"An automated teller machine or automatic teller machine" (ATM) (American, Australian, Singaporean, Indian, and Hiberno-English), also known as an automated banking machine (ABM) (Canadian English), cash machine, cashpoint, cashline or hole in the wall (British, South African, and Sri Lankan English), is an electronic telecommunications device that enables the clients of a financial institution to perform financial transactions without the need for a cashier, human clerk or bank teller.
On most modern ATMs, the customer is identified by inserting a plastic ATM card with a magnetic stripe or a plastic smart card with a chip that contains a unique card number and some security information such as an expiration date or CVVC (CVV). Authentication is provided by the customer entering a personal identification number (PIN). The newest ATM at Royal Bank of Scotland allows customers to withdraw cash up to £100 without a card by inputting a six-digit code requested through their smartphones.
Using an ATM, customers can access their bank accounts in order to make cash withdrawals, get debit card cash advances, and check their account balances as well as purchase pre-paid mobile phone credit. If the currency being withdrawn from the ATM is different from that which the bank account is denominated in (e.g.: Withdrawing Japanese yen from a bank account containing US dollars), the money will be converted at an official wholesale exchange rate. Thus, ATMs often provide one of the best possible official exchange rates for foreign travellers, and are also widely used for this purpose." [Automated teller machine. Wikipedia]
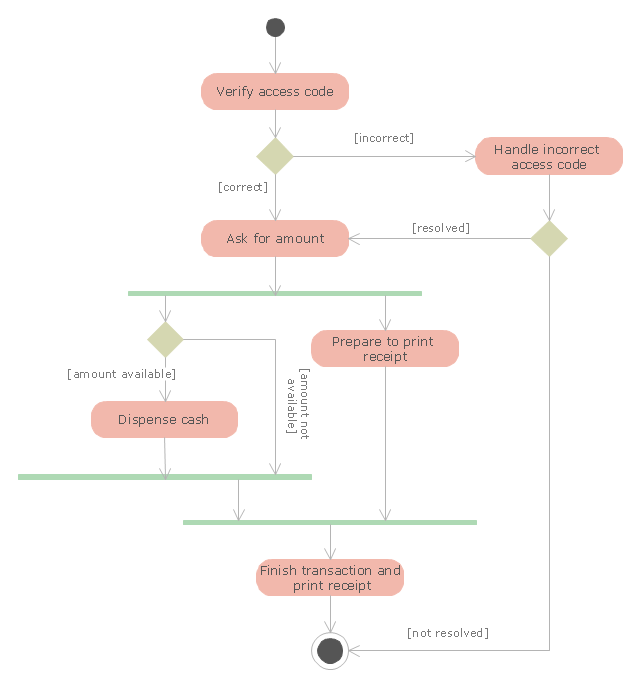
The UML activity diagram example "Cash withdrawal from ATM" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
On most modern ATMs, the customer is identified by inserting a plastic ATM card with a magnetic stripe or a plastic smart card with a chip that contains a unique card number and some security information such as an expiration date or CVVC (CVV). Authentication is provided by the customer entering a personal identification number (PIN). The newest ATM at Royal Bank of Scotland allows customers to withdraw cash up to £100 without a card by inputting a six-digit code requested through their smartphones.
Using an ATM, customers can access their bank accounts in order to make cash withdrawals, get debit card cash advances, and check their account balances as well as purchase pre-paid mobile phone credit. If the currency being withdrawn from the ATM is different from that which the bank account is denominated in (e.g.: Withdrawing Japanese yen from a bank account containing US dollars), the money will be converted at an official wholesale exchange rate. Thus, ATMs often provide one of the best possible official exchange rates for foreign travellers, and are also widely used for this purpose." [Automated teller machine. Wikipedia]
The UML activity diagram example "Cash withdrawal from ATM" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
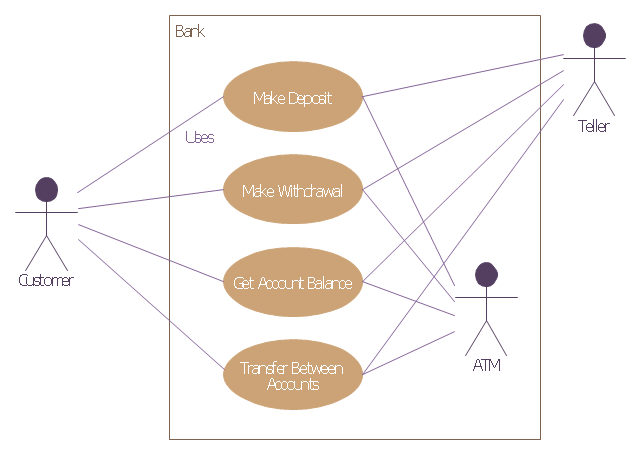
This example of bank ATM UML activity diagram was created on the base of UML use case diagram of automated teller machine from the course "Thinking in Java, 2nd edition, Revision 9" by Bruce Eckel published on the website of the Computer Science and Electrical Engineering Department of the University of Maryland, Baltimore (UMBC).
