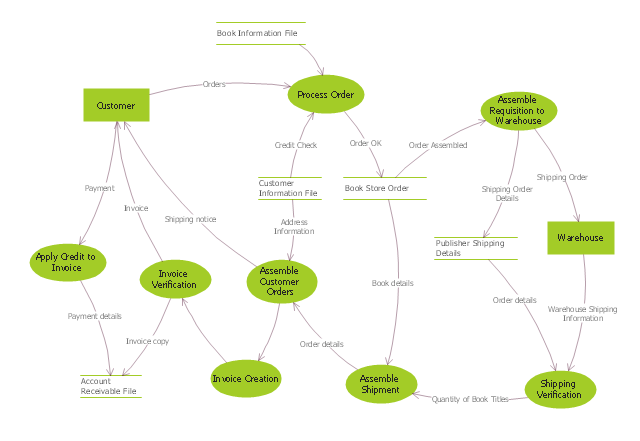
"Data flow diagrams are one of the three essential perspectives of the structured-systems analysis and design method SSADM. The sponsor of a project and the end users will need to be briefed and consulted throughout all stages of a system's evolution. With a data flow diagram, users are able to visualize how the system will operate, what the system will accomplish, and how the system will be implemented. The old system's dataflow diagrams can be drawn up and compared with the new system's data flow diagrams to draw comparisons to implement a more efficient system. Data flow diagrams can be used to provide the end user with a physical idea of where the data they input ultimately has an effect upon the structure of the whole system from order to dispatch to report. How any system is developed can be determined through a data flow diagram model.
In the course of developing a set of levelled data flow diagrams the analyst/ designers is forced to address how the system may be decomposed into component sub-systems, and to identify the transaction data in the data model.
Data flow diagrams can be used in both Analysis and Design phase of the SDLC.
There are different notations to draw data flow diagrams (Yourdon & Coad and Gane & Sarson), defining different visual representations for processes, data stores, data flow, and external entities." [Data flow diagram. Wikipedia]
The DFD (Yourdon and Coad notation) example "Process of account receivable" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Data Flow Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
In the course of developing a set of levelled data flow diagrams the analyst/ designers is forced to address how the system may be decomposed into component sub-systems, and to identify the transaction data in the data model.
Data flow diagrams can be used in both Analysis and Design phase of the SDLC.
There are different notations to draw data flow diagrams (Yourdon & Coad and Gane & Sarson), defining different visual representations for processes, data stores, data flow, and external entities." [Data flow diagram. Wikipedia]
The DFD (Yourdon and Coad notation) example "Process of account receivable" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Data Flow Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Applications
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is a multipurpose software from ConceptDraw suite intended for diagramming, business and technical drawing, and visual documenting. You can reach a lot of practical benefits from the use of ConceptDraw DIAGRAM. The list of ConceptDraw DIAGRAM applications and versatile possibilities is extremely great. Among them network and system diagramming, business diagramming, Cisco network design, network visualization, software and database design, software development, business flowcharting, data flow design, databases modeling and visualization, business processes modeling, business drawing, technical drawing, GUI prototyping, Organizational charts construction, business processes fixing, web site planning and design, Internet solutions design, information architecture design, UML modeling, ER diagrams design, home and landscape design, and a lot of other applications. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM offers the users a beneficial collaboration, compatibility with MS Visio and many other popular programs, including other products from ConceptDraw suite.The vector stencils library "Bank UML composite structure diagram" contains 10 shapes for drawing UML composite structure diagrams.
Use it for object-oriented modeling of your bank information system.
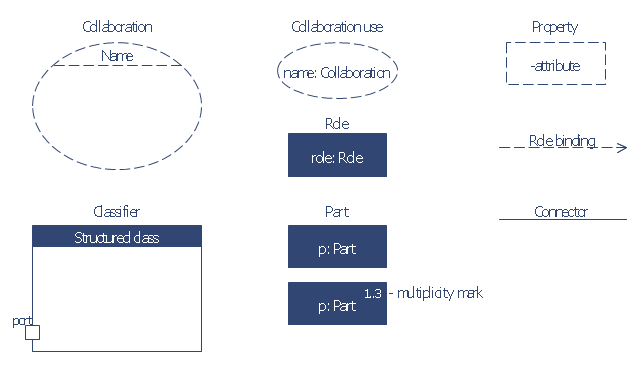
"The key composite structure entities identified in the UML 2.0 specification are structured classifiers, parts, ports, connectors, and collaborations.
* Part : A part represents a role played at runtime by one instance of a classifier or by a collection of instances. The part may only name the role, it may name an abstract superclass, or it may name a specific concrete class. The part can include a multiplicity factor, such as the [0..*] shown for Viewer in the diagram.
