"A root cause is an initiating cause of a causal chain which leads to an outcome or effect of interest. Commonly, root cause is used to describe the depth in the causal chain where an intervention could reasonably be implemented to change performance and prevent an undesirable outcome." [Root cause. Wikipedia]
"Problem-solving consists of using generic or ad hoc methods, in an orderly manner, for finding solutions to problems. Some of the problem-solving techniques developed and used in artificial intelligence, computer science, engineering, mathematics, medicine, etc. are related to mental problem-solving techniques studied in psychology." [Problem solving. Wikipedia]
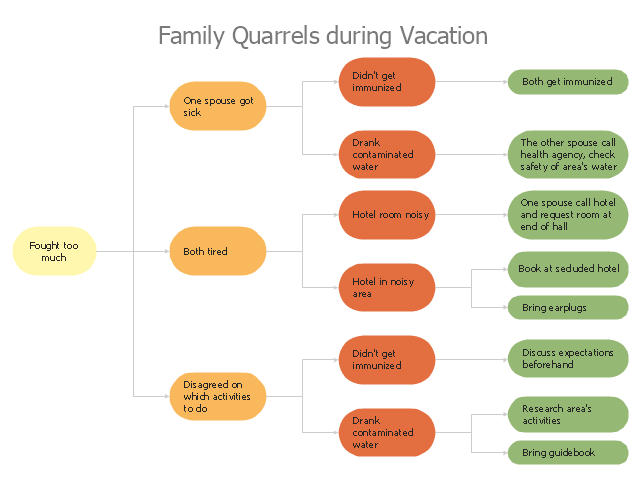
This root cause analysis (RCA) tree diagram example "Personal problem solution" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Seven Management and Planning Tools solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Problem-solving consists of using generic or ad hoc methods, in an orderly manner, for finding solutions to problems. Some of the problem-solving techniques developed and used in artificial intelligence, computer science, engineering, mathematics, medicine, etc. are related to mental problem-solving techniques studied in psychology." [Problem solving. Wikipedia]
This root cause analysis (RCA) tree diagram example "Personal problem solution" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Seven Management and Planning Tools solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Root cause analysis (RCA) is a method of problem solving that tries to identify the root causes of faults or problems.
RCA practice tries to solve problems by attempting to identify and correct the root causes of events, as opposed to simply addressing their symptoms. Focusing correction on root causes has the goal of preventing problem recurrence. RCFA (Root Cause Failure Analysis) recognizes that complete prevention of recurrence by one corrective action is not always possible.
Conversely, there may be several effective measures (methods) that address the root causes of a problem. Thus, RCA is an iterative process and a tool of continuous improvement.
RCA is typically used as a reactive method of identifying event(s) causes, revealing problems and solving them. Analysis is done after an event has occurred. Insights in RCA may make it useful as a preemptive method. In that event, RCA can be used to forecast or predict probable events even before they occur. While one follows the other, RCA is a completely separate process to Incident Management." [Root cause analysis. Wikipedia]
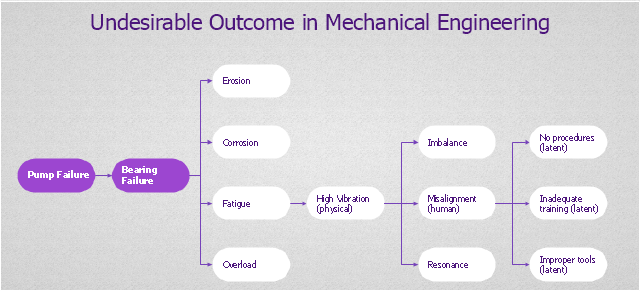
The root cause analysis (RCA) tree diagram example "Manufacturing problem solution" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the solution "Seven Management and Planning Tools" from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
RCA practice tries to solve problems by attempting to identify and correct the root causes of events, as opposed to simply addressing their symptoms. Focusing correction on root causes has the goal of preventing problem recurrence. RCFA (Root Cause Failure Analysis) recognizes that complete prevention of recurrence by one corrective action is not always possible.