"If you are designing an auto-teller, for example, the use case for a particular aspect of the functionality of the system is able to describe what the auto-teller does in every possible situation. Each of these “situations” is referred to as a scenario, and a use case can be considered a collection of scenarios. You can think of a scenario as a question that starts with: “What does the system do if...?” For example, “What does the auto-teller do if a customer has just deposited a check within the last 24 hours, and there’s not enough in the account without the check having cleared to provide a desired withdrawal?”
Use case diagrams are intentionally simple to prevent you from getting bogged down in system implementation details prematurely...
Each stick person represents an “actor,” which is typically a human or some other kind of free agent. (These can even be other computer systems, as is the case with “ATM.”) The box represents the boundary of your system. The ellipses represent the use cases, which are descriptions of valuable work that can be performed with the system. The lines between the actors and the use cases represent the interactions.
It doesn’t matter how the system is actually implemented, as long as it looks like this to the user."
[csee.umbc.edu/ courses/ 331/ resources/ tij/ text/ TIJ213.gif]
This automated teller machine (ATM) UML use case diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"If you are designing an auto-teller, for example, the use case for a particular aspect of the functionality of the system is able to describe what the auto-teller does in every possible situation. Each of these “situations” is referred to as a scenario, and a use case can be considered a collection of scenarios. You can think of a scenario as a question that starts with: “What does the system do if...?” For example, “What does the auto-teller do if a customer has just deposited a check within the last 24 hours, and there’s not enough in the account without the check having cleared to provide a desired withdrawal?”
Use case diagrams are intentionally simple to prevent you from getting bogged down in system implementation details prematurely...
Each stick person represents an “actor,” which is typically a human or some other kind of free agent. (These can even be other computer systems, as is the case with “ATM.”) The box represents the boundary of your system. The ellipses represent the use cases, which are descriptions of valuable work that can be performed with the system. The lines between the actors and the use cases represent the interactions.
It doesn’t matter how the system is actually implemented, as long as it looks like this to the user."
[csee.umbc.edu/ courses/ 331/ resources/ tij/ text/ TIJ213.gif]
This automated teller machine (ATM) UML use case diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Data Flow Diagrams (DFD)
Data Flow Diagrams (DFD)
Data Flow Diagrams solution extends ConceptDraw PRO software with templates, samples and libraries of vector stencils for drawing the data flow diagrams (DFD).
 Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD)
Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD)
Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) solution extends ConceptDraw PRO software with templates, samples and libraries of vector stencils from drawing the ER-diagrams by Chen's and crow’s foot notations.
 Computers and Communications
Computers and Communications
Computers and communications solution extends ConceptDraw PRO software with illustration samples, templates and vector stencils libraries with clip art of computers, control devices, communications, technology, Apple machines.
 Plant Layout Plans
Plant Layout Plans
This solution extends ConceptDraw PRO v.9.5 plant layout software (or later) with process plant layout and piping design samples, templates and libraries of vector stencils for drawing Plant Layout plans. Use it to develop plant layouts, power plant desig
 Rapid UML
Rapid UML
Rapid UML solution extends ConceptDraw PRO software with templates, samples and libraries of vector stencils for quick drawing the UML diagrams using Rapid Draw technology.
 Rapid UML
Rapid UML
Rapid UML solution extends ConceptDraw PRO software with templates, samples and libraries of vector stencils for quick drawing the UML diagrams using Rapid Draw technology.
- UML activity diagram - Cash withdrawal from ATM | Data Flow ...
- UML activity diagram - Cash withdrawal from ATM | ATM UML ...
- UML activity diagram - Cash withdrawal from ATM | UML Activity ...
- UML Activity Diagram | UML activity diagram - Cash withdrawal from ...
- UML activity diagram - Cash withdrawal from ATM | State Machine ...
- UML activity diagram - Cash withdrawal from ATM | UML Activity ...
- Bank Atm Machine For Withdrawing Cash For Activity Diagram
- Use Case Diagram For Withdrawal From An Atm Machine
- Activity Diagram Of Uml For Atm Machine
- Activity Diagram Of An Atm Machine
- UML Deployment Diagram Example - ATM System | UML activity ...
- Activity Diagram For Bank Atm Machine For Withdrawing Cash
- Diagram For Withdrawing Cash From Atm Machine
- Activity Diagram Tutorial For Financial And Accounting
- UML activity diagram - Cash withdrawal from ATM | UML activity ...
- UML activity diagram - Cash withdrawal from ATM | ATM UML ...
- UML activity diagram - Cash withdrawal from ATM | UML Use Case ...
- UML Deployment Diagram Example - ATM System | ATM UML ...
- UML activity diagram - Cash withdrawal from ATM | UML activity ...
- UML Activity Diagram