* Port : A port is an interaction point that can be used to connect structured classifiers with their parts and with the environment. Ports can optionally specify the services they provide and the services they require from other parts of the system. In the diagram, each of the small squares is a port. Each port has a type and is labelled with a name... in the diagram. Ports may contain a multiplicity factor...
* Connector : A connector binds two or more entities together, allowing them to interact at runtime. The connector is shown as a line between some combination of parts, ports and structured classifiers. The diagram shows three connectors between ports, and one connector between a structured classifier and a part.
* Collaboration : A collaboration is generally more abstract than a structured classifier. It is shown as a dotted oval containing roles that instances can play in the collaboration.
* Structured classifier: A StructuredClassifier represents a class, often an abstract class, whose behavior can be completely or partially described through interactions between parts.
An EncapsulatedClassifier is a type of structured classifier that contains ports." [Composite structure diagram. Wikipedia]
This example of UML composite structure diagram symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it for object-oriented modeling of your bank information system.
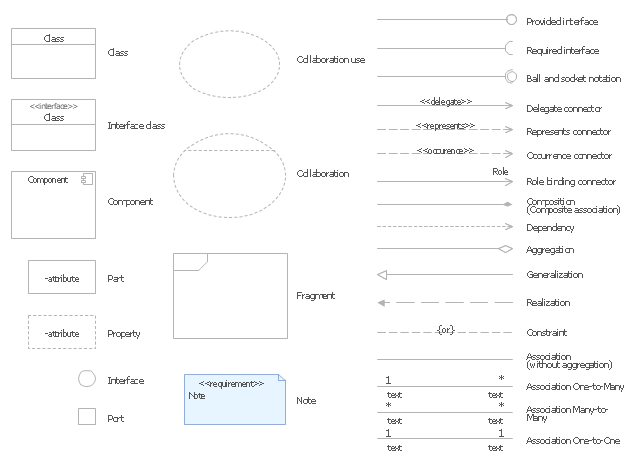
"The key composite structure entities identified in the UML 2.0 specification are structured classifiers, parts, ports, connectors, and collaborations.
* Part : A part represents a role played at runtime by one instance of a classifier or by a collection of instances. The part may only name the role, it may name an abstract superclass, or it may name a specific concrete class. The part can include a multiplicity factor, such as the [0..*] shown for Viewer in the diagram.
* Port : A port is an interaction point that can be used to connect structured classifiers with their parts and with the environment. Ports can optionally specify the services they provide and the services they require from other parts of the system. In the diagram, each of the small squares is a port. Each port has a type and is labelled with a name... in the diagram. Ports may contain a multiplicity factor...
* Connector : A connector binds two or more entities together, allowing them to interact at runtime. The connector is shown as a line between some combination of parts, ports and structured classifiers. The diagram shows three connectors between ports, and one connector between a structured classifier and a part.
* Collaboration : A collaboration is generally more abstract than a structured classifier. It is shown as a dotted oval containing roles that instances can play in the collaboration.
* Structured classifier: A StructuredClassifier represents a class, often an abstract class, whose behavior can be completely or partially described through interactions between parts.
An EncapsulatedClassifier is a type of structured classifier that contains ports." [Composite structure diagram. Wikipedia]
This example of UML composite structure diagram symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "UML composite structure diagrams" contains 36 symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"The key composite structure entities identified in the UML 2.0 specification are structured classifiers, parts, ports, connectors, and collaborations.
(1) Part : A part represents a role played at runtime by one instance of a classifier or by a collection of instances. The part may only name the role, it may name an abstract superclass, or it may name a specific concrete class. The part can include a multiplicity factor, such as the [0..*] shown for Viewer in the diagram.
(2) Port : A port is an interaction point that can be used to connect structured classifiers with their parts and with the environment. Ports can optionally specify the services they provide and the services they require from other parts of the system. In the diagram, each of the small squares is a port. Each port has a type and is labelled with a name, such as "var", "indVar1", or "view" in the diagram. Ports may contain a multiplicity factor, for example.
Ports can either delegate received requests to internal parts, or they can deliver these directly to the behavior of the structured classifier that the port is contained within. Public ports that are visible in the environment are shown straddling the boundary, while protected ports that are not visible in the environment are shown inside the boundary. All the ports in the diagram are public, except for the view port along the right boundary of FibonacciSystem.
(3) Connector : A connector binds two or more entities together, allowing them to interact at runtime. The connector is shown as a line between some combination of parts, ports and structured classifiers. The diagram shows three connectors between ports, and one connector between a structured classifier and a part.
(4) Collaboration : A collaboration is generally more abstract than a structured classifier. It is shown as a dotted oval containing roles that instances can play in the collaboration.
