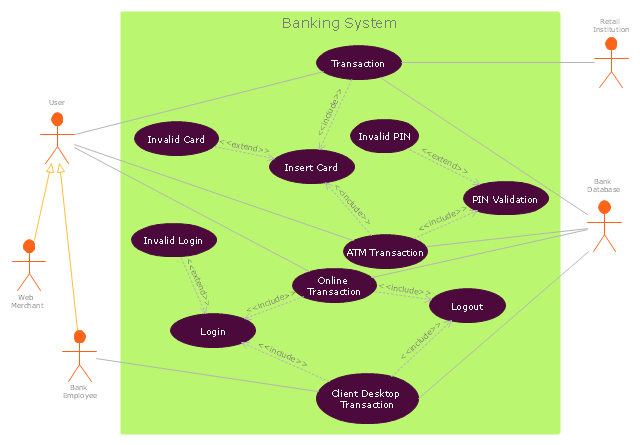
"Banks offer many different channels to access their banking and other services:
(1) Automated Teller Machines.
(2) A branch is a retail location.
(3) Call center.
(4) Mail: most banks accept cheque deposits via mail and use mail to communicate to their customers, e.g. by sending out statements.
(5) Mobile banking is a method of using one's mobile phone to conduct banking transactions.
(6) Online banking is a term used for performing multiple transactions, payments etc. over the Internet.
(7) Relationship Managers, mostly for private banking or business banking, often visiting customers at their homes or businesses.
(8) Telephone banking is a service which allows its customers to conduct transactions over the telephone with automated attendant or when requested with telephone operator.
(9) Video banking is a term used for performing banking transactions or professional banking consultations via a remote video and audio connection. Video banking can be performed via purpose built banking transaction machines (similar to an Automated teller machine), or via a video conference enabled bank branch clarification.
(10) DSA is a Direct Selling Agent, who works for the bank based on a contract. Its main job is to increase the customer base for the bank." [Bank. Wikipedia]
The UML use case diagram example "Banking system" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
(1) Automated Teller Machines.
(2) A branch is a retail location.
(3) Call center.
(4) Mail: most banks accept cheque deposits via mail and use mail to communicate to their customers, e.g. by sending out statements.
(5) Mobile banking is a method of using one's mobile phone to conduct banking transactions.
(6) Online banking is a term used for performing multiple transactions, payments etc. over the Internet.
(7) Relationship Managers, mostly for private banking or business banking, often visiting customers at their homes or businesses.
(8) Telephone banking is a service which allows its customers to conduct transactions over the telephone with automated attendant or when requested with telephone operator.
(9) Video banking is a term used for performing banking transactions or professional banking consultations via a remote video and audio connection. Video banking can be performed via purpose built banking transaction machines (similar to an Automated teller machine), or via a video conference enabled bank branch clarification.
