The vector stencils library "Office furniture" contains 36 shapes of office furnishings and work surfaces. Use these shapes for drawing floor plans and furniture arrangements and layouts of office suites and conference rooms in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Office Layout Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This floor plan example shows furniture and major appliance layout in the function hall.
"A function hall, reception hall, or banquet hall is a room or building for the purpose of hosting a party, banquet, wedding or other reception, or other social event." [Function hall. Wikipedia]
This example was designed using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Cafe and Restaurant Floor Plan solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A function hall, reception hall, or banquet hall is a room or building for the purpose of hosting a party, banquet, wedding or other reception, or other social event." [Function hall. Wikipedia]
This example was designed using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Cafe and Restaurant Floor Plan solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "HR department" contains 50 workflow symbols.
Use this department icon set to draw your HR process flowcharts, workflow diagrams and infographics with the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
The HR pictograms library "HR department" is included in the HR Flowcharts solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use this department icon set to draw your HR process flowcharts, workflow diagrams and infographics with the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
The HR pictograms library "HR department" is included in the HR Flowcharts solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Sales department" contains 49 company department icons.
Use these sales pictograms to draw your sales flowcharts, workflow diagrams and process charts with the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
The vector stencils library "Sales department" is included in the Sales Flowcharts solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these sales pictograms to draw your sales flowcharts, workflow diagrams and process charts with the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
The vector stencils library "Sales department" is included in the Sales Flowcharts solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Workflow diagrams" contains 54 symbol icons of workflow diagrams.
The workflow diagrams represent information flow, automation of business processes, business process re-engineering, accounting, management, and human resources tasks in industry, business, and manufacturing.
Use this library to draw workflow diagrams in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Workflow Diagrams solution from the Business Processes area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ business-process-workflow-diagrams
The workflow diagrams represent information flow, automation of business processes, business process re-engineering, accounting, management, and human resources tasks in industry, business, and manufacturing.
Use this library to draw workflow diagrams in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Workflow Diagrams solution from the Business Processes area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ business-process-workflow-diagrams
 Floor Plans
Floor Plans
Construction, repair and remodeling of the home, flat, office, or any other building or premise begins with the development of detailed building plan and floor plans. Correct and quick visualization of the building ideas is important for further construction of any building.
The vector stencils library "HR workflow" contains 60 HR workflow symbols.
Use this HR icon set to draw your HR flowcharts, workflow diagrams and process charts with the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
The HR pictograms library "HR workflow" is included in the HR Flowcharts solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use this HR icon set to draw your HR flowcharts, workflow diagrams and process charts with the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
The HR pictograms library "HR workflow" is included in the HR Flowcharts solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
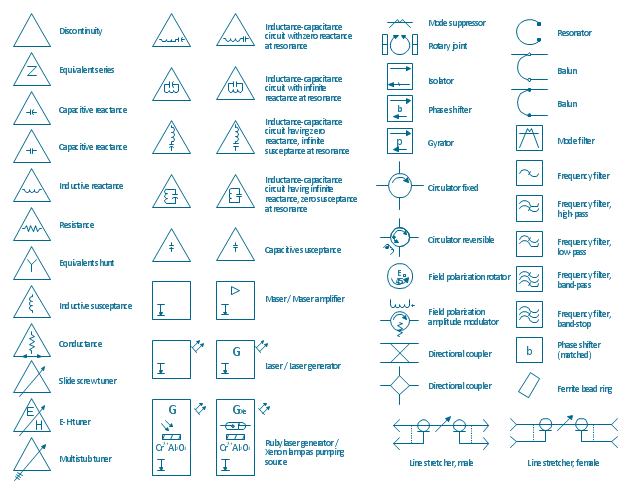
The vector stencils library "VHF UHF SHF" contains 52 symbols for VHF, UHF, and SHF circuit design, including capacitance measurers, nonreciprocal devices, modulators, phase shifters, field polarization devices, and filters.
"Very high frequency (VHF) is the ITU-designated range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves from 30 MHz to 300 MHz, with corresponding wavelengths of one to ten meters. Frequencies immediately below VHF are denoted high frequency (HF), and the next higher frequencies are known as ultra high frequency (UHF).