(5) Structured classifier : A StructuredClassifier represents a class, often an abstract class, whose behavior can be completely or partially described through interactions between parts." [Composite structure diagram. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - UML composite structure diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"The key composite structure entities identified in the UML 2.0 specification are structured classifiers, parts, ports, connectors, and collaborations.
(1) Part : A part represents a role played at runtime by one instance of a classifier or by a collection of instances. The part may only name the role, it may name an abstract superclass, or it may name a specific concrete class. The part can include a multiplicity factor, such as the [0..*] shown for Viewer in the diagram.
(2) Port : A port is an interaction point that can be used to connect structured classifiers with their parts and with the environment. Ports can optionally specify the services they provide and the services they require from other parts of the system. In the diagram, each of the small squares is a port. Each port has a type and is labelled with a name, such as "var", "indVar1", or "view" in the diagram. Ports may contain a multiplicity factor, for example.
Ports can either delegate received requests to internal parts, or they can deliver these directly to the behavior of the structured classifier that the port is contained within. Public ports that are visible in the environment are shown straddling the boundary, while protected ports that are not visible in the environment are shown inside the boundary. All the ports in the diagram are public, except for the view port along the right boundary of FibonacciSystem.
(3) Connector : A connector binds two or more entities together, allowing them to interact at runtime. The connector is shown as a line between some combination of parts, ports and structured classifiers. The diagram shows three connectors between ports, and one connector between a structured classifier and a part.
(4) Collaboration : A collaboration is generally more abstract than a structured classifier. It is shown as a dotted oval containing roles that instances can play in the collaboration.
(5) Structured classifier : A StructuredClassifier represents a class, often an abstract class, whose behavior can be completely or partially described through interactions between parts." [Composite structure diagram. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - UML composite structure diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Network layout floorplan" contain 34 symbol icons for drawing computer network floor plans, communication equipment layouts, and structured cabling diagrams.
"Structured cabling is building or campus telecommunications cabling infrastructure that consists of a number of standardized smaller elements (hence structured) called subsystems. ...
Structured cabling design and installation is governed by a set of standards that specify wiring data centers, offices, and apartment buildings for data or voice communications using various kinds of cable, most commonly category 5e (CAT-5e), category 6 (CAT-6), and fibre optic cabling and modular connectors. These standards define how to lay the cabling in various topologies in order to meet the needs of the customer, typically using a central patch panel (which is normally 19 inch rack-mounted), from where each modular connection can be used as needed. Each outlet is then patched into a network switch (normally also rack-mounted) for network use or into an IP or PBX (private branch exchange) telephone system patch panel." [Structured cabling. Wikipedia]
The design elements example "Network layout floorplan - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Network Layout Floor Plans solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Structured cabling is building or campus telecommunications cabling infrastructure that consists of a number of standardized smaller elements (hence structured) called subsystems. ...
Structured cabling design and installation is governed by a set of standards that specify wiring data centers, offices, and apartment buildings for data or voice communications using various kinds of cable, most commonly category 5e (CAT-5e), category 6 (CAT-6), and fibre optic cabling and modular connectors. These standards define how to lay the cabling in various topologies in order to meet the needs of the customer, typically using a central patch panel (which is normally 19 inch rack-mounted), from where each modular connection can be used as needed. Each outlet is then patched into a network switch (normally also rack-mounted) for network use or into an IP or PBX (private branch exchange) telephone system patch panel." [Structured cabling. Wikipedia]
The design elements example "Network layout floorplan - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Network Layout Floor Plans solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Structured Systems Analysis and Design Method (SSADM) with ...
- Process Flowchart | Structured Systems Analysis and Design ...
- Data Flow Diagram Model
- UML Diagram | Structured Systems Analysis and Design Method ...
- LLNL Flow Charts | Structured Systems Analysis and Design Method ...
- Data modeling with ConceptDraw PRO | Structured Systems ...
- Process Flowchart | Structured Systems Analysis and Design ...
- Pyramid Diagram | Pyramid Diagram | Structured Systems Analysis ...
- Structured Systems Analysis and Design Method (SSADM)
- Process Flowchart | Data Flow Diagram | Structured Systems ...
- Data Flow Diagram (DFD) | Structured Systems Analysis and Design ...
- Fault Tree Analysis Diagrams | Fishbone Diagram | Structured ...
- Process Flowchart | Structured Systems Analysis and Design ...
- Entity-relationship diagram (Crow's foot notation) | Structured ...
- Data Flow Diagrams | Data Flow Diagram | Structured Systems ...
- Pyramid Diagram | Process Flowchart | Structured Systems Analysis ...
- Data Flow Diagrams | Structured Systems Analysis and Design ...
- Data structure diagram with ConceptDraw PRO | Program Structure ...
- Total Quality Management with ConceptDraw | Structured Systems ...
- Process Flowchart | Structured Systems Analysis and Design ...