Conversely, there may be several effective measures (methods) that address the root causes of a problem. Thus, RCA is an iterative process and a tool of continuous improvement.
RCA is typically used as a reactive method of identifying event(s) causes, revealing problems and solving them. Analysis is done after an event has occurred. Insights in RCA may make it useful as a preemptive method. In that event, RCA can be used to forecast or predict probable events even before they occur. While one follows the other, RCA is a completely separate process to Incident Management." [Root cause analysis. Wikipedia]
The root cause analysis (RCA) tree diagram example "Manufacturing problem solution" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the solution "Seven Management and Planning Tools" from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Root cause analysis (RCA) is a method of problem solving that tries to identify the root causes of faults or problems. ...
RCA (in steps 3, 4 and 5) forms the most critical part of successful corrective action, because it directs the corrective action at the true root cause of the problem. Knowing the root cause is secondary to the goal of prevention, but without knowing the root cause, it is not possible to determine what an effective corrective action for the defined problem would be. ...
3. Ask "why" and identify the causes associated with each step in the sequence towards the defined problem or event. "Why" is taken to mean "What were the factors that directly resulted in the effect?"
4. Classify causes into causal factors that relate to an event in the sequence and root causes, that if eliminated, can be agreed to have interrupted that step of the sequence chain.
5. Identify all other harmful factors that have equal or better claim to be called "root causes." If there are multiple root causes, which is often the case, reveal those clearly for later optimum selection." [Root cause analysis. Wikipedia]
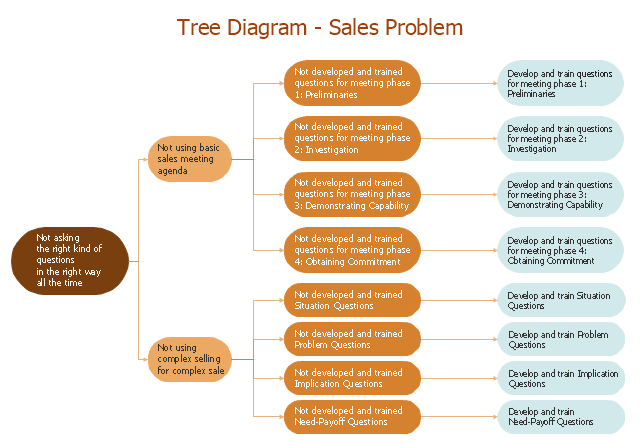
This root cause analysis (RCA) tree diagram example "Sale problem solution" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Seven Management and Planning Tools solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
RCA (in steps 3, 4 and 5) forms the most critical part of successful corrective action, because it directs the corrective action at the true root cause of the problem. Knowing the root cause is secondary to the goal of prevention, but without knowing the root cause, it is not possible to determine what an effective corrective action for the defined problem would be. ...
3. Ask "why" and identify the causes associated with each step in the sequence towards the defined problem or event. "Why" is taken to mean "What were the factors that directly resulted in the effect?"
4. Classify causes into causal factors that relate to an event in the sequence and root causes, that if eliminated, can be agreed to have interrupted that step of the sequence chain.
5. Identify all other harmful factors that have equal or better claim to be called "root causes." If there are multiple root causes, which is often the case, reveal those clearly for later optimum selection." [Root cause analysis. Wikipedia]
This root cause analysis (RCA) tree diagram example "Sale problem solution" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Seven Management and Planning Tools solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Root cause analysis tree diagram - Template
- Root cause analysis tree diagram - Manufacturing problem solution ...
- PROBLEM ANALYSIS. Root Cause Analysis Tree Diagram | How to ...
- Fault Tree Analysis Diagrams
- Cause and Effect Analysis | Cause and Effect Diagram | PROBLEM ...
- Root cause analysis tree diagram - Manufacturing problem solution ...
- Root cause analysis tree diagram - Sale problem solution | Root ...
- Problem solving | Fishbone Diagram Problem Solving | PROBLEM ...
- Root Cause Tree Diagram | PROBLEM ANALYSIS. Root Cause ...