(10) DSA is a Direct Selling Agent, who works for the bank based on a contract. Its main job is to increase the customer base for the bank." [Bank. Wikipedia]
The UML use case diagram example "Banking system" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
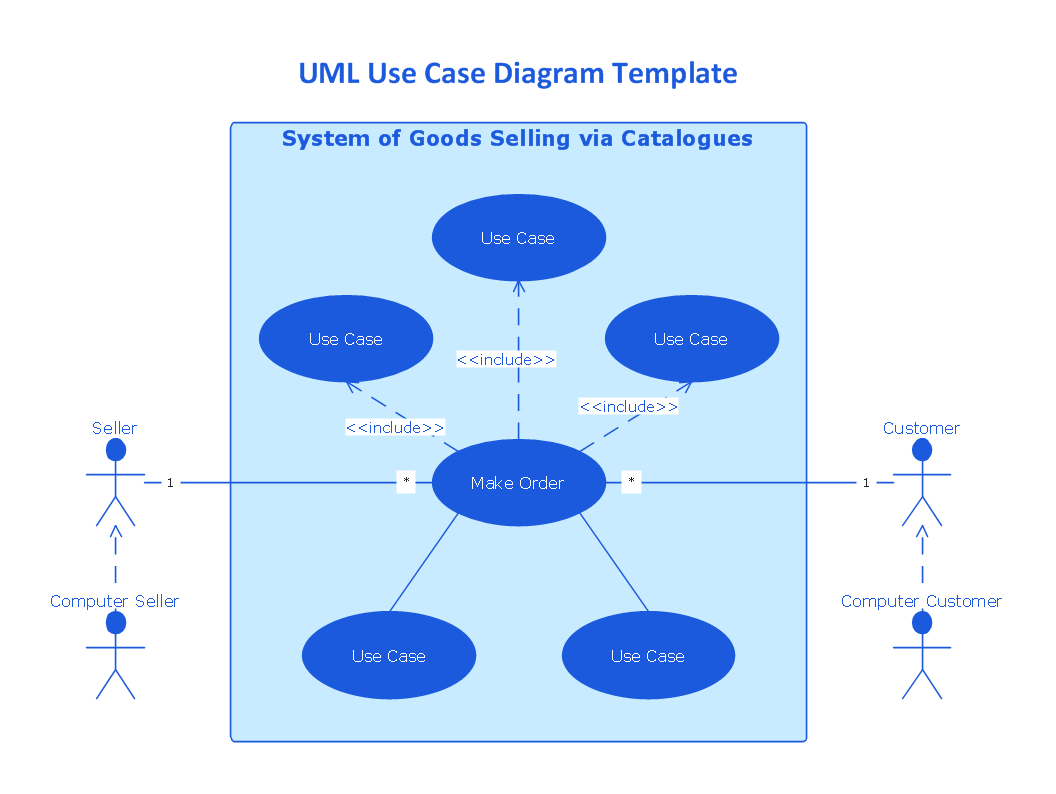
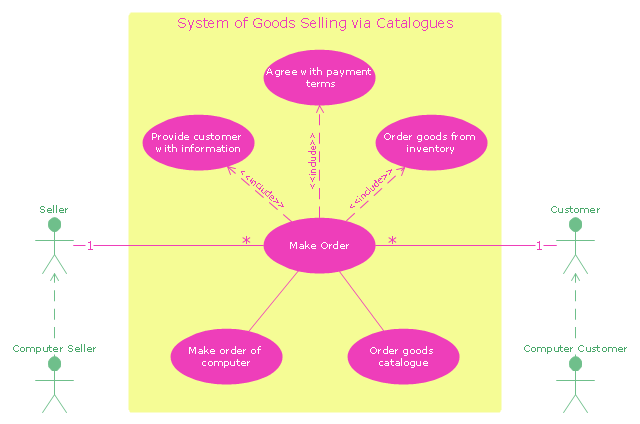
"A catalog merchant (catalogue merchant in British and Canadian English) is a form of retailing. The typical merchant sells a wide variety of household and personal products, with many emphasizing jewelry. Unlike a self-serve retail store, most of the items are not displayed; customers select the products from printed catalogs in the store and fill out an order form. The order is brought to the sales counter, where a clerk retrieves the items from the warehouse area to a payment and checkout station. ...
The catalog merchant has generally lower prices than other retailers and lower overhead expenses due to the smaller size of store and lack of large showroom space.
There are a few key benefits to this approach. By operating as an in-store catalog sales center, it could be exempt from the "Resale price maintenance" policy of the manufacturers, which can force conventional retailers to charge a minimum sales price to prevent price-cutting competition; it also reduces the risk of merchandise theft, known in the industry as shrinkage.
From the consumer's point of view, there are potential advantages and disadvantages. The catalog showroom approach allows customers to shop without having to carry their purchases throughout the store as they shop. Possible downsides include that customers may be required to give their contact information when an order is placed, take the time to fill out order forms, and wait a period of time for their order to be available for purchase. This wait may be days long, one of the chief vulnerabilities of the catalog showroom approach." [Catalog merchant. Wikipedia]
The UML use case diagram example "System of goods selling via catalogues" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The catalog merchant has generally lower prices than other retailers and lower overhead expenses due to the smaller size of store and lack of large showroom space.
There are a few key benefits to this approach. By operating as an in-store catalog sales center, it could be exempt from the "Resale price maintenance" policy of the manufacturers, which can force conventional retailers to charge a minimum sales price to prevent price-cutting competition; it also reduces the risk of merchandise theft, known in the industry as shrinkage.