Common uses for VHF are FM radio broadcasting, television broadcasting, land mobile stations (emergency, business, private use and military), long range data communication up to several tens of kilometres with radio modems, amateur radio, and marine communications. Air traffic control communications and air navigation systems (e.g. VOR, DME & ILS) work at distances of 100 kilometres or more to aircraft at cruising altitude.
VHF was previously used for analog television stations in the US." [Very high frequency. Wikipedia]
"Ultra-high frequency (UHF) designates the ITU radio frequency range of electromagnetic waves between 300 MHz and 3 GHz (3,000 MHz), also known as the decimetre band or decimetre wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decimetres; that is 1 decimetre to 1 metre. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the SHF (super-high frequency) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF (very high frequency) or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is high enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting (digital and analogue), cordless phones, walkie-talkies, satellite communication, and numerous other applications.
The IEEE defines the UHF radar band as frequencies between 300 MHz and 1 GHz. Two other IEEE radar band overlap the ITU UHF band: the L band between 1 and 2 GHz and the S band between 2 and 4 GHz." [Ultra high frequency. Wikipedia]
"Super high frequency (or SHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 3 GHz and 30 GHz. This band of frequencies is also known as the centimetre band or centimetre wave as the wavelengths range from ten to one centimetres. These frequencies fall within the microwave band, so radio waves with these frequencies are called microwaves. The small wavelength of microwaves allows them to be directed in narrow beams by aperture antennas such as parabolic dishes, so they are used for point-to-point communication and data links, and for radar. This frequency range is used for most radar transmitters, microwave ovens, wireless LANs, cell phones, satellite communication, microwave radio relay links, and numerous short range terrestrial data links. The commencing wireless USB technology will be using approximately 1/ 3 of this spectrum.
Frequencies in the SHF range are often referred to by their IEEE radar band designations: S, C, X, Ku, K, or Ka band, or by similar NATO or EU designations." [Super high frequency. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - VHF UHF SHF" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Very high frequency (VHF) is the ITU-designated range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves from 30 MHz to 300 MHz, with corresponding wavelengths of one to ten meters. Frequencies immediately below VHF are denoted high frequency (HF), and the next higher frequencies are known as ultra high frequency (UHF).
Common uses for VHF are FM radio broadcasting, television broadcasting, land mobile stations (emergency, business, private use and military), long range data communication up to several tens of kilometres with radio modems, amateur radio, and marine communications. Air traffic control communications and air navigation systems (e.g. VOR, DME & ILS) work at distances of 100 kilometres or more to aircraft at cruising altitude.
VHF was previously used for analog television stations in the US." [Very high frequency. Wikipedia]
"Ultra-high frequency (UHF) designates the ITU radio frequency range of electromagnetic waves between 300 MHz and 3 GHz (3,000 MHz), also known as the decimetre band or decimetre wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decimetres; that is 1 decimetre to 1 metre. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the SHF (super-high frequency) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF (very high frequency) or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is high enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting (digital and analogue), cordless phones, walkie-talkies, satellite communication, and numerous other applications.
The IEEE defines the UHF radar band as frequencies between 300 MHz and 1 GHz. Two other IEEE radar band overlap the ITU UHF band: the L band between 1 and 2 GHz and the S band between 2 and 4 GHz." [Ultra high frequency. Wikipedia]
"Super high frequency (or SHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 3 GHz and 30 GHz. This band of frequencies is also known as the centimetre band or centimetre wave as the wavelengths range from ten to one centimetres. These frequencies fall within the microwave band, so radio waves with these frequencies are called microwaves. The small wavelength of microwaves allows them to be directed in narrow beams by aperture antennas such as parabolic dishes, so they are used for point-to-point communication and data links, and for radar. This frequency range is used for most radar transmitters, microwave ovens, wireless LANs, cell phones, satellite communication, microwave radio relay links, and numerous short range terrestrial data links. The commencing wireless USB technology will be using approximately 1/ 3 of this spectrum.