From the consumer's point of view, there are potential advantages and disadvantages. The catalog showroom approach allows customers to shop without having to carry their purchases throughout the store as they shop. Possible downsides include that customers may be required to give their contact information when an order is placed, take the time to fill out order forms, and wait a period of time for their order to be available for purchase. This wait may be days long, one of the chief vulnerabilities of the catalog showroom approach." [Catalog merchant. Wikipedia]
The UML use case diagram example "System of goods selling via catalogues" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
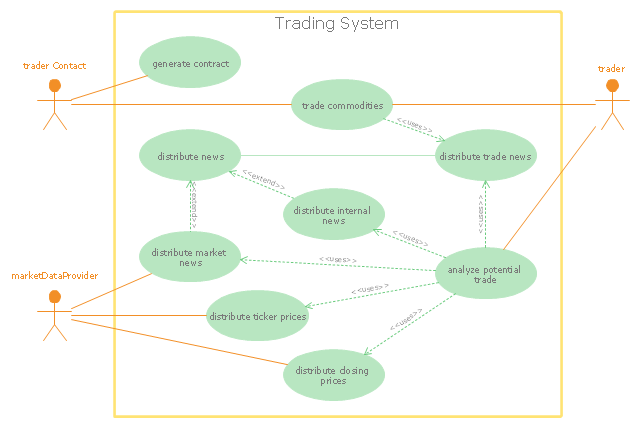
"Algorithmic trading, also called automated trading, black-box trading, or algo trading, is the use of electronic platforms for entering trading orders with an algorithm which executes pre-programmed trading instructions whose variables may include timing, price, or quantity of the order, or in many cases initiating the order by a "robot", without human intervention. Algorithmic trading is widely used by investment banks, pension funds, mutual funds, and other buy-side (investor-driven) institutional traders, to divide large trades into several smaller trades to manage market impact and risk. Sell side traders, such as market makers and some hedge funds, provide liquidity to the market, generating and executing orders automatically.
A special class of algorithmic trading is "high-frequency trading" (HFT), which is often most profitable during periods of high market volatility. During the past years, companies such as Algorates have employed HFT strategies, recording high profits even during periods in which the markets have seen steep declines." [Algorithmic trading. Wikipedia]
The UML use case diagram example "Trading system usage scenarios" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
A special class of algorithmic trading is "high-frequency trading" (HFT), which is often most profitable during periods of high market volatility. During the past years, companies such as Algorates have employed HFT strategies, recording high profits even during periods in which the markets have seen steep declines." [Algorithmic trading. Wikipedia]
The UML use case diagram example "Trading system usage scenarios" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 SYSML
SYSML
The SysML solution helps to present diagrams using Systems Modeling Language; a perfect tool for system engineering.
Communication Diagram UML2.0 / Collaboration UML1.x
UML Communication diagramming software with rich examples and template. ConceptDraw is ideal for software designers and software developers who need to draw UML Communication Diagrams.
Software Diagram Examples and Templates
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is a powerful tool for business and technical diagramming. Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park provides 5 solutions: Data Flow Diagrams, Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD), Graphic User Interface, IDEFO Diagrams, Rapid UML.BPMN
You need to draw professional looking BPMN diagrams quick and easy? Pay please your attention on ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software. Extended with Business Process Diagram Solution from the Business Processes Area it will be ideal for your.Types of Flowcharts
A Flowchart is a graphical representation of process, algorithm, workflow or step-by-step solution of the problem. It shows the steps as boxes of various kinds and connects them by arrows in a defined order depicting a flow. There are twelve main Flowchart types: Basic Flowchart, Business Process Modeling Diagram (BPMN), Cross Functional Flowchart, Data Flow Diagram (DFD), IDEF (Integrated DEFinition) Flowchart, Event-driven Process Chain (EPC) Diagram, Influence Diagram (ID), Swimlane Flowchart, Process Flow Diagram (PFD), Specification and Description Language (SDL) Diagram, Value Stream Mapping, Workflow Diagram. Using the Flowcharts solution from the Diagrams area of ConceptDraw Solution Park you can easy and quickly design a Flowchart of any of these types. This solution offers a lot of special predesigned vector symbols for each of these widely used notations. They will make the drawing process of Flowcharts much easier than ever. Pay also attention for the included collection of ready Flowchart examples, samples and quick-start templates. This is business process improvement tools. If you are looking for MS Visio for your Mac, then you are out of luck, because it hasn't been released yet. However, you can use Visio alternatives that can successfully replace its functions. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is an alternative to MS Visio for Mac that provides powerful features and intuitive user interface for the same.
- UML Use Case Diagram Example. Registration System | Jacobson ...
- UML use case diagram - Ticket processing system | Business ...
- UML use case diagram - Ticket processing system
- UML use case diagram - Ticket processing system | Ticketing ...
- UML activity diagram - Ticket processing system | UML Use Case ...
- Use Case Diagram For E Ticketing System
- UML use case diagram - Ticket processing system | UML activity ...
- UML activity diagram - Ticket processing system | UML use case ...
- Business Process Management | Trouble ticket system - BPMN 2.0 ...
- UML use case diagram - Ticket processing system | How to Create a ...
- Use Case Diagram For Eticketing
- Car Ticket Er Diagram
- Erd Ticketing System
- UML use case diagram - Banking system | Interactive Voice ...
- UML sequence diagram - Ticket processing system | UML sequence ...
- UML use case diagram - System of goods selling via catalogues ...
- UML use case diagram - Ticket processing system | PM Personal ...
- Use Case Diagram For Login System
- UML use case diagram - Ticket processing system - Conceptdraw.com