Frequencies in the SHF range are often referred to by their IEEE radar band designations: S, C, X, Ku, K, or Ka band, or by similar NATO or EU designations." [Super high frequency. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - VHF UHF SHF" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
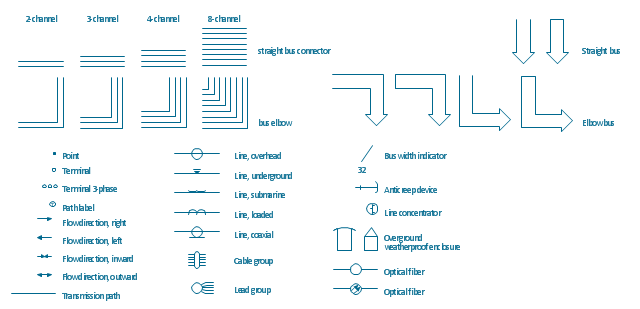
The vector stencils library "Transmission paths" contains 43 symbols of power transmission paths, electronic circuits, bus connectors and elbows, terminals, junctions, and concentrators.
Use it to annotate electrical diagrams, electronic schematics and circuit diagrams.
"A physical medium in data communications is the transmission path over which a signal propagates.
Many transmission media are used as communications channel.
For telecommunications purposes in the United States, Federal Standard 1037C, transmission media are classified as one of the following:
(1) Guided (or bounded) - waves are guided along a solid medium such as a transmission line.
(2) Wireless (or unguided) - transmission and reception are achieved by means of an antenna.
One of the most common physical medias used in networking is copper wire. Copper wire to carry signals to long distances using relatively low amounts of power. The unshielded twisted pair (UTP) is eight strands of copper wire, organized into four pairs.
Another example of a physical medium is optical fiber, which has emerged as the most commonly used transmission medium for long-distance communications. Optical fiber is a thin strand of glass that guides light along its length.
Multimode and single mode are two types of commonly used optical fiber. Multimode fiber uses LEDs as the light source and can carry signals over shorter distances, about 2 kilometers. Single mode can carry signals over distances of tens of miles.
Wireless media may carry surface waves or skywaves, either longitudinally or transversely, and are so classified.
In both communications, communication is in the form of electromagnetic waves. With guided transmission media, the waves are guided along a physical path; examples of guided media include phone lines, twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, and optical fibers. Unguided transmission media are methods that allow the transmission of data without the use of physical means to define the path it takes. Examples of this include microwave, radio or infrared. Unguided media provide a means for transmitting electromagnetic waves but do not guide them; examples are propagation through air, vacuum and seawater.
The term direct link is used to refer to the transmission path between two devices in which signals propagate directly from transmitters to receivers with no intermediate devices, other than amplifiers or repeaters used to increase signal strength. This term can apply to both guided and unguided media.
A transmission may be simplex, half-duplex, or full-duplex.
In simplex transmission, signals are transmitted in only one direction; one station is a transmitter and the other is the receiver. In the half-duplex operation, both stations may transmit, but only one at a time. In full duplex operation, both stations may transmit simultaneously. In the latter case, the medium is carrying signals in both directions at same time." [Transmission medium. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transmission paths" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it to annotate electrical diagrams, electronic schematics and circuit diagrams.
"A physical medium in data communications is the transmission path over which a signal propagates.
Many transmission media are used as communications channel.
For telecommunications purposes in the United States, Federal Standard 1037C, transmission media are classified as one of the following:
(1) Guided (or bounded) - waves are guided along a solid medium such as a transmission line.
(2) Wireless (or unguided) - transmission and reception are achieved by means of an antenna.
One of the most common physical medias used in networking is copper wire. Copper wire to carry signals to long distances using relatively low amounts of power. The unshielded twisted pair (UTP) is eight strands of copper wire, organized into four pairs.
Another example of a physical medium is optical fiber, which has emerged as the most commonly used transmission medium for long-distance communications. Optical fiber is a thin strand of glass that guides light along its length.
Multimode and single mode are two types of commonly used optical fiber. Multimode fiber uses LEDs as the light source and can carry signals over shorter distances, about 2 kilometers. Single mode can carry signals over distances of tens of miles.
Wireless media may carry surface waves or skywaves, either longitudinally or transversely, and are so classified.
In both communications, communication is in the form of electromagnetic waves. With guided transmission media, the waves are guided along a physical path; examples of guided media include phone lines, twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, and optical fibers. Unguided transmission media are methods that allow the transmission of data without the use of physical means to define the path it takes. Examples of this include microwave, radio or infrared. Unguided media provide a means for transmitting electromagnetic waves but do not guide them; examples are propagation through air, vacuum and seawater.
The term direct link is used to refer to the transmission path between two devices in which signals propagate directly from transmitters to receivers with no intermediate devices, other than amplifiers or repeaters used to increase signal strength. This term can apply to both guided and unguided media.
A transmission may be simplex, half-duplex, or full-duplex.
In simplex transmission, signals are transmitted in only one direction; one station is a transmitter and the other is the receiver. In the half-duplex operation, both stations may transmit, but only one at a time. In full duplex operation, both stations may transmit simultaneously. In the latter case, the medium is carrying signals in both directions at same time." [Transmission medium. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transmission paths" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
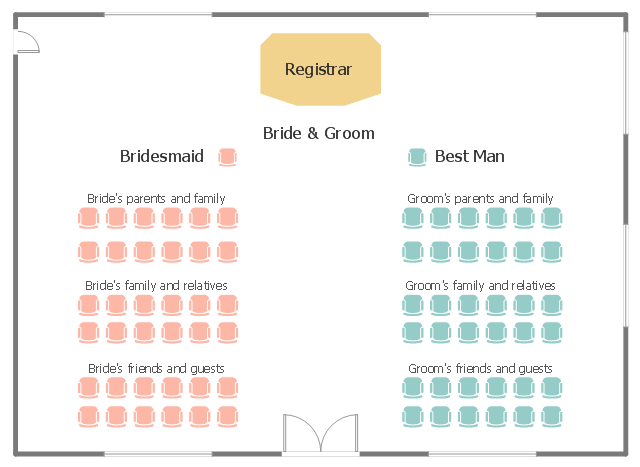
This seating plan sample shows the seat layout at the wedding ceremony.
"A wedding is a ceremony where people are united in marriage. Wedding traditions and customs vary greatly between cultures, ethnic groups, religions, countries, and social classes. Most wedding ceremonies involve an exchange of wedding vows by the couple, presentation of a gift (offering, ring(s), symbolic item, flowers, money), and a public proclamation of marriage by an authority figure or leader. Special wedding garments are often worn, and the ceremony is sometimes followed by a wedding reception. Music, poetry, prayers or readings from religious texts or literature are also commonly incorporated into the ceremony." [Wedding. Wikipedia]
The seat layout example "Wedding ceremony seating plan" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Seating Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A wedding is a ceremony where people are united in marriage. Wedding traditions and customs vary greatly between cultures, ethnic groups, religions, countries, and social classes. Most wedding ceremonies involve an exchange of wedding vows by the couple, presentation of a gift (offering, ring(s), symbolic item, flowers, money), and a public proclamation of marriage by an authority figure or leader. Special wedding garments are often worn, and the ceremony is sometimes followed by a wedding reception. Music, poetry, prayers or readings from religious texts or literature are also commonly incorporated into the ceremony." [Wedding. Wikipedia]
The seat layout example "Wedding ceremony seating plan" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Seating Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Draw Floor Plan Of The Reception Area
- Modern Reception Counter Detail Drawings
- Banquet Hall Plan Software | Floor Plan Of Birthday Reception
- Reception Chairs Top View
- Floor Plans | Architectural Symbol Of A Reception Desk
- Reception Table Photoshop
- Reception Flow Plan
- Reception Workflow Process Diagram
- Drawing Symbol Of Office Reception Desk
- Reception Counter Top View
- Reception Drawing Plan Of A Hotel
- Generation Transmission And Reception Of Radio Waves
- Office Reception With Toilet Plan
- Reception Table Top View
- Wedding Reception Floor Plan
- Reception Hall Layouts
- Function hall floor plan | Oval Shape Reception Tables With ...
- Samples Of Hotel Reception Layout
- Png Reception
- Restaurant Floor Plans Samples | Reception Top View Png




































































































































































-hr-workflow---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)































-hr-workflow---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)